|
|

This chapter provides an overview of the Cisco H.323 Signaling Interface (HSI) system and subsystems and contains the following sections:
The Cisco HSI adds an H.323 interface to the Cisco Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN) Gateway (PGW 2200). This interface allows calls to be established between the PSTN and an H.323 network (see Figure 1-1).
The Cisco HSI provides the following services:
The Cisco HSI does not operate in an active/standby configuration and, therefore, does not provide the same level of redundancy as the PGW 2200 which is configured as active/standby. We therefore recommend that you use enough HSI nodes to support the number of simultaneous calls plus one. This ensures (Trunk Group Caveats dependant) that, if one HSI fails, the calls would be supported adequately by the remaining active HSI's.
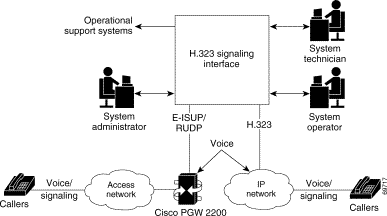
The PGW 2200 consists of the hardware and software that perform the signaling and call control tasks (such as digit analysis, routing, and circuit selection) and seamlessly switch calls from the PSTN through to the IP network.
The purpose of the Cisco HSI is to enable the PGW 2200 to interoperate with the H.323 network.
The Cisco HSI system has two subsystems (see Figure 1-2):
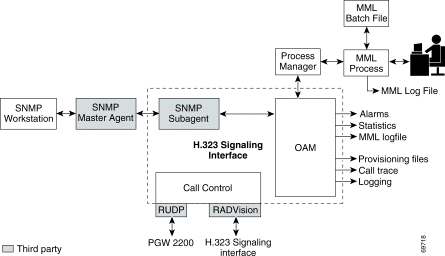
The OAM subsystem provides the following services:
The call control subsystem provides the following services:
RUDP transports the E-ISUP messages between the PGW 2200 and the Cisco HSI.
RUDP is a Cisco proprietary, connection-oriented, packet-based transport protocol.
The Cisco HSI uses the RADVision H.323 stack. The system uses the H.225 (Q.931 and registration, admission, and status [RAS] protocol) and H.245 protocols to implement the H.323 endpoint signaling function.
RADVision H.323 enables the creation of real-time voice H.323 calls over IP networks.
The Cisco HSI provides a conversion between the E-ISUP call control protocol originating from the PGW 2200 and the H.323 call control protocol originating from the IP network (see Figure 1-1).
This section provides operational environment requirements for the Cisco HSI.
The Cisco HSI is targeted to run on a Sun Netra T1 100/105 platform with an 18-GB hard disk drive, a Sun Netra 120 platform with a 36-GB hard disk drive, or a Sun Fire V120 platform with a 36-GB hard disk drive. These platforms run on the Sun Solaris 8 operating system.
The Sun Netra T1 100/105platform, Sun Netra 120 platform, and Sun Fire V120 platform run on the Solaris 8 operating system.
The application does not directly provide security features. All security must be implemented at the UNIX level.
The Cisco HSI automatically restarts the main application process if that process terminates.
The Cisco HSI does not implement security features.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Thu Aug 15 15:36:58 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.