|
|

This chapter provides a product overview and describes how to power on the access server to configure it using the prompt-driven setup script.
The following sections are included:
If you prefer to configure the access server manually, proceed to the next chapter "Cisco IOS Software Survival Skills" to familiarize yourself with the command line interface and then proceed to the following chapter, "Configuring the Access Server Manually" for step-by-step instructions.
The Cisco AS5200 universal access server is a versatile data communications platform that provides the functions of an access server, a router, and digital modems in a single modular chassis. The Cisco AS5200 is intended for Internet service providers (ISPs), telecommunications carriers, and other providers that offer managed Internet connections, and also small- to medium-size sites that provide both digital and analog access to users on an enterprise network.
The Cisco AS5200 receives and routes both analog and digital calls on the same chassis simultaneously. By doing so, it provides you with a clear, simple, and easy migration path from today's predominantly analog dial-in services to tomorrow's digital dial-in services. The access server enables dial-in clients to make remote asynchronous and ISDN connections to the access server.
To configure remote services, you must configure three interrelated interfaces on the access server. The loopback interface makes the network appear as if the dial-in users exist on one Ethernet segment. The loopback interface has the following four types of neighboring interfaces used for dial-in operations: ISDN interface, dialer interface, group asynchronous interface, and asynchronous interface. Figure 1-1 shows an internal view of the components used to process incoming ISDN and analog calls on an access server.
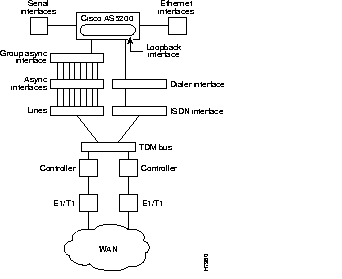
All dial-in users exist on one dial-in subnet. Remote asynchronous users dial in through the group asynchronous interface to the access server. Remote ISDN users dial in through the ISDN dialer interface to the access server. Figure 1-2 shows an external view of how remote users dial in to the access server.
The setup script has been updated in Cisco IOS Release 11.3(2)T to reflect the options available for CAS options. In addition, once you select the number of controllers to be used for ISDN PRI, the system automatically configures all the selected controllers for ISDN PRI.
Before you turn on the access server and begin to use the setup script in the System Configuration dialog, make sure you have already connected the cables to the access server and configured your PC terminal emulation program for 9600 baud, 8 data bits, no parity, and 2 stop bits. All configuration will be performed from your PC terminal emulation program window.
The prompts and resulting messages vary depending on your responses. For most configurations, you can press Return to accept the default entries displayed in square ([]) brackets.
boldface font. Also note that if you make a mistake during the configuration, you can exit and run the System Configuration dialog again. Press Ctrl-c, and then type setup at the enable prompt (5200#).
To use the setup script take the following steps:
Step 1 Power ON the access server. The power switch is on the rear panel, at the upper right corner near the power cord.

Messages will begin to appear in your terminal emulation program window.
 Caution Do not press any keys on the keyboard until the messages stop. Any keys pressed during this time will be interpreted as the first command typed when the messages stop, which might cause you to power cycle the access server and start over. It will take a few minutes for the messages to stop.
Caution Do not press any keys on the keyboard until the messages stop. Any keys pressed during this time will be interpreted as the first command typed when the messages stop, which might cause you to power cycle the access server and start over. It will take a few minutes for the messages to stop.
The messages look similar to the following:
System Bootstrap, Version 11.3(2)T, RELEASED SOFTWARE
Copyright (c) 1994-1998 by cisco Systems, Inc.
AS5200 processor with 16384 Kbytes of main memory
program load complete, entry point: 0x3000060, size: 0x23d454
Restricted Rights Legend
Use, duplication, or disclosure by the Government is
subject to restrictions as set forth in subparagraph
(c) of the Commercial Computer Software - Restricted
Rights clause at FAR sec. 52.227-19 and subparagraph
(c) (1) (ii) of the Rights in Technical Data and Computer
Software clause at DFARS sec. 252.227-7013.
cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, California 95134-1706
Cisco Internetwork Operating System Software
IOS (tm) 5200 Software (C5200-JS-L), Version 11.3(2)T, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc1)
Copyright (c) 1986-1998 by cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Wed 11-Feb-98 22:25 by ppalleti
Image text-base: 0x2204097C, data-base: 0x00005000
cisco AS5200 (68030) processor (revision B) with 16384K/4096K bytes of memory.
Processor board ID 04277316
Bridging software.
SuperLAT software copyright 1990 by Meridian Technology Corp).
X.25 software, Version 2.0, NET2, BFE and GOSIP compliant.
TN3270 Emulation software.
Primary Rate ISDN software, Version 1.0.
Mother board with terminator card.
1 Ethernet/IEEE 802.3 interface(s)
2 Serial network interface(s)
24 terminal line(s)
2 Channelized T1/PRI port(s)
128K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.
8192K bytes of processor board System flash (Read ONLY)
8192K bytes of processor board Boot flash (Read/Write)
Notice: NVRAM invalid, possibly due to write erase.
--- System Configuration Dialog ---
At any point you may enter a question mark '?' for help.
Use ctrl-c to abort configuration dialog at any prompt.
Default settings are in square brackets '[]'.
Step 2 When the following message appears, press Return to accept the default entry (yes) in square brackets:
Step 3 When the following message appears, press Return to see the current interface summary:
Interface IP-Address OK? Method Status Protocol
Ethernet0 unassigned NO unset up up
Serial0 unassigned NO unset down down
Serial1 unassigned NO unset down down
Step 4 Enter a host name for the access server:
5200
Step 5 Enter an enable secret password. This password is encrypted (more secure) and cannot be seen when viewing the configuration:
lab
Step 6 Enter an enable password. This password is not encrypted (less secure) and can be seen when viewing the configuration:
guessme
Step 7 Enter the virtual terminal password, which is used for remote console access:
guessagain
Step 8 Respond to the following prompts as appropriate for your network:
yes
yes
15
yes
Step 9 Configure the asynchronous serial lines for the integrated modems or terminal adapters on the modules installed in the access server:
172.20.30.40
172.20.30.88
no
yes
yes
Step 10 Configure the Ethernet 0 interface:
172.21.40.10
8
yes
10
etherzone
yes
Step 11 Configure the Serial 0 interface:
172.22.50.10
8
yes
no
11
serialzone
yes
Step 12 Configure the Serial 1 interface:
172.23.60.10
8
yes
This section continues the setup script for T1/PRI cards.
Step 1 Enter the letter corresponding to the ISDN switch type that matches your telco switch type:
Do you want to configure ISDN switch type? [yes]:
The following ISDN switch types are available:
[a] primary-4ess
[b] primary-5ess
[c] primary-dms100
[d] primary-net5
[e] primary-ntt
[f] primary-ts014
Enter the switch type [b]:
Step 2 Enter yes to allow users to dial in via ISDN or analog modems:
Next, you will be prompted to configure controllers.
These controllers enable users to dial in via ISDN or analog modems.
There are 2 controllers on this access server. If you want to use
Step 3 Enter the number of controllers you will be using for the PRI configuration:
Enter # of controllers, you will be using for PRI configuration [4]:
Configuring controller parameters:
Configuring controller T1 0:
Configuring PRI on this controller.
Configuring controller T1 1:
Configuring PRI on this controller.
Step 4 Set the CAS configuration options for the first controller you are configuring. First, press Enter to set robbed-bit signaling on the controller:
Configuring controller T1 2:
Will you be using CT1 (robbed bit signaling) on this controller? [yes]:
Step 5 Enter your telco framing type:
The following framing types are available:
esf | sf
Enter the framing type [esf]:
Step 6 Enter your telco line code type:
The following linecode types are available:
ami | b8zs
Enter the line code type [b8zs]:
Step 7 Enter the letter corresponding to the signaling type to support modem pooling over the T1 lines:
The following line signaling types are available:
[a] e&m-fgb
[b] e&m-fgd
[c] e&m-immediate-start
[d] fxs-ground-start
[e] fxs-loop-start
[f] sas-ground-start
[g] sas-loop-start
Enter the line signaling type [a]:
Step 8 Enter the tone signaling type:
The following tone signaling types are available:
dtmf | mf
Enter the tone signal type [dtmf]:
Step 9 Enter yes to configure digital number identification service (DNIS) over T1 lines:
Do you want to provision DNIS address information? [yes]:
Step 10 Set the CAS configuration options for the next controller you are configuring. Repeat Steps 5 to 9 to configure the options:
Configuring controller T1 1:
Will you be using CT1 (robbed bit signaling) on this controller? [yes]:
The following framing types are available:
esf | sf
Enter the framing type [esf]:
The following linecode types are available:
ami | b8zs
Enter the line code type [b8zs]:
The following line signaling types are available:
[a] e&m-fgb
[b] e&m-fgd
[c] e&m-immediate-start
[d] fxs-ground-start
[e] fxs-loop-start
[f] sas-ground-start
[g] sas-loop-start
Enter the line signaling type [a]:
After you complete the configuration script, messages similar to the following appear:
Current configuration:
!
version 11.3
no service password-encryption
!
hostname Router
!
enable secret 5 $1$BzCj$3WnJoC.GO0SmB2U7Bd.Kb1
enable password b
!
no ip routing
isdn switch-type primary-5ess
!
!
controller T1 0
framing esf
clock source line internal
linecode b8zs
pri-group timeslots 1-24
!
controller T1 1
framing esf
clock source internal
linecode b8zs
cas-group 0 timeslots 1-24 type e&m-fgd
!
interface Ethernet0
no ip address
no ip route-cache
shutdown
!
interface Serial0:23
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
encapsulation ppp
no ip mroute-cache
dialer-group 1
isdn incoming-voice modem
peer default ip address pool setup_pool
ppp authentication chap pap
ppp multilink
!
interface Serial1:23
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
encapsulation ppp
no ip mroute-cache
dialer-group 1
isdn incoming-voice modem
peer default ip address pool setup_pool
ppp authentication chap pap
ppp multilink
!
interface FastEthernet0
no ip address
no ip route-cache
shutdown
!
ip classless
access-list 101 permit ip any any
dialer-list 1 protocol ip list 101
!
line con 0
logging synchronous
line 1 48
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
password b
login
!
scheduler interval 1000
end
Step 11 Enter yes to save the configuration, or enter no to erase it:
yes
Step 12 When the messages stop displaying on your screen, press Return to get the following prompt:
Step 13 The 5200> prompt indicates that you are now at the command-line interface (CLI) and you have just completed the basic access server configuration. However, this is not a complete configuration. At this point you have two options:
enable
This section continues the setup script for E1/PRI cards for WAN access.
Step 1 Enter the letter corresponding to the ISDN switch type that matches your telco switch type:
Do you want to configure ISDN switch type? [yes]:
The following ISDN switch types are available:
[a] primary-4ess
[b] primary-5ess
[c] primary-dms100
[d] primary-net5
[e] primary-ntt
[f] primary-ts014
Enter the switch type [d]:
Step 2 Enter yes to allow users to dial in via ISDN or analog modems:
Next, you will be prompted to configure controllers.
These controllers enable users to dial in via ISDN or analog modems.
Do you intend to allow users to dial in? [yes]:
There are 2 controllers on this access server. If you want to use
the full capacity of the access server configure all controllers.
Controller E1 0,1,..etc in software corresponds to Port 0,1,..etc
on the back of the access server.
PRI configuration can be configured to controllers all at once
based on your PRI controllers selection. Where as CAS configuration
will be configured individually for each controller.
Step 3 Enter the number of controllers you will be using for the PRI configuration:
Enter # of controllers, you will be using for PRI configuration [4]:
Configuring controller parameters:
Configuring controller E1 0:
Is this controller in use? [yes]:
Will you be using PRI on this controller? [yes]:
Would you like to enable multilink PPP? [yes]:
Step 4 Set the CAS configuration options for first controller you are configuring. First, enter yes to set channel-associated signaling on the controller:
Configuring controller E1 0:
Is this controller in use? [yes]:
Will you be using PRI on this controller? [yes]:no
Will you be using CE1 (channel associated signaling) on this controller? [yes]:
Step 5 Enter your telco framing type:
The following framing types are available:
no-crc4 | crc4
Enter the framing type [crc4]:
Step 6 Enter your telco line code type:
The following linecode types are available:
ami | hdb3
Enter the line code type [hdb3]:
Step 7 Enter the letter corresponding to the signaling type to support modem pooling over the E1 lines:
The following line signaling types are available:
[a] e&m-fgb
[b] e&m-fgd
[c] e&m-immediate-start
[d] fxs-ground-start
[e] fxs-loop-start
[f] sas-ground-start
[g] sas-loop-start
[h] r2-analog
[i] r2-digital
[j] r2-pulse
[k] p7
Enter the line signaling type [i]:
Step 8 Enter the letter corresponding to the tone signaling type:
The following tone signaling types are available:
[a] dtmf
[b] r2-compelled
[c] r2-non-compelled
[d] r2-semi-compelled
Enter the tone signaling type [b]:
Step 9 Press Enter to provision ANI address information over E1 lines:
Do you want to provision ANI address information? [yes]:
Step 10 Enter the number corresponding to the country for which you are configuring R2 signaling:
R2 signaling is available for the following countries:
[0] itu
[1] argentina
[2] australia
[3] brazil
[4] china
[5] columbia
[6] costarica
[7] easteurope
[8] ecuador itu
[9] ecuador lme
[10] greece
[11] guatemala
[12] hongkong-china
[13] indonesia
[14] israel
[15] korea
[16] malaysia
[17] newzealand
[18] paraguay
[19] peru
[20] philippines
[21] singapore
[22] saudiarabia
[23] southafrica-panaftel
[24] telmex
[25] telnor
[26] thailand
[27] uruguay
[28] venezuela
[29] vietnam
Enter the country name [0]:
Step 11 Set the CAS configuration options for the next controller you are configuring. Repeat Steps 4 to 10 to configure the options:
Configuring controller E1 1:
Will you be using CE1 (channel associated signaling) on this controller? [yes]:
The following framing types are available:
no-crc4 | crc4
Enter the framing type [crc4]:
The following linecode types are available:
ami | hdb3
Enter the line code type [hdb3]:
The following line signaling types are available:
[a] e&m-fgb
[b] e&m-fgd
[c] e&m-immediate-start
[d] fxs-ground-start
[e] fxs-loop-start
[f] sas-ground-start
[g] sas-loop-start
[h] r2-analog
[i] r2-digital
[j] r2-pulse
[k] p7
Enter the line signaling type [i]:
The following tone signaling types are available:
[a] dtmf
[b] r2-compelled
[c] r2-non-compelled
[d] r2-semi-compelled
Enter the tone signaling type [b]:
Do you want to provision ANI address information? [yes]:
R2 signaling is available for the following countries:
[0] itu
[1] argentina
[2] australia
[3] brazil
[4] china
[5] columbia
[6] costarica
[7] easteurope
[8] ecuador itu
[9] ecuador lme
[10] greece
[11] guatemala
[12] hongkong-china
[13] indonesia
[14] israel
[15] korea
[16] malaysia
[17] newzealand
[18] paraguay
[19] peru
[20] philippines
[21] singapore
[22] saudiarabia
[23] southafrica-panaftel
[24] telmex
[25] telnor
[26] thailand
[27] uruguay
[28] venezuela
[29] vietnam
Enter the country name [0]:
After you complete the configuration script, messages similar to the following appear:
5200# wr t
Building configuration...
Current configuration:
!
version 11.3
no service password-encryption
!
hostname Router
!
enable secret 5 $1$R20d$Yh/u1cqh63haVfbmHI0r.0
enable password b
!
no ip routing
isdn switch-type primary-net5
!
!
controller E1 0
clock source line primary
pri-group timeslots 1-31
!
controller E1 1
clock source line secondary
cas-group 0 timeslots 1-15,17-31 type r2-digital r2-compelled ani
cas-custom 0
!
interface Ethernet0
no ip address
no ip route-cache
shutdown
!
interface Serial0:15
ip unnumbered Ethernet0
encapsulation ppp
no ip mroute-cache
dialer-group 1
isdn incoming-voice modem
peer default ip address pool setup_pool
ppp authentication chap pap
ppp multilink
!
interface FastEthernet0
no ip address
no ip route-cache
shutdown
!
ip classless
access-list 101 permit ip any any
dialer-list 1 protocol ip list 101
!
line con 0
logging synchronous
line 1 96
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
password b
login
!
scheduler interval 1000
end
Step 12 Enter yes to save the configuration, or enter no to erase it:
yes
Step 13 When the messages stop displaying on your screen, press Return to get the following prompt:
Step 14 The 5200> prompt indicates that you are now at the command-line interface (CLI) and you have just completed the basic access server configuration. However, this is not a complete configuration. At this point you have two options:
enable
The access server now has a basic configuration for ISDN or channelized T1 or E1 (depending on your responses to the prompts). The access server should be able to accept incoming calls. However, this is not a complete access server configuration. For more advanced configuration topics, proceed to:
If you have questions or need assistance, see the next section, "Cisco Connection Online."
Cisco Connection Online (CCO) is Cisco Systems' primary, real-time support channel. Maintenance customers and partners can self-register on CCO to obtain additional information and services.
Available 24 hours a day, 7 days a week, CCO provides a wealth of standard and value-added services to Cisco's customers and business partners. CCO services include product information, product documentation, software updates, release notes, technical tips, the Bug Navigator, configuration notes, brochures, descriptions of service offerings, and download access to public and authorized files.
CCO serves a wide variety of users through two interfaces that are updated and enhanced simultaneously: a character-based version and a multimedia version that resides on the World Wide Web (WWW). The character-based CCO supports Zmodem, Kermit, Xmodem, FTP, and Internet e-mail, and it is excellent for quick access to information over lower bandwidths. The WWW version of CCO provides richly formatted documents with photographs, figures, graphics, and video, as well as hyperlinks to related information.
You can access CCO in the following ways:
For a copy of CCO's Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ), contact cco-help@cisco.com. For additional information, contact cco-team@cisco.com.
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in a CD-ROM package, which ships with your product. The Documentation CD-ROM, a member of the Cisco Connection Family, is updated monthly. Therefore, it might be more current than printed documentation. To order additional copies of the Documentation CD-ROM, contact your local sales representative or call customer service. The CD-ROM package is available as a single package or as an annual subscription. You can also access Cisco documentation on the World Wide Web at http://www.cisco.com, http://www-china.cisco.com, or http://www-europe.cisco.com.
If you are reading Cisco product documentation on the World Wide Web, you can submit comments electronically. Click Feedback in the toolbar, select Documentation, and click Enter the feedback form. After you complete the form, click Submit to send it to Cisco. We appreciate your comments.
For additional information, refer to the following resources:
|
|