|
|

The Access Server 5100 provides the greatest benefit for organizations that need to centralize processing capabilities for mobile users and telecommuters.
The Access Server 5100 is optimized for high-speed modem access, and is ideally suited for all traditional dial-up applications, such as access to a host, electronic mail, file transfer, and dial-in access to a local area network. It incorporates Adaptive Speed Leveling (ASL), U.S. Robotics' proprietary method of monitoring phone line quality and adjusting speeds to ensure data integrity.
The Access Server 5100 is available with the following modems:
The Access Server 5100 consists of the following components:
Figure 1-1 shows a typical configuration of the Access Server 5100.
Figure 1-2 is a top view of the chassis, and shows the relationship between the NACs, NICs, and the chassis midplane.
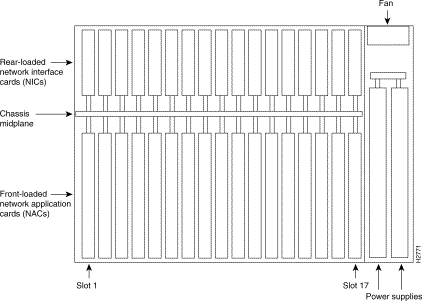
The Access Server 5100 is built around a four bus chassis that can be managed by optional Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) management software. The four buses on the midplane are as follows:
The midplane design supports a wide array of NACs and NICs that can be configured and installed in the chassis to meet diverse connectivity needs. All NACs and most NICs support hot-swapping, which enables insertion and removal while power is on.
The midplane can accommodate an aggregate data bandwidth in excess of 1 gigabit per second (Gbps). The midplane data buses enable any NAC to communicate with any other NAC in the chassis. For example, the T1-to-EIA/TIA-232 application uses the TDM bus. This synchronous serial bus provides 256 full-duplex, 64-kbps time slots, and carries traffic between circuit-switched devices such as the T1 card and the quad modems.
Two power supplies provides AC or DC power input, and supplies DC power to the installed cards via connectors in the midplane. Both power supplies are required in the chassis.
The AS51card functions as a communication server system with 16 asynchronous serial ports, one synchronous serial port, and one 10BaseT Ethernet port.
Each of the two 68-pin asynchronous serial ports support eight EIA/TIA-232 serial ports. A supplied breakout cable splits each 68-pin port into two 50-pin connectors, which in turn connect to the quad modem NICs.
Each chassis houses up to 48 high-speed analog or digital modems. Digital modems connect to the phone system by a direct T1 link through the T1 interface card. Analog modems connect to standard telephone lines through the modem interface card. Modems can be managed with software ranging from a simple terminal interface menu system for device configuration to an SNMP network manager.
The quad modem provides four dial-up modems on a single card. Each modem is capable of supporting V.32 bisPlus (19.2 kbps) modulation and MNP Levels 1-5 or V.42/V.42 bis error correction and data compression, or V.34 (28.8 kbps).
The quad modem NAC can either direct its digital interfaces to external EIA/TIA-232 ports via an EIA/TIA-232 NIC, or it can direct this data to other NACs via the midplane.
The modem can also make use of the dialed number identification string (DNIS) and automatic number identification (ANI) information provided by the public 950 services, feature groups B and D, and enhanced 800 services to customize the configuration of the modem before answering a call. For example, the dialed phone number can be associated with specific applications, and the same modem pool can be dynamically configured on a call-by-call basis to adjust to the requirements of the application.
The quad modem EIA/TIA-232 NIC provides the physical interface for four EIA/TIA-232 ports via a 50-pin connector. A breakout cable is provided to adapt this interface to standard DB-25/DB-9 EIA/TIA-232 connectors.
Each EIA/TIA-232 port supports the full complement of EIA/TIA-232 signals necessary for synchronous or asynchronous operation. The ports support operation at speeds up to 115.2 kbps, and provide four serial interfaces to the quad modem NAC.
See the chapter "Quad Modems" for a full description of the installation and operation of the modem cards in the Access Server 5100.
The T1 NIC and T1 NAC route incoming digital T1 lines to the quad modems.
The T1 NIC handles up to 48 DS0 channels from two trunks. Each channel carries either a pulse code modulation (PCM)-encoded voice channel or digital data. The T1 NAC supports 64-kbps clear channel operation for data channels, and feature group B for voice channels. Each of the DS0 channels connects to other NACs via the midplane.
The T1 NIC provides RJ-48 connector(s) to terminate the trunk(s). It also provides an RJ-45 connector for the EIA/TIA-232 interface port. The T1 NIC performs all necessary auto-equalization and auto-gain functions to support 6,000 feet of 24-gage shielded cable. This card complies with all Bell Core standards relating to T1 alarms, loopbacks, error detection, and so forth. The T1 NIC is compatible with an external channel service unit (CSU) if required, and provides a serial interface to the T1 NAC.
The T1 NAC allows you to use DNIS and ANI information provided by the public 950 services, feature groups B and D and enhanced 800 services to route data. Using this call information, the Access Server 5100 chassis can independently route the individual DS0 channels of the T1 signal to specific modems.
See the chapter "T1 Cards" for a detailed description of the features of the T1 cards.
The network management NAC and NIC manage all the devices in the Access Server 5100 using SNMP. See the chapter "Management Cards" for a detailed description of the features of the network management cards.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Oct 1 03:14:56 PDT 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.