|
|

The two H.323 enhancements summarized below are enhancements to the H.323 protocol and do not require a different configuration. These enhancements are described for you understand the new protocol functionality introduced in Cisco IOS Release 12.0(7)T. This document describes the following new enhancements:
This document contains the following sections:
This feature is an enhancement to the admissions request (ARQ) message to allow a source call-signal address field.
Currently, in Cisco IOS implementation of H.323 gateway software, if the terminating gateway is registered to an H.323 gatekeeper and uses RAS, the ARQ message sent for each incoming call does not contain the H.225 source call signal address (CSA). The Source CSA is an optional parameter in the ARQ message. The source CSA is also an optional parameter in the H.225 call setup message sent by the originating endpoint.
This feature enhances the H.323 gateway software to add support for source CSA parameter in the ARQ message, as illustrated by the message sequence shown in Figure 1.
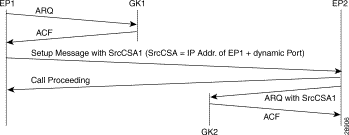
In the message sequence shown in Figure 1, the ARQ messages are enhanced to send the source CSA. The originating gateway sends the H.225 setup message to the destination gateway. The setup message contains the source CSA parameter, which is the combination of the IP address of the originator and the dynamic TCP port number used or obtained for the H.225 call signaling channel. If the terminating gateway accepts the call upon receipt of the setup message, the gateway sends an ARQ message to the registered gatekeeper. The terminating gateway retrieves the source CSA parameter sent by the originating gateway in the setup message. It then sends an ARQ message to the gatekeeper with the source CSA parameter. The CSA parameter is optional and has the same value as the source CSA in the received setup message. If the setup message does not contain the source CSA parameter, the terminating gateway determines the source CSA by using the H.225 call-signaling TCP socket connection of the peer endpoint and uses it in the ARQ message.
If the originating gateway is registered to a gatekeeper and RAS is used as the session target, the originating gateway also sends an ARQ message. This ARQ does not include the optional source CSA parameter.
Empty capabilities set support is a mandatory part of H.323, Version 2. It is used by applications to redirect the voice media stream, which is a new address after a call is established. This feature is particularly useful for applications such as the following:
This feature was added to provide a way to redirect Real-Time Transport Protocol (RTP) streams. The RTP streams are redirected as follows:
In other words, the exchange of the capabilities message determines a master/slave relationship and a new OLC message is created to open a new logical channel with another endpoint. All the RTP streams after this are sent to the new endpoint.
H.323 Version 2 Phase 2 features will not interoperate with H.323 Version 1 features in Cisco IOS releases earlier than 11.3(9)NA or 12.0(3)T. Earlier Cisco IOS releases contain H.323 Version 1 software that does not support protocol messages with an H.323 Version 2 protocol identifier.
To use H.450 services (call transfer or call deflection), you must use Release 12.1(2)T of the gatekeeper; H.450 on the gateways is incompatible with previous releases of the Cisco gatekeeper.
If you are planning to use a Cisco AS5300 universal access server, your system requires VCWare version 4.04.
Cisco H.323 Version 2 technologies are typically configured by using a number of available compression and decompression (CODECs) and the following high density DSP/voice modules.
The following table lists the documentation available for configuring and using Cisco IOS H.323 gatekeepers, gateways, and proxies:
The gatekeeper and proxy features apply to the following platforms:
None.
Before you can use H.323 Version 2 Phase 2 features, you must:
These two enhancements to the H.323 protocol do not require different configuration tasks, nor are there any new Cisco IOS command line interface commands.
For specific information about configuration tasks, see the "Related Documents" section.
ACF—Admissions Confirmation RAS Message. This message type is sent from an H.323 endpoint to an H.323 gateway.
ARJ—Admissions Reject RAS Message. This message type is sent from an H.323 endpoint to an H.323 gateway.
ARQ—Admissions Request Query RAS Message. This message type is sent from an H.323 endpoint to an H.323 gateway.
CODEC—Compression/decompression software.
CSA—Call signal address.
endpoint—An H.323 terminal or gateway. An endpoint can call and be called. It generates or terminates the information stream.
gatekeeper—An H.323 entity on the LAN that provides address translation and control access to the LAN for H.323 terminals and gateways. The gatekeeper can provide other services to the H.323 terminals and gateways, such as bandwidth management and locating gateways. A gatekeeper maintains a registry of devices in the multimedia network. The devices register with the gatekeeper at startup and request admission to a call from the gatekeeper.
gateway—An H.323 endpoint on the LAN that provides real-time, two-way communication between H.323 terminals on the LAN, other ITU-T terminals in the WAN, or to another H.323 gateway. A gateway allows H.323 terminals to communicate with non-H.323 terminals by converting protocols. A gateway is the point where a circuit-switched call is encoded and repackaged into IP packets.
GRQ—Gatekeeper Request RAS Message. This message type is sent from an H.323 endpoint to an H.323 gateway.
H.323—An ITU-T standard that describes packet-based video, audio, and data conferencing. H.323 is an umbrella standard that describes the architecture of the conferencing system and refers to a set of other standards (H.245, H.225.0, and Q.931) to describe its actual protocol.
H.323 RAS—Registration, admission, and status. The RAS signaling protocol performs registration, admissions, bandwidth changes, status and disengage procedures between the VoIP gateway and the gatekeeper.
ITU-T—International Telecommunications Union-Telecommunication Standardization Sector.
LRJ—Location Reject Response RAS Message. This message type is sent from an H.323 endpoint to an H.323 gateway.
LRQ—Location Request RAS Message. This message type is sent from an H.323 endpoint to an H.323 gateway.
RAS—Registration, Admissions, and Status protocol. RAS message types are sent from an H.323 endpoint to an H.323 gateway. These messages include ARQ, LRQ, URQ, GRQ, RRQ, LCF, LRJ, and so on.
RCF—Registration Confirmation RAS Message. This message type is sent from an H.323 endpoint to an H.323 gateway.
RRJ—Registration Reject Response RAS Message. This message type is sent from an H.323 endpoint to an H.323 gateway.
RRQ—Registration Request RAS Message. This message type is sent from an H.323 endpoint to an H.323 gateway.
RTP—Real Time Transport protocol. See RFC 1889.
VoIP—Voice over IP. The ability to carry normal telephone-style voice over an IP-based Internet with POTS-like functionality, reliability, and voice quality. VoIP is a blanket term that generally refers to Cisco's standards-based (for example, H.323) approach to IP voice traffic.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Sat Sep 28 03:55:43 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.