|
|

Feature History
| Release | Modification |
|---|---|
12.1(3)T | This feature was introduced. |
12.1(5)T | Support for the Cisco AS5800 universal access server was added. |
This feature introduces new infrastructure to the Interactive Voice Response (IVR) and Tool Command Language (TCL) verbs which increases scalability and provides enhanced functionality to the Cisco Voice over IP Gateways. The Cisco VoIP gateway software now provides IVR post and prepaid application (or the Debit Card feature), and announcement support under both Media Gateway Control Protocol (MGCP) and H.323 protocols. It also utilizes Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) which enables an external RTSP server to play announcements and interact with voice mail servers.
The IVR Version 2.0 feature is introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.1(3)T. This document contains the following sections:
IVR Version 2.0 is the fourth release of IVR and TCL scripting on Cisco IOS VoIP gateways. The Cisco IVR feature (first made available in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(3)T and 12.0(7)T) provides IVR capabilities using TCL scripts.
IVR is a term that is used to describe systems that provide information in the form of recorded messages over telephone lines in response to user input in the form of spoken words, or more commonly dual tone multifrequency (DTMF) signaling. For example, when a user makes a call with a debit card, an IVR application is used to prompt the caller to enter a specific type of information, such as a PIN. After playing the voice prompt, the IVR application collects the predetermined number of touch tones (digit collection), forwards the collected digits to a server for storage and retrieval, and then places the call to the destination phone or system. Call records can be kept and a variety of accounting functions performed.
The IVR application (or script) is a voice application designed to handle calls on a voice gateway, which is a router that is equipped with Voice over IP (VoIP) features and capabilities.
The IVR feature allows an IVR script to be used during call processing. The scripts interact with the IVR software to perform the various functions. Typically, IVR scripts contain both executable files and audio files that interact with the system software.
IVR Version 2.0 is made up of several separate components which are described individually in the section that follows. These new features include:
These features add scalability and enable the IVR scripting functionality on VoIP legs. In addition, support for RTSP enables VoIP gateways to play messages from RTSP-compliant announcement servers.
IVR infrastructure is greatly enhanced with the addition of support for MGCP using the application package model. MGCP defines application packages to run scripts on the media gateways. These application packages initiate scripts on the gateway and receive return values after execution completes. MGCP scripting allows external call agents (CA) to instruct a media gateway to run an IVR/TCL script in order to perform a specific task and return the end result. For example, you can request and collect the PIN and account number from a caller. Two Cisco VoIP features previously released which can be implemented are the Debit Card for Packet Telephony and Interactive Voice Response.
Both of these features use the TCL scripting language. The TCL scripts that run with MGCP are written in TCL IVR API Version 2.0 and are able to receive calls through hand off. MGCP scripts can run any TCL command.
 |
Note MGCP is not supported on the Cisco AS5800 universal accesss server. |
 |
Note For more information about MGCP, see "Media Gateway Control Protocol for the
Cisco AS5300 Voice/Gateway" documentation located at the following URL: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios120/120newft/120limit/12 0xr/mgcp1206.htm |
Figure 1 displays the call agent controlling the IVR scripts. MGCP is the protocol that is running on the call agent. The RTSP server is configured to interact with the gateways which have IVR scripts installed and running. The RADIUS server running AAA also interacts with the gateways.
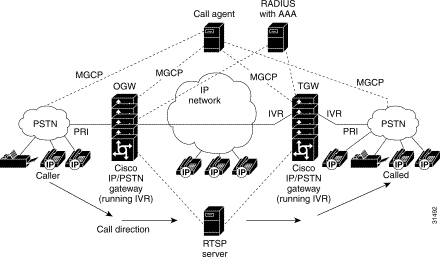
Real Time Streaming Protocol (RTSP) is an application level protocol used for control over the delivery of data with real-time properties. RTSP provides an extensive framework to enable control, and perform on-demand delivery of real-time data. For example, RTSP is used to control the delivery of audio streams from an audio server.
By implementing an RTSP client on VoIP gateways, an application running on the gateway is able to connect calls with audio streams from an external audio server. It also:
IVR Version 2.0 scripts can be configured for incoming POTS or VoIP call legs to play announcements to the user or collect user input (digits). With IVR Version 2.0 the prompts can be triggered from both the PSTN side of the call leg and the IP side of the call leg. This enables the audio files (or prompts) to be played out over the IP network.
IVR scripts played toward a VoIP call leg are subject to the following conditions:
 |
Note SIP is not supported on the Cisco AS5800 universal accesss server. |
 |
Note For additional information about the DTMF relay see the "Multiservice Application
Configuration Guide" in the Cisco IOS 12.1 documentation set. See: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/software/ios121/121cgcr/multi_c/mcpr t1/mcdvoip.htm |
With Cisco IOS Release 12.1(3)T, the system can accept calls initiated from the IP side using G.711 and terminate the call to the terminating gateway using the same Codec.
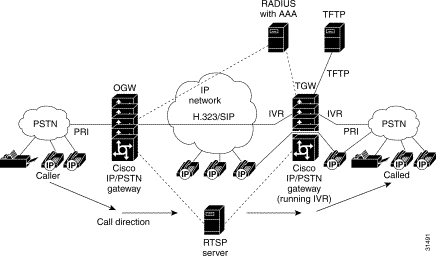
Figure 2, displays the IVR application on the gateways controlling the scripts. IP phones can also originate a call to a gateway running an IVR script.
The IVR Version 2.0 feature delivers a new set of Tool Command Language (TCL) verbs and TCL scripts which replace the previous TCL Version 1.0 verbs and scripts. These TCL verbs are used to utilize the RTSP audio servers. The TCL verbs are used to develop TCL scripts that interact with the IVR application. These scripts are used to pass events to the Media Gateway Controller, which is a call agent.
The IVR version 2.0 feature is not backward compatible with the IVR 1.0 scripts. The MGCP scripting package can only be implemented using the new IVR 2.0 TCL verbs.
 |
Note For in depth information about the 2.0 TCL verb set and how to develop scripts, see the
TCL IVR API Version 2.0 Programmers Guide which is located on CCO at the following
location: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/acs_serv/vapp_dev/index.htm |
The IVR scripts use the Tool Command Language (TCL) verbs to interact with the gateway during call processing in order to collect the required digits. For example, to request the PIN or account number for the caller. The TCL scripts are the default scripts for all Cisco voice features using IVR, and are secured with a proprietary Cisco locking mechanism, or signature. Only Cisco internal technical support personnel are authorized to open and modify these scripts. When a TCL script is activated, the system verifies the Cisco signature level. If the script is inconsistent with the authorized signature level, the script does not load, and the console screen displays an error message.
Refer to the TCL IVR API Version 2.0 Programmers Guide for information about developing TCL scripts. These TCL scripts are configured to control calls coming into or going out of the gateway. The programmers guide also contains an annotated example of a TCL IVR script and includes instructions for testing and loading TCL IVR scripts.
 |
Note Ensure that you have the correct 2.0 version of TCL scripts loaded that supports this
feature. These TCL scripts can be downloaded from the following CCO site: http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/tclware |
The list of restrictions apply to the combination of features described in "Feature Overview" section.
 |
Caution RTSP does not support dynamic prompt playouts. Dynamic prompt refers to a media play URL list that contains Text-to-Speech (TTS) notation to play out monetary amounts, time and other information by using TCL IVR TTS format characters in combination with a TCL variable or numeric constant. See note below for example of dynamic prompt playouts. See Troubleshooting Tips for a workaround. |
 |
Note Example: 'media play $legD%a$amt' is a dynamic prompt that will play the dollar amount
specified by the $amt variable. If $amt is `3.45', this command will play `3 dollars and 45
cents' to the specified call leg. For more information, refer to the media play section of the
TCL IVR Version 2.0 Programmer's Guide which is located on CCO at the following
location: http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/product/access/acs_serv/vapp_dev/tclivrv2.htm |
MIBs
CISCO-CALL-APPLICATION-MIB (ciscoMgmt 146) supports this feature.
This is a Cisco Management Information Base (MIB) to support the management of TCL scripts on the gateway using Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). This includes monitoring which scripts are loaded, loading a script, and unloading a script.
For descriptions of supported MIBs and how to use MIBs, see the Cisco MIB web site on CCO at http://www.cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml.
RFCs
Before you can configure your access server platform with this feature complete the following activities:
 |
Note A Cisco IP/TV Server (version 3.0 or later) can be used as an alternative RTSP server. |
 |
Note The Cisco AS5800 universal access server uses portware, not VCWare, with its modems. |
Before starting the software configuration tasks for theIVR Version 2.0 features, complete the following pre-installation tasks:
 |
Note When using an IVR script to detect a "long #" from a caller connected to the H.323 call leg, either cisco-rtp or H.245-signal DTMF relay must be used. H.245-alphanumeric DTMF-relay does not report the actual duration of the digit, causing long pound (#) detection to fail. |
 |
Note When configuring a voice port use the following configuration designations: For the Cisco AS5300 access server, port designation is port. For the Cisco AS5800 access server, port designation is shelf/slot/port. |
The application that is to be called to interact with the dial peer (that collects digits from the caller), needs to be created before configuring the dial peer that will call this application. Use the call application voice command as shown. Each command line is optional depending on the type of action desired, or which digits to collect.
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | Router# configure terminal
| Enters global configuration mode. |
Step 2 | Router(config)# call application voice | Defines the name of the application to be used with your IVR script, and indicate the location of the appropriate IVR script to be used with this application. The location can be a URL, directory, or a TFTP server, |
Step 3 | | Specifies the two digit variable to specify the language. This will define the language of the audio file for the designated application. Examples: en = English, ch = Mandarin, sp = Spanish |
Step 4 | | Defines the number of characters in the PIN for the designated application. Values are 0—10. |
Step 5 | | Defines the number of times a caller is permitted to reenter the PIN for the designated application. Values are 1—5. |
Step 6 | | Defines the number of characters allowed to be entered for the user ID for the designated application. Values are 1 —20. |
Step 7 | | Defines the location, language, and category of the audio files for the designated application. For example, |
To configure the inbound POTS dial peer, use the following commands:
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | | Enters global configuration mode. |
Step 2 | | Enables AAA security and accounting services. |
Step 3 | | Enables gateway specific H.323 accounting. |
Step 4 | | Defines a method list called H.323 where RADIUS is defined as the only method of login authentication. |
Step 5 | | Defines a method list called H.323 where RADIUS is used to perform connection accounting, providing start-stop records. |
Step 6 | | Identifies the RADIUS server and the ports that will be used for authentication and accounting services. |
Step 7 | | Specifies the password used between the gateway and the RADIUS server. |
Step 8 | | Enters dial-peer configuration mode to configure the incoming POTS dial-peer. The number value of the dial-peer voice pots command is a tag that uniquely identifies the dial peer. |
Step 9 | | Associates the IVR application with the incoming POTS dial peer. Enter the selected IVR/TCL application name. |
Step 10 | Router(config-dial-peer)# | Enters the telephone number associated with this dial peer. The pattern is a series of digits that specify the E.164 or private dialing plan telephone number. Valid entries are the digits 0-9 and the letters A-D. The following special characters can be entered in the string:
The timer (T) character can be used to configure variable length dial plans.
|
Step 11 | Router(config-dial-peer)# | Specifies the session target and IP address. |
| Command | Purpose | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Step 1 | | Enters global configuration mode. | ||
Step 2 | Router(config)#dial-peer voice 4401 voip
| Enters the dial peer configuration mode and identify the call leg. | ||
Step 3 | Router(config-dial-peer)#application application-name
| Specifies the name of the application and script to use. | ||
Step 4 | Router(config-dial-peer)# | Enters the destination pattern. | ||
Step 5 | Router(config-dial-peer)# | Specifies the session protocol. The default session protocol is H.323. Configure sipv2 to enable SIP. | ||
Step 6 | Router(config-dial-peer)# | Specifies the session target IP address. | ||
Step 7 | Router(config-dial-peer)# | Specifies the DTMF relay method. Other options include:
| ||
Step 8 | Router(config-dial-peer)# | Specifies the voice Codec to use.
|
The MGCP script package needs to be enabled to perform MGCP scripting. This is achieved in Configuration mode and by entering the mgcp package-capability script package command.
The example MGCP configuration shown in this section is for DS0s on T1 lines. The configuration tasks consist of:
 |
Note MGCP is not supported on the Cisco AS5800 universal access server. |
| Command | Purpose | |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | Router | Enters global configuration mode. |
Step 2 | Router(config)# mgcp
| Starts the MGCP daemon. |
Step 3 | Router(config)# mgcp request timeout timeout
| Specifies how long the gateway should wait for a response to a request. |
Step 4 | Router(config)# mgcp request retries count
| Specifies the number of times to retry sending the mgcp command. |
Step 5 | Router(config)# mgcp call-agent {ipaddr | hostname} [port]
| Configures the call agent's address. |
Step 6 | Router(config)# mgcp max-waiting-delay value
| Configures the maximum waiting delay to be used in an RSIP message as restart instructions for the call agent. |
Step 7 | Router(config)# mgcp restart-delay value
| Configures the restart delay value to be used in an RSIP message as graceful tear down instructions for the gateway connection. |
Step 8 | Router(config)# mgcp vad
| Configure voice activity detection. |
Step 9 | Router(config)# mgcp package-capability {as-package |
dtmf-package | gm-package | rtp-package | trunk-package}
| Specifies an MGCP package capability. |
Step 10 | Router(config)# mgcp default-package {as-package |
dtmf-package | gm-package | rtp-package | trunk-package}
| Configures the default package capability type. |
Step 11 | Router(config)# mgcp quality-threshold {hwm-jitter-buffer
value | hwm-latency value | hwm-packet-loss value |
lwm-jitter-buffer value | lwm-latency value |
lwm-packet-loss value}
| Configures the jitter buffer size, packet-loss threshold, and latency threshold. |
Step 12 | Router(config)# mgcp playout {adaptive init-value min-value
max-value} | {fixed init-value}
| Tunes the jitter buffer packet size used for MGCP connections. |
Step 13 | Router(config)# mgcp codec type [packetization-period value]
| Configures the default codec type. |
Step 14 | Router(config)# mgcp ip-tos {high-reliability |
high-throughput | low-cost | low-delay | precedence value}
| Enables the IP Type of Service for MGCP connections. |
Step 15 | Router(config)# controller t1 slot#
| Uses the controller configuration mode for the T1 controller in the specified slot. |
Step 16 | Router(config-controller)# framing type
| Configures the framing type. |
Step 17 | Router(config-controller)# clock source type
| Configures the clock source. |
Step 18 | Router(config-controller)# linecode type
| Configures the line coding. |
Step 19 | Router(config-controller)# ds0-group n timeslots range type
signaling-type service mgcp
| Configures the DS-0s to support MGCP. |
Router# show call application voice summary
name description
DEFAULT NEW::Basic app to do DID, or supply dialtone.
fax_hop_on Script to talk to a fax redialer
clid_authen Authenticate with (ani, dnis)
clid_authen_collect Authenticate with (ani, dnis), collect if that fails
clid_authen_npw Authenticate with (ani, NULL)
clid_authen_col_npw Authenticate with (ani, NULL), collect if that fails
clid_col_npw_3 Authenticate with (ani, NULL), and 3 tries collecting
clid_col_npw_npw Authenticate with (ani, NULL) and 3 tries without pw
SESSION Default system session application
hotwo tftp://hostname/scripts/nb/nb_handoffTwoLegs.tcl
hoone tftp://hostname/scripts/nb/nb_dohandoff.tcl
hodest tftp://hostname/scripts/nb/nb_handoff.tcl
clid tftp://hostname/scripts/tcl_ivr/clid_authen_collect.tcl
db102 tftp://hostname/scripts/1.02/debitcard.tcl
*hw tftp://171.69.184.xxx/tr_hello.tcl
*hw1 tftp://san*tr_db
tftp://171.69.184.235/tr_debitcard.answer.tcl
TCL Script Version 2.0 supported.
TCL Script Version 1.1 supported.
Router#
 |
Note In the output shown, an asterisk (*) in an application, indicates that this application was not loaded successfully. Use the show call application voice name command to view information for a particular application. |
Step 2 Enter the show dial-peer voice peer tag command and verify that the application associated with the dial-peer is correct.
Step 3 Enter the show running-config command to display the entire configuration.
Use the show running-config command to display the entire configuration. Figure 3 shows the type of topology used in the configuration for the example.

In this example configuration, GW1 is running IVR for phone A, and GW2 is running IVR for phone B.
The output shown below is the result of using the show running-config command.
GW1
Router# show running-config
Building configuration...
Current configuration:
!
! Last configuration change at 08:39:29 PST Mon Jan 10 2000 by lab
!
version 12.1
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
!
hostname GW1
!
logging buffered 100000 debugging
aaa new-model
aaa authentication login default local group radius
aaa authentication login h323 group radius
aaa authentication login con none
aaa authorization exec h323 group radius
aaa accounting connection h323 start-stop group radius
enable password xxx
!
username lab password 0 lab
!
!
resource-pool disable
!
!
clock timezone PST -8
ip subnet-zero
ip host baloo 1.14.124.xxx
ip host dirt 223.255.254.254
ip host rtspserver3 1.14.1xx.2
ip host rtspserver1 1.14.1xx.2
!
mgcp package-capability trunk-package
mgcp default-package trunk-package
isdn switch-type primary-net5
isdn voice-call-failure 0
!
!
tftp://dirt/hostname/WV/en_new/
call application voice debit_card tftp://dirt/Router/scripts.new/app_debitcard.tcl
call application voice debit_card uid-len 6
call application voice debit_card language 1 en
call application voice debit_card language 2 ch
call application voice debit_card set-location ch 0 tftp://dirt/hostname/WV/ch_new/
call application voice debit_card set-location en 0 tftp://dirt/hostname/WV/en_new/
call application voice debit_card_rtsp tftp://dirt/IVR 2.0/scripts.new/app_debitcard.tcl
call application voice debit_card_rtsp uid-len 6
call application voice debit_card_rtsp language 1 en
call application voice debit_card_rtsp language 2 ch
call application voice debit_card_rtsp set-location ch 0 rtsp://rtspserver1:554/
call application voice debit_card_rtsp set-location en 0 rtsp://rtspserver1:554/
mta receive maximum-recipients 0
!
!
controller E1 0
clock source line primary
pri-group timeslots 1-31
!
controller E1 1
!
controller E1 2
!
controller E1 3
!
gw-accounting h323
gw-accounting h323 vsa
gw-accounting voip
!
!
interface Ethernet0
ip address 1.14.128.35 255.255.255.xxx
no ip directed-broadcast
h323-gateway voip interface
h323-gateway voip id gk1 ipaddr 1.14.128.19 1xxx
h323-gateway voip h323-id gw1@cisco.com
h323-gateway voip tech-prefix 5#
!
interface Serial0:15
no ip address
no ip directed-broadcast
isdn switch-type primary-net5
isdn incoming-voice modem
fair-queue 64 256 0
no cdp enable
!
!
interface FastEthernet0
ip address 16.0.0.1 255.255.xxx.0
no ip directed-broadcast
duplex full
speed auto
no cdp enable
!
ip classless
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.14.128.33
ip route 1.14.xxx.0 255.xxx.255.xxx 16.0.0.2
ip route 1.14.xxx.16 255.xxx.255.240 1.14.xxx.33
no ip http server
!
!
radius-server host 1.14.132.2 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646
radius-server key cisco
radius-server vsa send accounting
radius-server vsa send authentication
!
voice-port 0:D
cptone DE
!
!
dial-peer voice 200 voip
incoming called-number 53
destination-pattern 34.....
session target ipv4:16.0.0.2
dtmf-relay h245-alphanumeric
codec g711ulaw
!
dial-peer voice 102 pots
application debit_card_rtsp
incoming called-number 3450072
shutdown
destination-pattern 53.....
port 0:D
!
!
dial-peer voice 202 voip
shutdown
destination-pattern 34.....
session protocol sipv2
session target ipv4:16.0.0.2
dtmf-relay cisco-rtp
codec g711ulaw
!
dial-peer voice 101 pots
application debit_card
incoming called-number 3450070
destination-pattern 53.....
port 0:D
!
!
gateway
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
transport input none
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
password xxx
!
ntp clock-period 17180740
ntp server 1.14.42.23
end
GW1#
GW2#
Router# show running-config
Building configuration...
Current configuration:
!
! Last configuration change at 08:41:12 PST Mon Jan 10 2000 by lab
!
version 12.1
service timestamps debug uptime
service timestamps log uptime
no service password-encryption
!
hostname GW2
!
logging buffered 100000 debugging
aaa new-model
aaa authentication login default local group radius
aaa authentication login h323 group radius
aaa authentication login con none
aaa authorization exec h323 group radius
aaa accounting connection h323 start-stop group radius
!
username lab password xxx
username 111119 password xxx
!
!
resource-pool disable
!
!
!
!
!
clock timezone PST -8
ip subnet-zero
ip host radiusserver2 1.14.132.2
ip host radiusserver1 1.14.138.11
ip host baloo 1.14.124.254
ip host rtspserver2 1.14.136.2
ip host dirt 223.255.254.254
ip host rtspserver3 1.14.126.2
!
mgcp package-capability trunk-package
mgcp default-package trunk-package
isdn switch-type primary-5ess
isdn voice-call-failure 0
!
!
call application voice clid_authen_sky
tftp://dirt/hostname/sky_scripts/clid_authen_collect_cli_sky.tcl
call application voice rtsp_demo tftp://dirt/hostname/sky_scripts/rtsp_demo.tcl
tftp://dirt/hostname/WV/en_new/
call application voice debit_card tftp://dirt/IVR 2.0/scripts.new/app_debitcard.tcl
call application voice debit_card uid-len 6
call application voice debit_card language 1 en
call application voice debit_card language 2 ch
call application voice debit_card set-location ch 0 tftp://dirt/hostname/WV/ch_new/
call application voice debit_card set-location en 0 tftp://dirt/hostname/WV/en_new/
call application voice clid_authen_rtsp tftp://dirt/IVR
2.0/scripts.new/app_clid_authen_collect_cli_rtsp.tcl
call application voice clid_authen_rtsp location rtsp://rtspserver2:554/
call application voice clid_authen1 tftp://dirt/IVR
2.0/scripts.new/app_clid_authen_collect_cli_rtsp.tcl
call application voice clid_authen1 location tftp://dirt/hostname/WV/en_new/
call application voice clid_authen1 uid-len 6
call application voice clid_authen1 retry-count 4
mta receive maximum-recipients 0
!
!
controller T1 0
framing esf
clock source line primary
linecode b8zs
pri-group timeslots 1-24
!
controller T1 1
clock source line secondary 1
!
controller T1 2
!
controller T1 3
!
gw-accounting h323
gw-accounting h323 vsa
gw-accounting voip
!
!
interface Ethernet0
ip address 1.14.xxx.4 255.255.xxx.240
no ip directed-broadcast
h323-gateway voip interface
h323-gateway voip id gk2 ipaddr 1.14.xxx.18 1719
h323-gateway voip h323-id gw2@cisco.com
h323-gateway voip tech-prefix 3#
!
interface Serial0:23
no ip address
no ip directed-broadcast
isdn switch-type primary-5ess
isdn incoming-voice modem
fair-queue 64 256 0
no cdp enable
!
interface FastEthernet0
ip address 16.0.0.2 255.xxx.255.0
no ip directed-broadcast
duplex full
speed 10
no cdp enable
!
ip classless
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 1.14.xxx.5
ip route 1.14.xxx.32 255.255.xxx.240 16.0.0.1
no ip http server
!
!
radius-server host 1.14.132.2 auth-port 1645 acct-port 1646
radius-server key cisco
radius-server vsa send accounting
radius-server vsa send authentication
!
voice-port 0:D
!
dial-peer voice 100 voip
application debit_card
incoming called-number 34
shutdown
destination-pattern 53.....
session target ras
dtmf-relay h245-alphanumeric
codec g711ulaw
!
dial-peer voice 200 pots
incoming called-number 30001
destination-pattern 3450070
port 0:D
prefix 50070
!
dial-peer voice 101 voip
application debit_card
incoming called-number 34.....
shutdown
session protocol sipv2
session target ipv4:16.0.0.1
dtmf-relay cisco-rtp
codec g711ulaw
!
dial-peer voice 102 voip
incoming called-number 34.....
destination-pattern 53.....
session target ipv4:16.0.0.1
dtmf-relay h245-alphanumeric
codec g711ulaw
!
gateway
!
line con 0
exec-timeout 0 0
transport input none
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
password xxx
!
ntp clock-period 17180933
ntp server 1.14.42.23
end
GW2#
The example shown below displays only the MGCP specific portion of the configuration.
!
mgcp
mgcp request timeout 10000
mgcp request retries 1
mgcp call-agent 1.14.138.11
mgcp restart-delay 10
mgcp codec g723ar63 packetization-period 30
mgcp vad
mgcp package-capability gm-package
mgcp package-capability dtmf-package
mgcp package-capability trunk-package
mgcp package-capability rtp-package
mgcp package-capability as-package
mgcp package-capability script-package
mgcp default-package trunk-package
isdn switch-type primary-5ess
isdn voice-call-failure 0
!
!
mta receive maximum-recipients 0
!
!
controller T1 0
framing esf
clock source line primary
linecode b8zs
ds0-group 0 timeslots 1-24 type none service mgcp
!
controller T1 1
framing esf
clock source line secondary 1
linecode b8zs
ds0-group 0 timeslots 1-24 type none service mgcp
!
controller T1 2
framing esf
linecode b8zs
ds0-group 0 timeslots 1-24 type none service mgcp
!
controller T1 3
framing esf
linecode b8zs
ds0-group 0 timeslots 1-24 type none service mgcp
!
!
end
Dynamic prompt playouts continue to be supported for the tftp/flash based audio files. The files are loaded into DRAM in one of two ways:
1. The user can use the `ivr autoload' command to pre-load audio files at bootup.
2. The file can be loaded dynamically when needed.
Once the file is loaded into DRAM, it remains cached so that it does not need to be loaded the next time it is needed. Option 2 has the disadvantage of adding playout delay due to the time needed for the file loading. This delay is only seen the FIRST time the prompt is loaded into memory.
This section documents new or modified commands. All other commands used with this feature are documented in the Cisco IOS Release 12.1T command reference publications.
To configure the router to reload the MGCP scripts from cache on a regular interval, use the call application cache reload time bg-minutes Global configuration command. The no form of this command sets the value to the default.
call application cache reload time bg-minutes
Syntax Description
bg-minutes Specifies the number of minutes to wake up the background process. This background process checks to see how long it has been since the script has been used, and if the script is current.
Defaults
30 minutes.
Command Modes
Global Configuration
Command History
12.1(3)T This command was introduced. 12.1(5)T Support the Cisco AS5800 universal access servers added.
Release
Modification
Examples
The following example displays the call application cache reload time command.
call application cache reload time 30
Related Commands
show call application voice Displays all TCL or MGCP scripts that are loaded. call application voice load Allows reload of an application which was loaded via the MGCP scripting package.
Command
Description
To set the parameter values to be used with the IVR feature, use the call application voice name {url | {param} value1 [value2]} command in Global configuration command mode. The new word parameter is being added to this command in Cisco IOS Release 12.1(3)T. The no form of this command sets the value to the default.
call application voice name {url | {param} value1[value2]}
Syntax Description
name The name of the application to which the parameters are being passed. You can only configure the param if the application named name has been configured. url Designates where to look for the file and the protocol to use to access it. Examples: Note You can only configure a URL if the application named name has NOT been configured. param Name of the parameter that is being passed. See Valid Parameters below. value 1 Value of the first parameter being passed. value 2 Value of the second parameter being passed.
flash:scripts/session.tcl
tftp://dirt/sarvi/scripts/session.tcl
tftp://sarvi-ultra/scripts/session.tcl
slot0:scripts/tcl/session..tcl
The set of parameters, or keywords, are displayed only if the URL for the defined application is a TCL script, determined with the extension ".tcl" on the URL.
language | The number that identifies the language used by the audio files. For example, enter "1" for English language or "2" for Spanish language audio files. Any number can represent any language. Enter: language digit language. For example: Parameter values are:
|
number | The designated operator telephone number of the service provider (or any other number designated by the service provider). This is the number that calls are terminated to when debit time allowed has run out or the debit amount is exceeded. |
pin-length | The number of characters in the PIN number (0-10). |
retry-count | The number of times the caller is permitted to enter digits. Enter retry-count number of retries(1-5). |
set-location | The location where the audio files are stored. This command connects both the category and language arguments that are used with the call application voice language command. Enter: set-location language category audio files URL or directory Parameter values are:
The audio files can be divided into category groups (0 - 4). For example, audio files representing the days and months can be category 1, audio files representing units of currency can be category2, audio files representing units of time: seconds, minutes, and hours can be category 3. For example: |
uid-length | The number of characters allowed to be entered for the user ID or PIN. (1-20) |
warning-time | The number of seconds the user is warned before the allowed calling time has run out. Enter warning-time number of seconds. (10-600) |
word | Specify a generic word which will be passed into the script (opaque strings to Cisco IOS software). |
Defaults
Each parameter must be defined for the system interaction with the voice prompt. See the command syntax description for individual parameter defaults.
Command Modes
Dial-peer configuration mode.
Command History
12.0(4)XH This command was introduced. 12.0(7)T Added the URL, uid-length, and pin-length parameters. 12.1(3)T Generic "word" parameter added for and AV pair. 12.1(5)T Support for Cisco AS5800 universal access servers added.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
The capability for a generic AV pair is added in Cisco IOS Release 12.1(3)T.
This command is used with the Debit Card feature and when creating an application to interact with IVR and TCL scripts.
Examples
Examples of syntax entered:
call application voice debitcard set-location en 2
tftp://keyer/faryaman/debitcard
call application voice debitcard set-location aa 0
tftp://keyer/debitaudio/
Router(config) #call application voice prepaid tftp://keyer/debitcard.tcl
Router(config) #call application voice prepaid uid-len 4
Router(config) #call application voice prepaid language 1 en
Router(config) #call application voice prepaid language 2 sp
Router(config) #call application voice prepaid set-location en 0 tftp://keyer/
Router(config) #call application voice prepaid pin-len 4
Router(config) #call application voice prepaid retry-count 3
Router(config) #call application voice prepaid uid-len 10
call app voice my_app tftp://server/joe/script.tcl
call app voice my_app num-calls-allowed unlimited
Related Commands
show call application voice Displays all TCL or MGCP scripts that are loaded. call application voice load Allows reload of an application which was loaded via the MGCP scripting package. call application cache reload time Configures the interval for reloading MGCP scripts.
Command
Description
To reload the selected TCL script from the URL, use the call application voice load command. The software checks the signature lock to ensure it is a Cisco supported TCL script. Dynamic MGCP loading capability was added for Cisco IOS Release 12.1(3)T.
call application voice load name
Syntax Description
name Defines the TCL script to use for the call. Enter the name of the TCL or MCGP script you want this dial-peer to use.
Defaults
None. TCL or scripts are not loaded.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
12.0(7)T This command was introduced. 12.1(3)T Dynamic script loading of MGCP scripts. 12.1(5)T Support for Cisco AS5800 universal access servers added.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
If the TCL script does not have a valid Cisco supported signature, the software fails to load the script and generates the following error message:
00:02:54: %IVR-3-BAD_IVR_SIG: Script signature is invalid
Examples
Example of syntax entered to load a MGCP script package:
call application voice load mgcp-script-pkg
Related Commands
Related Commands Related Commands
call application voice Creates and then calls the application that will interact with the IVR feature. show call application voice Displays a list of the voice applications that are configured. call application cache reload time Configures the interval for reloading MGCP scripts.
Command
Description
To specify the length of time to keep RTSP session history records in memory, use the rtsp client session history duration number Global configuration command. The no form of this command sets the value to the default.
rtsp client session history duration number
Syntax Description
number Specify the number of minutes to keep the record.
Defaults
10 minutes.
Command Modes
Global configuration
Command History
12.1(3)T This command was introduced. 12.1(5)T Support for Cisco AS5800 universal access servers added.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
None.
Examples
rtsp client session history dur 500
Related Commands
show call application voice Displays all TCL or MGCP scripts that are loaded. call application voice load Allows reload of an aplication which was loaded via the MGCP scripting package. rtsp client session history records number Specifies the number of RTSP client session history records during the session. show rtsp client session Displays cumulative information about the RTSP session records.
Command
Description
To configure the number of records to keep in the RTSP client session history, use the rtsp client session history records number Global configuration command mode command. The no form of this command sets the value to the default.
rtsp client session history records number
Syntax Description
number Specify the number of records to retain a session history record. Values = 1 —100,000.
Defaults
50 records.
Command Modes
Global configuration.
Command History
12.1(3)T This command was introduced. 12.1(5)T Support for Cisco AS5800 universal access servers added.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
None.
Examples
rtsp client session hist rec 500
Related Commands
show call application voice Displays all TCL or MGCP scripts that are loaded. call application voice load Allows reload of an aplication which was loaded via the MGCP scripting package. rtsp client session history duration number Specifies the length of time the RTSP are kept during the session.
Command
Description
To display cumulative information about RTSP session records, use the show rtsp client session Exec mode command. The no form of this command sets the value to the default.
show rtsp client session {history | active} [detailed] |
Note Session refers to a session between the application and the RTSP client. Each call leg that is configured to use RTSP streaming has a session. |
Syntax Description
history Cumulative information about the session is displayed, packet statistics, along with general call information, such as call ID, session ID, individual RTSP stream URLs, packet statistics, and play duration. active If detailed option is not specified, the session information and stream information for the stream that is currently active is displayed. detailed If the detailed flag is set, the show command displays the session information and stream information for alll streams that are associated with the session.
Defaults
Active (current) stream information is displayed.
Command Modes
Privileged EXEC
Command History
12.1(3)T This command was introduced. 12.1(5)T Support for Cisco AS5800 universal access servers added.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
Examples
Two examples are shown following, show rtsp client session active and show rtsp client session detailed.
show rtsp client session active
The following output is displayed when using the show rtsp client session active command during an active session:
Router# show rtsp client session active
RTSP Session ID:0x8 Current Status:RTSP_STATUS_PLAYING
Associated CallID:0xF
Active Request:RTSP_API_REQ_PLAY
Control Protocol:TCP Data Protocol:RTP
Total Packets Transmitted:0 (0 bytes)
Total Packets Received:708 (226560 bytes)
Cumulative Elapsed Play Time:00:00:28.296
Cumulative Elapsed Record Time:00:00:00.000
Session ID:0x8 State:ACTIVE
Local IP Address:1.13.79.45 Local Port 16660
Server IP Address:1.13.79.6 Server Port 11046
Stream URL:rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/chinna.au/streamid=0
Packets Transmitted:0 (0 bytes)
Packets Received:708 (226560 bytes)
Elapsed Play Time:00:00:28.296
Elapsed Record Time:00:00:00.000
ReceiveDelay:85 LostPackets:0
Router#
show rtsp client session detailed
The following output is displayed when using the show rtsp client session history detailed command:
Router# show rtsp client session history detailed
RTSP Session ID:0x8
Associated CallID:0xF
Control Protocol:TCP Data Protocol:RTP
Total Packets Transmitted:0 (0 bytes)
Total Packets Received:2398 (767360 bytes)
Cumulative Elapsed Play Time:00:01:35.916
Cumulative Elapsed Record Time:00:00:00.000
Session ID:0x8 State:INACTIVE
Local IP Address:1.13.79.45 Local Port 16660
Server IP Address:1.13.79.6 Server Port 11046
Stream URL:rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/chinna.au/streamid=0
Packets Transmitted:0 (0 bytes)
Packets Received:2398 (767360 bytes)
Play Time:00:01:35.916
Record Time:00:00:00.000
OntimeRcvPlayout:93650
GapFillWithSilence:0
GapFillWithPrediction:70
GapFillWithInterpolation:0
GapFillWithRedundancy:0
HighWaterPlayoutDelay:85
LoWaterPlayoutDelay:64
ReceiveDelay:85 LostPackets:0
EarlyPackets:2 LatePackets:12
rtsp-5#
Router#
Related Commands
rtsp client session history duration num Specifies the length of time the RTSP is kept during the session. rtsp client session history records num Specifies the number of RTSP client session history records during the session.
Command
Description
This section documents the new debug commands related to the RTSP, MGCP scripting features. The new debug commands documented include:
To show status of the RTSP client server, use the debug rstp type command. The no form of this command disables the display of output.
[no] debug rstp type [all | api |pmh | session | socket]
Syntax Description
all Displays debug messages for all RTSP Client debug trace. api Displays debug output for the RTSP client API. pmh Displays debug output for the RTSP Protocol Message Handler. session Displays debug output for the RTSP client session information. socket Displays debug output for the RTSP client socket data.
Defaults
Debug is not enabled.
Command History
12.1(3)T This command was introduced. 12.2(1)Xx Support for the Cisco AS5800 universal access server was added.
Release
Modification
For a description and examples of each type of debug rtsp command, see the following:
Related Commands
Displays debug output for the RTSP client API. Displays debug output for the RTSP client data. Displays debug output for the RTSP client session information. Displays debug output for the RTSP client socket data.
Command
Description
To display information about the RTSP API messages passed down to the RTSP client, use the debug rtsp api command. To disable the output, use the no form of this command.
[no] debug rtsp apiSyntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Defaults
Debug is not enabled.
Command History
12.1(3)T This command was introduced. 12.2(1)Xx Support for the Cisco AS5800 universal access server was added.
Release
Modification
Examples
The following example displays the output from entering the debug rtsp api command:
router# debug rtsp api
RTSP client API debugging is on
router#
Jan 1 00:23:15.775:rtsp_api_create_session:sess_id=0x61A07C78,
evh=0x60D6E62C context=0x61A07B28
Jan 1 00:23:15.775:rtsp_api_request:msg=0x61C2B10C
Jan 1 00:23:15.775:rtsp_api_handle_req_set_params:msg=0x61C2B10C
Jan 1 00:23:15.775:rtsp_api_free_msg_buffer:msg=0x61C2B10C
Jan 1 00:23:15.775:rtsp_api_request:msg=0x61C293CC
Jan 1 00:23:15.775:rtsp_api_handle_req_set_params:msg=0x61C293CC
Jan 1 00:23:15.775:rtsp_api_free_msg_buffer:msg=0x61C293CC
Jan 1 00:23:15.775:rtsp_api_request:msg=0x61C2970C
Jan 1 00:23:15.775:rtsp_api_handle_req_set_params:msg=0x61C2970C
Jan 1 00:23:15.775:rtsp_api_free_msg_buffer:msg=0x61C2970C
router#
Jan 1 00:23:15.775:rtsp_api_request:msg=0x61C29A4C
router#
Jan 1 00:23:22.099:rtsp_api_free_msg_buffer:msg=0x61C29A4C
Jan 1 00:23:22.115:rtsp_api_request:msg=0x61C2A40C
Jan 1 00:23:22.115:rtsp_api_free_msg_buffer:msg=0x61C2A40C
Router#
Related Commands
Displays debug output for the RTSP client data. debug rtsp pmh Displays debug messages for the Protocol Message Handler (PMH). Displays debug output for the RTSP client session information. Displays debug output for the RTSP client socket data.
Command
Description
To display debug messages about the RTSP client, or the current session, use the debug rtsp [client | session] command. To disable the output, use the no form of this command.
[no] debug rtsp [client | session]
Syntax Description
session Cumulative information about the session is displayed, packet statistics, along with general call information, such as call ID, session ID, individual RTSP stream URLs, packet statistics, and play duration. client Client information and stream information for the stream that is currently active is displayed.
Defaults
Debug is not enabled.
Command History
12.1(3)T This command was introduced. 12.2(1)Xx Support for the Cisco AS5800 universal access server was added.
Release
Modification
Examples
The following example output displays the result from entering the debug rtsp session command:
Related Commands
Displays debug output for the RTSP client API. Displays debug output for the RTSP client data. debug rtsp pmh Displays debug messages for the Protocol Message Handler (PMH). Displays debug output for the RTSP client session information. Displays debug output for the RTSP client socket data.
Command
Description
To display debug information about the Protocol Message Handler (PMH), use the debug rtsp pmh command. To disable the output, use the no form of this command.
[no] debug rtsp pmhSyntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Defaults
Debug is not enabled.
Command History
12.1(3)T This command was introduced. 12.2(1)Xx Support for the Cisco AS5800 universal access server was added.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
Use the debug rtsp pmh debug command for the following instances:
Mar 1 02:25:11.447:SendBuf:DESCRIBE rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com/en_welcome.au
RTSP/1.0
CSeq:0
Mar 1 02:25:11.947:########################################
Mar 1 02:25:11.947:Mesg_line :RTSP/1.0 200 OK
Mar 1 02:25:11.951:Content_length :459
Mar 1 02:25:11.951:Header list
Mar 1 02:25:11.951:Content-length:459
Mar 1 02:25:11.951:Content-type:application/sdp
Mar 1 02:25:11.951:Content-base:rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com/en_welcome.au/
Mar 1 02:25:11.951:X-TSPort:7802
Mar 1 02:25:11.951:Last-Modified:Thu, 07 Oct 1999 13:51:28 GMT
Mar 1 02:25:11.951:Date:Mon, 10 Jan 2000 16:40:59 GMT
Mar 1 02:25:11.951:CSeq:0
Examples
The following example output displays the result from entering the debug rtsp pmh command.
Router# debug rtsp pmh
RTSP client Protocol Message Handler debugging is on
Router#
Jan 1 00:22:34.087:rtsp_pmh_update_play_req_url:
Jan 1 00:22:34.087:rtsp_pmh_parse_url:
Jan 1 00:22:34.087:Input-Url:rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au
Jan 1 00:22:34.087:Hostname:rtsp-cisco.cisco.com
Jan 1 00:22:34.087:Port :554
Jan 1 00:22:34.087:Path :en_welcome.au
Jan 1 00:22:34.091:rtsp_pmh_build_desc_req:
Jan 1 00:22:34.091:rtsp_pmh_add_req_line:
Jan 1 00:22:34.091:RequestLine:(DESCRIBE rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au
RTSP/1.0
)
Jan 1 00:22:34.091:SendBuf:DESCRIBE rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au
RTSP/1.0
CSeq:0
Jan 1 00:22:34.091:last_req = 0
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:rtsp_pmh_parse_svr_response:
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:rtsp_pmh_create_mesg:
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:########################################
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:Mesg_line :RTSP/1.0 200 OK
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:Content_length :482
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:Header list
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:Content-length:482
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:Content-type:application/sdp
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:Content-base:rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au/
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:Last-Modified:Thu, 07 Oct 1999 13:51:28 GMT
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:X-TSPort:7802
Jan 1
00:22:34.739:vsrc:http://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:8080/viewsource/template.html?nuyhtgywkgz6m
c9AbhC4gn5gBsqp4eA1v1yeC3d4ngEt5o5gwuw4t6x05jbhcv66ngE8xg8f
Jan 1
00:22:34.739:Set-Cookie:cbid=ekeghhiljgekgihheoqohpptrrjrktlufkegkioihgjfdlplrnqogpoqlrps
kqnuffgjcmcl;path=/;expires=Thu,31-Dec-2037 23:59:59 GMT
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:Date:Mon, 10 Apr 2000 15:39:17 GMT
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:CSeq:0
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:Message Body
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:v=0
o=- 939300688 939300688 IN IP4 1.13.79.6
s=<No title>
i=<No author> <No copyright>
a=StreamCount:integer;1
t=0 0
m=audio 0 RTP/AVP 0
a=control:streamid=0
a=rtpmap:0 L8/8000/1
a=length:npt=3.249000
a=range:npt=0-3.249000
a=mimetype:string;"audio/x-pn-au"
a=StartTime:integer;0
a=AvgBitRate:integer;64000
a=AvgPacketSize:integer;320
a=Preroll:integer;0
a=MaxPacketSize:integer;320
a=MaxBitRate:integer;64000
a=OpaqueData:buffer;"AQABAEAfAAA="
a=StreamName:string;"audio/x-pn-au"
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:########################################
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:rtsp_pmh_get_header_value:
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:Cseq=1
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:rtsp_pmh_get_resp_line:
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:Response Status
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:Status Code:200
Jan 1 00:22:34.739:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:Reason Phrase:OK
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:rtsp_pmh_parse_mesg_body:
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:Response
URL:rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au/streamid=0
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:RealServer Duration
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:IP/TV Duration
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:rtsp_pmh_get_range_from_npt:
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:rtsp_pmh_get_range_from_npt:Duration:3249 msecs
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:rtsp_pmh_update_resp_status:
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:rtsp_pmh_update_resp_status:Control Not active
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:########################################
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:Mesg_line :RTSP/1.0 200 OK
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:Content_length :482
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:Header list
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:Content-length:482
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:Content-type:application/sdp
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:Content-base:rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au/
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:Last-Modified:Thu, 07 Oct 1999 13:51:28 GMT
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:X-TSPort:7802
Jan 1
00:22:34.743:vsrc:http://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:8080/viewsource/template.html?nuyhtgywkgz6m
c9AbhC4gn5gBsqp4eA1v1yeC3d4ngEt5o5gwuw4t6x05jbhcv66ngE8xg8f
Jan 1
00:22:34.743:Set-Cookie:cbid=ekeghhiljgekgihheoqohpptrrjrktlufkegkioihgjfdlplrnqogpoqlrps
kqnuffgjcmcl;path=/;expires=Thu,31-Dec-2037 23:59:59 GMT
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:Date:Mon, 10 Apr 2000 15:39:17 GMT
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:CSeq:0
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:Message Body
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:v=0
o=- 939300688 939300688 IN IP4 1.13.79.6
s=<No title>
i=<No author> <No copyright>
a=StreamCount:integer;1
t=0 0
m=audio 0 RTP/AVP 0
a=control:streamid=0
a=rtpmap:0 L8/8000/1
a=length:npt=3.249000
a=range:npt=0-3.249000
a=mimetype:string;"audio/x-pn-au"
a=StartTime:integer;0
a=AvgBitRate:integer;64000
a=AvgPacketSize:integer;320
a=Preroll:integer;0
a=MaxPacketSize:integer;320
a=MaxBitRate:integer;64000
a=OpaqueData:buffer;"AQABAEAfAAA="
a=StreamName:string;"audio/x-pn-au"
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:########################################
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:rtsp_pmh_free_mesg:
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:rtsp_pmh_build_setup_req:
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:rtsp_pmh_add_req_line:
Jan 1 00:22:34.743:RequestLine:(SETUP
rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au/streamid=0 RTSP/1.0
)
Jan 1 00:22:34.747:rtsp_pmh_build_setup_req:SendBuf:SETUP
rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au/streamid=0 RTSP/1.0
CSeq:1
Transport:rtp/avp;unicast;client_port=18084
Jan 1 00:22:35.243:rtsp_pmh_parse_svr_response:
Jan 1 00:22:35.243:rtsp_pmh_create_mesg:
Jan 1 00:22:35.243:########################################
Jan 1 00:22:35.243:Mesg_line :RTSP/1.0 200 OK
Jan 1 00:22:35.243:Content_length :0
Jan 1 00:22:35.243:Header list
Jan 1
00:22:35.243:Transport:rtp/avp;unicast;client_port=18084-18085;server_port=23192-23193
Jan 1 00:22:35.243:Session:24457-1
Jan 1 00:22:35.243:Date:Mon, 10 Apr 2000 15:39:17 GMT
Jan 1 00:22:35.243:CSeq:1
Jan 1 00:22:35.243:Message Body
Jan 1 00:22:35.243:########################################
Jan 1 00:22:35.243:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:
Jan 1 00:22:35.243:rtsp_pmh_get_header_value:
Jan 1 00:22:35.243:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:Cseq=2
Jan 1 00:22:35.243:rtsp_pmh_get_resp_line:
Jan 1 00:22:35.243:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:Response Status
Jan 1 00:22:35.243:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:Status Code:200
Jan 1 00:22:35.243:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:Reason Phrase:OK
Jan 1 00:22:35.243:rtsp_pmh_get_header_value:
Jan 1 00:22:35.247:rtsp_pmh_get_header_value:
Jan 1 00:22:35.247:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:RTP PORT= 23192
Jan 1 00:22:35.247:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:RTP PORT= 23192
Jan 1 00:22:35.247:rtsp_pmh_update_resp_status:
Jan 1 00:22:35.247:rtsp_pmh_update_resp_status:Control Not active
Jan 1 00:22:35.247:########################################
Jan 1 00:22:35.247:Mesg_line :RTSP/1.0 200 OK
Jan 1 00:22:35.247:Content_length :0
Jan 1 00:22:35.247:Header list
Jan 1
00:22:35.247:Transport:rtp/avp;unicast;client_port=18084-18085;server_port=23192-23193
Jan 1 00:22:35.247:Session:24457-1
Jan 1 00:22:35.247:Date:Mon, 10 Apr 2000 15:39:17 GMT
Jan 1 00:22:35.247:CSeq:1
Jan 1 00:22:35.247:Message Body
Jan 1 00:22:35.247:########################################
Jan 1 00:22:35.247:rtsp_pmh_free_mesg:
Jan 1 00:22:35.247:rtsp_pmh_build_play_req:
Jan 1 00:22:35.247:rtsp_pmh_add_req_line:
Jan 1 00:22:35.247:RequestLine:(PLAY
rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au/streamid=0 RTSP/1.0
)
Jan 1 00:22:35.247:rtsp_pmh_build_play_req:SendBuf:PLAY
rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au/streamid=0 RTSP/1.0
Session:24457-1
CSeq:2
Jan 1 00:22:35.735:rtsp_pmh_parse_svr_response:
Jan 1 00:22:35.735:rtsp_pmh_create_mesg:
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:########################################
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:Mesg_line :RTSP/1.0 200 OK
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:Content_length :0
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:Header list
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:Date:Mon, 10 Apr 2000 15:39:18 GMT
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:CSeq:2
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:Message Body
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:########################################
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:rtsp_pmh_get_header_value:
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:Cseq=3
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:rtsp_pmh_get_resp_line:
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:Response Status
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:Status Code:200
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:Reason Phrase:OK
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:rtsp_pmh_update_resp_status:
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:rtsp_pmh_update_resp_status:Control Not active
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:########################################
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:Mesg_line :RTSP/1.0 200 OK
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:Content_length :0
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:Header list
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:Date:Mon, 10 Apr 2000 15:39:18 GMT
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:CSeq:2
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:Message Body
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:########################################
Jan 1 00:22:35.739:rtsp_pmh_free_mesg:
Jan 1 00:22:40.011:rtsp_pmh_build_teardown_req:
Jan 1 00:22:40.011:rtsp_pmh_add_req_line:
Jan 1 00:22:40.011:RequestLine:(TEARDOWN
rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au/streamid=0 RTSP/1.0
)
Jan 1 00:22:40.011:SendBuf:TEARDOWN
rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au/streamid=0 RTSP/1.0
Session:24457-1
CSeq:3
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:rtsp_pmh_parse_svr_response:
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:rtsp_pmh_create_mesg:
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:########################################
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:Mesg_line :RTSP/1.0 200 OK
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:Content_length :0
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:Header list
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:Date:Mon, 10 Apr 2000 15:39:23 GMT
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:CSeq:3
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:Message Body
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:########################################
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:rtsp_pmh_get_header_value:
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:Cseq=4
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:rtsp_pmh_get_resp_line:
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:Response Status
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:Status Code:200
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:rtsp_pmh_process_resp_headers:Reason Phrase:OK
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:rtsp_pmh_update_resp_status:
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:rtsp_pmh_update_resp_status:Control Not active
Jan 1 00:22:40.443:########################################
Jan 1 00:22:40.447:Mesg_line :RTSP/1.0 200 OK
Jan 1 00:22:40.447:Content_length :0
Jan 1 00:22:40.447:Header list
Jan 1 00:22:40.447:Date:Mon, 10 Apr 2000 15:39:23 GMT
Jan 1 00:22:40.447:CSeq:3
Jan 1 00:22:40.447:Message Body
Jan 1 00:22:40.447:########################################
Jan 1 00:22:40.447:rtsp_pmh_free_mesg:
Router#
Jan 1 00:14:20.483:rtsp_tcp_socket_connect:
Jan 1 00:14:20.483:rtsp_tcp_socket_connect:Socket = 0
Jan 1 00:14:20.483: Dest_addr = 1.13.79.6 Dest_Port=554
Jan 1 00:14:20.487:rtsp_send_req_to_svr:Socket = 0 send_buf = DESCRIBE
rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au RTSP/1.0
CSeq:0
len = 76
Jan 1 00:14:20.491:rtsp_send_req_to_svr:bytes_sent = 76
Jan 1 00:14:20.491:rtsp_read_svr_resp:Socket = 0
Jan 1 00:14:20.491:rtsp_read_svr_resp:NBYTES = -1
Jan 1 00:14:21.155:rtsp_read_svr_resp:Socket = 0
Jan 1 00:14:21.159:rtsp_read_svr_resp:NBYTES = 996
Jan 1 00:14:21.223:rtsp_read_svr_resp:rtsp_pmh_parse_svr_response complete
Jan 1 00:14:21.227:rtsp_read_svr_resp:RESP received OK
Jan 1 00:14:21.227:rtsp_send_req_to_svr:Socket = 0 send_buf = SETUP
rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au/streamid=0 RTSP/1.0
CSeq:1
Transport:rtp/avp;unicast;client_port=18074
len = 130
Jan 1 00:14:21.227:rtsp_send_req_to_svr:bytes_sent = 130
Jan 1 00:14:21.663:rtsp_read_svr_resp:Socket = 0
Jan 1 00:14:21.663:rtsp_read_svr_resp:NBYTES = 159
Jan 1 00:14:21.663:rtsp_read_svr_resp:rcv_buf = RTSP/1.0 200 OK
CSeq:1
Date:Mon, 10 Apr 2000 15:31:04 GMT
Session:24455-1
Transport:rtp/avp;unicast;client_port=18074-18075;server_port=15562-15563
Jan 1 00:14:21.663:rtsp_read_svr_resp:rtsp_pmh_parse_svr_response complete
Jan 1 00:14:21.663:rtsp_read_svr_resp:RESP received OK
Jan 1 00:14:21.663:rtsp_send_req_to_svr:Socket = 0 send_buf = PLAY
rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au/streamid=0 RTSP/1.0
Session:24455-1
CSeq:2
len = 101
Jan 1 00:14:21.667:rtsp_send_req_to_svr:bytes_sent = 101
Jan 1 00:14:22.155:rtsp_read_svr_resp:Socket = 0
Jan 1 00:14:22.155:rtsp_read_svr_resp:NBYTES = 65
Jan 1 00:14:22.155:rtsp_read_svr_resp:rcv_buf = RTSP/1.0 200 OK
CSeq:2
Date:Mon, 10 Apr 2000 15:31:04 GMT
Jan 1 00:14:22.155:rtsp_read_svr_resp:rtsp_pmh_parse_svr_response complete
Jan 1 00:14:22.155:rtsp_read_svr_resp:RESP received OK
rtsp-5#
Jan 1 00:14:26.411:rtsp_send_req_to_svr:Socket = 0 send_buf = TEARDOWN
rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au/streamid=0 RTSP/1.0
Session:24455-1
CSeq:3
len = 105
Jan 1 00:14:26.411:rtsp_send_req_to_svr:bytes_sent = 105
Jan 1 00:14:26.863:rtsp_read_svr_resp:Socket = 0
Jan 1 00:14:26.863:rtsp_read_svr_resp:NBYTES = 65
Jan 1 00:14:26.863:rtsp_read_svr_resp:rcv_buf = RTSP/1.0 200 OK
CSeq:3
Date:Mon, 10 Apr 2000 15:31:09 GMT
Jan 1 00:14:26.863:rtsp_read_svr_resp:rtsp_pmh_parse_svr_response complete
Jan 1 00:14:26.863:rtsp_read_svr_resp:RESP received OK
Jan 1 00:14:26.863:rtsp_close_svr_connection:closing socket 0
Router#
Related Commands
Displays debug output for the RTSP client API. Displays debug output for the RTSP client data. Displays debug output for the RTSP client session information. Displays debug output for the RTSP client socket data.
Command
Description
To display debug messages of the RTSP session, or client , use the debug rtsp session command.
[no] debug rtsp [client | session]
Syntax Description
session Cumulative information about the session is displayed, packet statistics, along with general call information, such as call ID, session ID, individual RTSP stream URLs, packet statistics, and play duration. client Client information and stream information for the stream that is currently active is displayed.
Defaults
Debug is not enabled.
Command History
12.1(3)T This command was introduced. 12.2(1)Xx Support for the Cisco AS5800 universal access server was added.
Release
Modification
Examples
Router# debug rtsp session
RTSP client session debugging is on
router#
Jan 1 00:08:36.099:rtsp_get_new_scb:
Jan 1 00:08:36.099:rtsp_initialize_scb:
Jan 1 00:08:36.099:rtsp_control_process_msg:
Jan 1 00:08:36.099:rtsp_control_process_msg:received MSG request of TYPE 0
Jan 1 00:08:36.099:rtsp_set_event:
Jan 1 00:08:36.099:rtsp_set_event:api_req_msg_type=RTSP_API_REQ_PLAY
Jan 1 00:08:36.103:rtsp_set_event:url:[rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au]
Jan 1 00:08:36.103:rtsp_process_async_event:SCB=0x62128F08
Jan 1 00:08:36.103:rtsp_process_async_event:rtsp_state = RTSP_SES_STATE_IDLE
rtsp_event = RTSP_EV_PLAY_OR_REC
Jan 1 00:08:36.103:act_idle_event_play_or_rec_req:
Jan 1 00:08:36.103:rtsp_resolve_dns:
Jan 1 00:08:36.103:rtsp_resolve_dns:IP Addr = 1.13.79.6:
Jan 1 00:08:36.103:rtsp_connect_to_svr:
Jan 1 00:08:36.103:rtsp_connect_to_svr:socket=0, connection_state = 2
Jan 1 00:08:36.103:rtsp_start_timer:timer (0x62128FD0)starts - delay (10000)
Jan 1 00:08:36.107:rtsp_control_main:SOCK= 0 Event=0x1
Jan 1 00:08:36.107:rtsp_stop_timer:timer(0x62128FD0) stops
Jan 1 00:08:36.107:rtsp_process_async_event:SCB=0x62128F08
Jan 1 00:08:36.107:rtsp_process_async_event:rtsp_state = RTSP_SES_STATE_IDLE
rtsp_event = RTSP_EV_SVR_CONNECTED
Jan 1 00:08:36.107:act_idle_event_svr_connected:
Jan 1 00:08:36.107:rtsp_control_main:SOCK= 0 Event=0x1
Jan 1 00:08:36.783:rtsp_control_main:SOCK= 0 Event=0x1
Jan 1 00:08:36.783:rtsp_process_async_event:SCB=0x62128F08
Jan 1 00:08:36.783:rtsp_process_async_event:rtsp_state = RTSP_SES_STATE_READY
rtsp_event = RTSP_EV_SVR_DESC_OR_ANNOUNCE_RESP
Jan 1 00:08:36.783:act_ready_event_desc_or_announce_resp:
Jan 1
00:08:36.783:act_ready_event_desc_or_announce_resp:RTSP_STATUS_DESC_OR_ANNOUNCE_RESP_OK
Jan 1 00:08:37.287:rtsp_control_main:SOCK= 0 Event=0x1
Jan 1 00:08:37.287:rtsp_process_async_event:SCB=0x62128F08
Jan 1 00:08:37.287:rtsp_process_async_event:rtsp_state = RTSP_SES_STATE_READY
rtsp_event = RTSP_EV_SVR_SETUP_RESP
Jan 1 00:08:37.287:act_ready_event_setup_resp:
Jan 1 00:08:37.287:act_ready_event_setup_resp:Remote RTP Port=13344
Jan 1 00:08:37.287:rtsp_rtp_stream_setup:scb=0x62128F08, callID=0x7 record=0
Jan 1 00:08:37.287:rtsp_rtp_stream_setup:Starting RTCP session.
Local IP addr = 1.13.79.45, Remote IP addr = 1.13.79.6,
Local RTP port = 18748, Remote RTP port = 13344 CallID=8
Jan 1 00:08:37.291:xmit_func = 0x0 vdbptr = 0x61A0FC98
Jan 1 00:08:37.291:rtsp_control_main:CCAPI Queue Event
Jan 1 00:08:37.291:rtsp_rtp_associate_done:ev=0x62070E08, callID=0x7
Jan 1 00:08:37.291:rtsp_rtp_associate_done:scb=0x62128F08
Jan 1 00:08:37.291:rtsp_rtp_associate_done:callID=0x7, pVdb=0x61F4FBC8,
Jan 1 00:08:37.291: spi_context=0x6214145C
Jan 1 00:08:37.291: disposition=0, playFunc=0x60CA2238,
Jan 1 00:08:37.291: codec=0x5, vad=0, mediaType=6,
Jan 1 00:08:37.291: stream_assoc_id=1
Jan 1 00:08:37.291:rtsp_rtp_modify_session:scb=0x62128F08, callID=0x7
Jan 1 00:08:37.291:rtsp_process_async_event:SCB=0x62128F08
Jan 1 00:08:37.291:rtsp_process_async_event:rtsp_state = RTSP_SES_STATE_READY
rtsp_event = RTSP_EV_ASSOCIATE_DONE
Jan 1 00:08:37.291:act_ready_event_associate_done:
Jan 1 00:08:37.291:rtsp_get_stream:
Jan 1 00:08:37.783:rtsp_control_main:SOCK= 0 Event=0x1
Jan 1 00:08:37.783:rtsp_process_async_event:SCB=0x62128F08
Jan 1 00:08:37.783:rtsp_process_async_event:rtsp_state = RTSP_SES_STATE_READY
rtsp_event = RTSP_EV_SVR_PLAY_OR_REC_RESP
Jan 1 00:08:37.783:act_ready_event_play_or_rec_resp:
Jan 1 00:08:37.783:rtsp_start_timer:timer (0x62128FB0)starts - delay (4249)
rtsp-5#
Jan 1 00:08:42.035:rtsp_process_timer_events:
Jan 1 00:08:42.035:rtsp_process_timer_events:PLAY OR RECORD completed
Jan 1 00:08:42.035:rtsp_process_async_event:SCB=0x62128F08
Jan 1 00:08:42.035:rtsp_process_async_event:rtsp_state = RTSP_SES_STATE_PLAY_OR_REC
rtsp_event = RTSP_EV_PLAY_OR_REC_TIMER_EXPIRED
Jan 1 00:08:42.035:act_play_event_play_done:
Jan 1 00:08:42.035:act_play_event_play_done:elapsed play time = 4249 total play time =
4249
Jan 1 00:08:42.035:rtsp_send_teardown_to_svr:
Jan 1 00:08:42.487:rtsp_control_main:SOCK= 0 Event=0x1
Jan 1 00:08:42.487:rtsp_process_async_event:SCB=0x62128F08
Jan 1 00:08:42.487:rtsp_process_async_event:rtsp_state = RTSP_SES_STATE_PLAY_OR_REC
rtsp_event = RTSP_EV_SVR_TEARDOWN_RESP
Jan 1 00:08:42.487:act_play_event_teardown_resp:
Jan 1 00:08:42.487:rtsp_server_closed:
Jan 1 00:08:42.487:rtsp_send_resp_to_api:
Jan 1 00:08:42.487:rtsp_send_resp_to_api:sending RESP=RTSP_STATUS_PLAY_COMPLETE
Jan 1 00:08:42.491:rtsp_rtp_teardown_stream:scb=0x62128F08, callID=0x7
Jan 1 00:08:42.491:rtsp_rtp_stream_cleanup:scb=0x62128F08, callID=0x7
Jan 1 00:08:42.491:rtsp_update_stream_stats:scb=0x62128F08, stream=0x61A43350,
Jan 1 00:08:42.491:call_info=0x6214C67C, callID=0x7
Jan 1 00:08:42.491:rtsp_update_stream_stats:rx_bytes = 25992
Jan 1 00:08:42.491:rtsp_update_stream_stats:rx_packetes = 82
Jan 1 00:08:42.491:rtsp_reinitialize_scb:
Jan 1 00:08:42.503:rtsp_control_process_msg:
Jan 1 00:08:42.503:rtsp_control_process_msg:received MSG request of TYPE 0
Jan 1 00:08:42.503:rtsp_set_event:
Jan 1 00:08:42.503:rtsp_set_event:api_req_msg_type=RTSP_API_REQ_DESTROY
Jan 1 00:08:42.503:rtsp_session_cleanup:
Jan 1 00:08:42.503:rtsp_create_session_history:scb=0x62128F08, callID=0x7
Jan 1 00:08:42.503:rtsp_insert_session_history_record:current=0x6214BDC8, callID=0x7
Jan 1 00:08:42.503:rtsp_insert_session_history_record:count = 3
Jan 1 00:08:42.503:rtsp_insert_session_history_record:starting history record
deletion_timer of10 minutes
Jan 1 00:08:42.503:rtsp_session_cleanup:deleting session:scb=0x62128F08
Router#
Related Commands
Displays debug output for the RTSP client API. Displays debug output for the RTSP client data. debug rtsp pmh Displays debug messages for the Protocol Message Handler (PMH). Displays debug output for the RTSP client socket data.
Command
Description
To display debug messages about the packets received or sent on the TCP or UDP sockets, use the debug rtsp socket command. To disable the output, use the no form of this command.
[no] debug rtsp socketSyntax Description
This command has no arguments or keywords.
Defaults
Debug is not enabled.
Command History
12.1(3)T This command was introduced. 12.2(1)Xx Support for the Cisco AS5800 universal access server was added.
Release
Modification
Usage Guidelines
Each RTSP session has a TCP port for control and UDP (RTP) port for delivery of data. The control connection (TCP socket) is used to exchange a set of messages (Request from the RTSP client and the response from the server) for playing a prompt. The debug rtsp socket command enables the user to debug the message exchanges being done on the TCP control connection.
Examples
The following example displays output from the debug rtsp socket command:
Router# show debug rtsp socket
Jan 1 00:14:20.483:rtsp_tcp_socket_connect:
Jan 1 00:14:20.483:rtsp_tcp_socket_connect:Socket = 0
Jan 1 00:14:20.483: Dest_addr = 1.13.79.6 Dest_Port=554
Jan 1 00:14:20.487:rtsp_send_req_to_svr:Socket = 0 send_buf = DESCRIBE
rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au RTSP/1.0
CSeq:0
len = 76
Jan 1 00:14:20.491:rtsp_send_req_to_svr:bytes_sent = 76
Jan 1 00:14:20.491:rtsp_read_svr_resp:Socket = 0
Jan 1 00:14:20.491:rtsp_read_svr_resp:NBYTES = -1
Jan 1 00:14:21.155:rtsp_read_svr_resp:Socket = 0
Jan 1 00:14:21.159:rtsp_read_svr_resp:NBYTES = 996
Jan 1 00:14:21.223:rtsp_read_svr_resp:rtsp_pmh_parse_svr_response complete
Jan 1 00:14:21.227:rtsp_read_svr_resp:RESP received OK
Jan 1 00:14:21.227:rtsp_send_req_to_svr:Socket = 0 send_buf = SETUP
rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au/streamid=0 RTSP/1.0
CSeq:1
Transport:rtp/avp;unicast;client_port=18074
len = 130
Jan 1 00:14:21.227:rtsp_send_req_to_svr:bytes_sent = 130
Jan 1 00:14:21.663:rtsp_read_svr_resp:Socket = 0
Jan 1 00:14:21.663:rtsp_read_svr_resp:NBYTES = 159
Jan 1 00:14:21.663:rtsp_read_svr_resp:rcv_buf = RTSP/1.0 200 OK
CSeq:1
Date:Mon, 10 Apr 2000 15:31:04 GMT
Session:24455-1
Transport:rtp/avp;unicast;client_port=18074-18075;server_port=15562-15563
Jan 1 00:14:21.663:rtsp_read_svr_resp:rtsp_pmh_parse_svr_response complete
Jan 1 00:14:21.663:rtsp_read_svr_resp:RESP received OK
Jan 1 00:14:21.663:rtsp_send_req_to_svr:Socket = 0 send_buf = PLAY
rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au/streamid=0 RTSP/1.0
Session:24455-1
CSeq:2
len = 101
Jan 1 00:14:21.667:rtsp_send_req_to_svr:bytes_sent = 101
Jan 1 00:14:22.155:rtsp_read_svr_resp:Socket = 0
Jan 1 00:14:22.155:rtsp_read_svr_resp:NBYTES = 65
Jan 1 00:14:22.155:rtsp_read_svr_resp:rcv_buf = RTSP/1.0 200 OK
CSeq:2
Date:Mon, 10 Apr 2000 15:31:04 GMT
Jan 1 00:14:22.155:rtsp_read_svr_resp:rtsp_pmh_parse_svr_response complete
Jan 1 00:14:22.155:rtsp_read_svr_resp:RESP received OK
rtsp-5#
Jan 1 00:14:26.411:rtsp_send_req_to_svr:Socket = 0 send_buf = TEARDOWN
rtsp://rtsp-cisco.cisco.com:554/en_welcome.au/streamid=0 RTSP/1.0
Session:24455-1
CSeq:3
len = 105
Jan 1 00:14:26.411:rtsp_send_req_to_svr:bytes_sent = 105
Jan 1 00:14:26.863:rtsp_read_svr_resp:Socket = 0
Jan 1 00:14:26.863:rtsp_read_svr_resp:NBYTES = 65
Jan 1 00:14:26.863:rtsp_read_svr_resp:rcv_buf = RTSP/1.0 200 OK
CSeq:3
Date:Mon, 10 Apr 2000 15:31:09 GMT
Jan 1 00:14:26.863:rtsp_read_svr_resp:rtsp_pmh_parse_svr_response complete
Jan 1 00:14:26.863:rtsp_read_svr_resp:RESP received OK
Jan 1 00:14:26.863:rtsp_close_svr_connection:closing socket 0
Router#
Related Commands
Displays debug output for the RTSP client API. Displays debug output for the RTSP client data. debug rtsp pmh Displays debug messages for the Protocol Message Handler (PMH). Displays debug output for the RTSP client session information.
Command
Description
To display debug messages for VoIP IVR interactions, use the debug voip ivr type command. To disable the debug output, use the no form of this command.
[no] debug voip ivr type
Syntax Description
all Displays all IVR messages applib Displays IVR API libraries being processed. callsetup Displays IVR callsetup being processed. digitcollect Displays IVR digits collected during the call. dynamic Displays IVR dynamic prompt play debug error Displays IVR errors script Displays IVR script debug settlement Displays IVR settlement acctivities states Displays IVR states tclcommands Displays the TCL commands used in the script.
Defaults
Debug is not enabled.
Command History
12.1(3)T This command was introduced. 12.2(1)Xx Support for the Cisco AS5800 universal access server was added.
Release
Modification
Examples
The following examples are from the code for Cisco IOS Release 12.1(3)T. The output is displayed when the debug voip ivr type command is entered.
Example debug voip ivr appilib
The following output is displayed when the debug voip ivr appilib command is entered.
Router1# debug voip ivr appilib
ivr:
ivr app library debugging is on
Router1#
Jan 10 17:42:04.180:AppManagerCCAPI_Interface:
Jan 10 17:42:04.180:AppNewLeg
Jan 10 17:42:04.180:AppPushLegORConnection:Pushing LEG[34 ][NULL
] Onto {HAN[TCL_HAND][NULL ] ( )}
Jan 10 17:42:04.180:Event CC_EV_CALL_SETUP_IND[29]:LEG[34
][TCL_HAND]
Jan 10 17:42:04.184:AppPushHandler:Pushing {HAN[DC_HAND ][NULL ]
( )} Onto {HAN[TCL_HAND][NULL ] ( LEG[34 ][TCL_HAND] )}
Jan 10 17:42:04.184:AppPushLegORConnection:Pushing LEG[34
][TCL_HAND] Onto {HAN[DC_HAND ][TCL_HAND] ( )}
Jan 10 17:42:04.184:$ mediaPlay():CallID 34
Jan 10 17:42:04.184:Event CC_EV_CALL_REPORT_DIGITS_DONE[45]:LEG[34
][DC_HAND ]
Jan 10 17:42:17.261:AppMediaCallback:CallID 34 received
response 'MSW_RESPONSE_TYPE_PLAY'
with reason 'MSW_REASON_GENERIC_SUCCESS'
Jan 10 17:42:17.261:Event APP_EV_MEDIA_CALLBACK[47]:LEG[34
][DC_HAND ]
Jan 10 17:42:18.209:%ISDN-6-DISCONNECT:Interface Serial0:0
disconnected from unknown , call lasted 13 seconds
Example debug voip ivr callsetup
The following output is displayed when the debug voip ivr callsetup command is entered.
Router# debug voip ivr callsetup
Jan 10 17:45:57.528:%SYS-5-CONFIG_I:Configured from console by lab on
console
Jan 10 17:46:37.682:InitiateCallSetup:Incoming[66] AlertTime -1
Destinations(1) [ 3450070 ]
Jan 10 17:46:37.682:DNInitiate:Destination[3450070]
Jan 10 17:46:37.682:DNSetupPeer:
Jan 10 17:46:37.682:Destination SetupPeer cid(66), destPat(3450070),
match(2), prefix(), peer(61CB5CAC)
Jan 10 17:46:37.762:DNHandler:
(DN_SETTING[1])--(CC_EV_CALL_ALERT[11])--IGNORED-->>(DN_SETTING[1])
Jan 10 17:46:37.762:CS_Setting_ALERT:
Jan 10 17:46:37.762:CSPopLegAndWait:
Jan 10 17:46:37.762:CallSetupHandler:
(CS_SETTING[0]) -----(CS_EV_ALERT[0])------->>>(CS_CONFINGALERT[4])
Jan 10 17:46:37.762:CS_ConfingAlert_CREATEDONE:
Jan 10 17:46:37.762:CallSetupHandler:
(CS_CONFINGALERT[4])
-----(CS_EV_CREATEDONE[4])------->>>(CS_CONFEDALERT[5])
Jan 10 17:46:37.762:CallSetupHandler:
(CS_CONFEDALERT[5])--(DN_SETTING[APP_EV_NULL])--IGNORED-->>>(CS_CONFEDALERT[5])
Router1#
Jan 10 17:46:47.682:CallSetupHandler:
(CS_CONFEDALERT[5])--(DN_SETTING[APP_EV_NULL])--IGNORED-->>>(CS_CONFEDALERT[5])
Jan 10 17:46:48.642:CS_ConfedAlert_CONNECTED:
Jan 10 17:46:48.642:CSDiscReturnAndEmptyLegALL:
Jan 10 17:46:48.642:DNCleanup:
Jan 10 17:46:48.642:DNSettlementCleanup:cid(66) trans=0, provider=0
Jan 10 17:46:48.642:CSReturnIFDone:CallSetup Returning(Status
CS_ACTIVE)
Jan 10 17:46:48.642:CallSetupHandler:
(CS_CONFEDALERT[5]) -----(CS_EV_CONNECTED[1])------->>>(CS_CONFED[3])
Jan 10 17:46:48.646:CallSetupCleanup:
Router #
Example debug voip ivr digitcollect
The following output is displayed when the debug voip ivr digitcollect command is entered.
Router# deb voip ivr digitcollect
ivr:
ivr digit collect debugging is on
Router1#
Router1#
Router1#
Jan 10 17:47:55.558:DigitCollect:DialPlan=FALSE AbortKey=* TermKey=#
NumPatts=1
Enable=FALSE InterruptPrompt=TRUE maxDigits=11
Jan 10 17:47:55.558:act_DCRunning_RDone:callid=68 Enable succeeded.
Router1#
Jan 10 17:48:04.006:DCHandlerFunc:PassingThrough
Jan 10 17:48:04.066:act_DCRunning_Digit::pLeg 68 Digit 1
Jan 10 17:48:04.066:act_DCRunning_RDone:callid=68 Reporting disabled.
Jan 10 17:48:04.066:DigitCollectComplete:Status 5=DC_MATCHED_PATTERN.
Digits=1
Jan 10 17:48:04.070:DigitCollect:DialPlan=FALSE AbortKey=* TermKey=#
NumPatts=0
Enable=FALSE InterruptPrompt=TRUE maxDigits=11
Jan 10 17:48:04.070:DCHandlerCleanup:
Jan 10 17:48:04.074:act_DCRunning_RDone:callid=68 Enable succeeded.
Router1#
Router1#
Jan 10 17:48:08.038:DCHandlerFunc:PassingThrough
Jan 10 17:48:09.246:DCHandlerFunc:PassingThrough
Jan 10 17:48:09.286:act_DCRunning_Digit::pLeg 68 Digit 1
Jan 10 17:48:09.478:DCHandlerFunc:PassingThrough
Jan 10 17:48:09.506:act_DCRunning_Digit::pLeg 68 Digit 1
Jan 10 17:48:10.739:DCHandlerFunc:PassingThrough
Jan 10 17:48:10.779:act_DCRunning_Digit::pLeg 68 Digit 1
Jan 10 17:48:11.027:DCHandlerFunc:PassingThrough
Jan 10 17:48:11.067:act_DCRunning_Digit::pLeg 68 Digit 1
Jan 10 17:48:11.687:DCHandlerFunc:PassingThrough
Jan 10 17:48:11.747:act_DCRunning_Digit::pLeg 68 Digit 1
Jan 10 17:48:12.219:DCHandlerFunc:PassingThrough
Jan 10 17:48:12.279:act_DCRunning_Digit::pLeg 68 Digit 2
Jan 10 17:48:14.227:DCHandlerFunc:PassingThrough
Jan 10 17:48:14.287:act_DCRunning_Digit::pLeg 68 Digit 1
Jan 10 17:48:14.779:DCHandlerFunc:PassingThrough
Jan 10 17:48:14.859:act_DCRunning_Digit::pLeg 68 Digit 1
Jan 10 17:48:15.307:DCHandlerFunc:PassingThrough
Jan 10 17:48:15.359:act_DCRunning_Digit::pLeg 68 Digit 1
Jan 10 17:48:15.719:DCHandlerFunc:PassingThrough
Jan 10 17:48:15.759:act_DCRunning_Digit::pLeg 68 Digit 2
Jan 10 17:48:16.219:DCHandlerFunc:PassingThrough
Jan 10 17:48:16.299:act_DCRunning_Digit::pLeg 68 Digit T
Jan 10 17:48:16.299:act_DCRunning_RDone:callid=68 Reporting disabled.
Jan 10 17:48:16.299:DigitCollectComplete:Status 5=DC_MATCHED_PATTERN.
Digits=1111121112
Jan 10 17:48:16.303:DCHandlerCleanup:
Jan 10 17:48:16.335:DigitCollect:DialPlan=TRUE AbortKey=* TermKey=#
NumPatts=0
Enable=FALSE InterruptPrompt=TRUE maxDigits=0
Jan 10 17:48:16.339:act_DCRunning_RDone:callid=68 Enable succeeded.
Router #
Example debug voip ivr script
The following output is displayed when the debug voip ivr script command is entered.
Router# deb voip ivr script
ivr:
ivr script debugging is on
Router1#
Jan 10 17:49:10.250:FSM Transtion:([1
]CALL_INIT,[29]ev_setup_indication)---([10]act_Setup)--->([4
]LANGSELECTION)
Jan 10 17:49:10.250:TotalLanguages= 2
Router1#
Router1#
Jan 10 17:49:16.662:FSM Transtion:([4
]LANGSELECTION,[55]ev_digitcollect_done)---([1 ]act_LangSelect)--->([5
]CARDSELECTION)
Router1#
Router1#
Jan 10 17:49:20.630:([5 ]CARDSELECT,[47]ev_media_d) ------> NOTHANDLED
Jan 10 17:49:26.770:FSM Transtion:([5
]CARDSELECTION,[55]ev_digitcollect_done)---([2
]act_GotCardNumber)--->([6 ]AUTHORIZE)
Jan 10 17:49:26.806:FSM Transtion:([6
]AUTHORIZE,[49]ev_authorize_done)---([8 ]act_FirstAuthorized)--->([7
]GETDEST)
Jan 10 17:49:26.806: aaa authorize Status=ao_000
Router1#
Router1#
Router1#
Jan 10 17:49:33.395:([7 ]GETDEST ,[47]ev_media_d) ------> NOTHANDLED
Jan 10 17:49:36.411:FSM Transtion:([7
]GETDEST,[55]ev_digitcollect_done)---([3 ]act_GotDest)--->([8
]SECONDAUTHORIZE)
Jan 10 17:49:36.451:FSM Transtion:([8
]SECONDAUTHORIZE,[49]ev_authorize_done)---([5
]act_SecondAuthorized)--->([10]PLACECALL)
Jan 10 17:49:36.451: aaa authorize Status=ao_000
Jan 10 17:49:42.179:FSM Transtion:
([10]PLACECALL,[47]ev_media_done)---([9
]act_CallSetup)--->([10]PLACECALL)
Example debug voip ivr tclcommands
The following output is displayed when the debug voip ivr tclcommands command is entered.
Router# debug voip ivr tclcommands
ivr tcl commands debugging is on
Router1#
Jan 10 17:50:29.106:tcl_infotagCmd:infotag get leg_ani
Jan 10 17:50:29.106:tcl_getInfoCmd:get leg_ani
Jan 10 17:50:29.106:vtr_ci_incani:argc 2 argindex 2
Jan 10 17:50:29.106:tcl_infotagCmd:infotag set med_language 1
Jan 10 17:50:29.106:tcl_setInfoCmd:set med_language 1
Jan 10 17:50:29.106:vtw_ms_language:
Jan 10 17:50:29.106:tcl_legCmd:leg setupack leg_incoming
Jan 10 17:50:29.106:tcl_setupAckCmd:setupack leg_incoming
Jan 10 17:50:29.106:vtd_lg_incoming:Legs [71 ]VARTAG Translation Leg
Count=1
Jan 10 17:50:29.106:tcl_legCmd:leg proceeding leg_incoming
Jan 10 17:50:29.106:tcl_callProceedingCmd:proceeding leg_incoming
Jan 10 17:50:29.106:vtd_lg_incoming:Legs [71 ]VARTAG Translation Leg
Count=1
Jan 10 17:50:29.110:tcl_legCmd:leg connect leg_incoming
Jan 10 17:50:29.110:tcl_callConnectCmd:connect leg_incoming
Jan 10 17:50:29.110:vtd_lg_incoming:Legs [71 ]VARTAG Translation Leg
Count=1
Jan 10 17:50:29.110:tcl_legCmd:leg collectdigits leg_incoming param1
patterns
Jan 10 17:50:29.110:tcl_collectDigitsCmd:collectdigits leg_incoming
param1 patterns
Jan 10 17:50:29.110:vtd_lg_incoming:Legs [71 ]VARTAG Translation Leg
Count=1
Jan 10 17:50:29.110:tcl_mediaCmd:media play leg_incoming _welcome.au
%s1000 %c1 _lang_sel1.au %s1000 %c2 _lang_sel2.au
Jan 10 17:50:29.110:tcl_mediaPlayCmd:play leg_incoming _welcome.au
%s1000 %c1 _lang_sel1.au %s1000 %c2 _lang_sel2.au
Jan 10 17:50:29.110:vtd_lg_incoming:Legs [71 ]VARTAG Translation Leg
Count=1
Router1#
continued...
Router1#
Jan 10 17:50:35.506:tcl_infotagCmd:infotag get evt_status
Jan 10 17:50:35.506:tcl_getInfoCmd:get evt_status
Jan 10 17:50:35.506:vtr_ev_status:
Jan 10 17:50:35.510:tcl_infotagCmd:infotag get evt_dcdigits
Jan 10 17:50:35.510:tcl_getInfoCmd:get evt_dcdigits
Jan 10 17:50:35.510:vtr_ev_dcdigits:
Jan 10 17:50:35.510:DCDIGITS [1]
Jan 10 17:50:35.510:tcl_infotagCmd:infotag set med_language 1
Jan 10 17:50:35.510:tcl_setInfoCmd:set med_language 1
Jan 10 17:50:35.510:vtw_ms_language:
Jan 10 17:50:35.510:tcl_legCmd:leg collectdigits leg_incoming param1
Jan 10 17:50:35.510:tcl_collectDigitsCmd:collectdigits leg_incoming
param1
Jan 10 17:50:35.510:vtd_lg_incoming:Legs [71 ]VARTAG Translation Leg
Count=1
Jan 10 17:50:35.510:tcl_mediaCmd:media play leg_incoming
_enter_card_num.au
Jan 10 17:50:35.510:tcl_mediaPlayCmd:play leg_incoming
_enter_card_num.au
Jan 10 17:50:35.514:vtd_lg_incoming:Legs [71 ]VARTAG Translation Leg
Count=1
Router1#
Jan 10 17:50:43.878:tcl_infotagCmd:infotag get evt_status
Jan 10 17:50:43.878:tcl_getInfoCmd:get evt_status
Jan 10 17:50:43.878:vtr_ev_status:
Jan 10 17:50:43.882:tcl_infotagCmd:infotag get evt_dcdigits
Jan 10 17:50:43.882:tcl_getInfoCmd:get evt_dcdigits
Jan 10 17:50:43.882:vtr_ev_dcdigits:
Jan 10 17:50:43.882:DCDIGITS [1111121112]
Jan 10 17:50:43.882:tcl_aaaCmd:aaa authorize 111112 1112 50073
leg_incoming
Jan 10 17:50:43.882:tcl_AuthorizeCmd:authorize 111112 1112 50073
leg_incoming
Jan 10 17:50:43.882:vtd_lg_incoming:Legs [71 ]VARTAG Translation Leg
Count=1
Jan 10 17:50:43.882:Authorize
Jan 10 17:50:43.882: account=111112
Jan 10 17:50:43.882: password=1112
Jan 10 17:50:43.882: ani =50073
Jan 10 17:50:43.882: dnis =
Jan 10 17:50:43.910:tcl_infotagCmd:infotag get evt_status
Jan 10 17:50:43.910:tcl_getInfoCmd:get evt_status
Jan 10 17:50:43.910:vtr_ev_status:
Jan 10 17:50:43.914:tcl_infotagCmd:infotag get aaa_avpair_exists
creditAmount
Jan 10 17:50:43.914:tcl_getInfoCmd:get aaa_avpair_exists creditAmount
Jan 10 17:50:43.914:vtr_ra_avpair_exists:
Jan 10 17:50:43.914:tcl_infotagCmd:infotag get aaa_avpair creditAmount
Jan 10 17:50:43.914:tcl_getInfoCmd:get aaa_avpair creditAmount
Jan 10 17:50:43.914:vtr_ra_avpair:
Jan 10 17:50:43.914:tcl_legCmd:leg collectdigits leg_incoming param2
Jan 10 17:50:43.914:tcl_collectDigitsCmd:collectdigits leg_incoming
param2
Jan 10 17:50:43.914:vtd_lg_incoming:Legs [71 ]VARTAG Translation Leg
Count=1
Jan 10 17:50:43.914:tcl_mediaCmd:media play leg_incoming _you_have.au
%a1000 %s1000 _enter_dest.au
Jan 10 17:50:43.914:tcl_mediaPlayCmd:play leg_incoming _you_have.au
%a1000 %s1000 _enter_dest.au
Jan 10 17:50:43.918:vtd_lg_incoming:Legs [71 ]VARTAG Translation Leg
Count=1
Related Commands
debug voip ivr call setup Displays the call setup information. debug voip ivr digit collect Displays the digits collected during the call. debug voip ivr script Displays the scripts being processed. debug voip ivr tclcommands Displays the TCL commands being called.
Command
Description
CA—Call Agent.
DRAM—dynamic random-access memory. RAM that stores information in capacitors that must be periodically refreshed.
ISP—Internet Service Provider.
IVR—Interactive Voice Response.
Media Stream—A single media instance. For example, an audio stream.
MGC—Media gateway controller.
MGCP—Media Gateway Control Protocol.
PMH—Protocol Message Handler.
PSTN—Public Switched Telephony Network.
RTSP—Real Time Streaming Protocol.
RTSP Session—Session refers to a session between the application and the RTSP client. Each call leg that is configured to use RTSP streaming has a session.
RTP—Real Time Protocol. A protocol used to transport real time frames over a UDP network.
TCL—Tool Command Language.
VoFR—Voice over Frame Relay.
VoIP—Voice over Internet Protocol (IP).
VSC—Virtual Switch Controller.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Aug 28 08:31:33 PDT 2001
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2001 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.