|
|

The Cisco Micro Hub is a small, desktop hub used for connecting network devices in a small branch or remote office. You can connect up to eight network devices to one Cisco Micro Hub.
If you have never set up a network before, then this user guide is written for you. We have tried to define networking terms that you may be unfamiliar with, and we have tried to identify the technical areas in which you may not have experience.
This chapter describes the Cisco Micro Hub, defines some network terms that you may not be familiar with, and includes the following information:
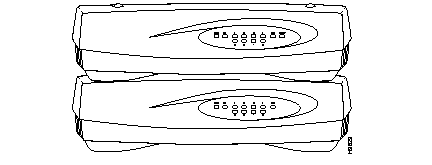
The hubs are available in three models. Up to four hubs can be stacked and interconnected, in any combination of the three models.
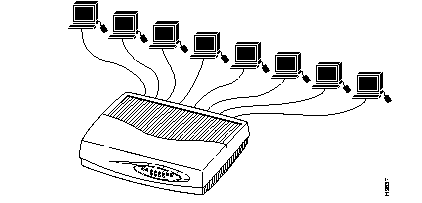
You can use any of the hub models as a standalone networking device, or connected to other compatible 10BaseT hubs or switches to form a larger network. You can also stack and connect up to four hubs through rear panel ports, to form a larger network.
By adding one Micro Hub 1503 to a stack of Micro Hub 1502s, you can configure and manage all the hubs in the stack from a remote location. Stacking four Cisco Micro Hubs together enables you to manage up to 32 hub ports.
Following are some terms that are used in this guide:
| bootp | Bootstrap Protocol--A protocol that can be used to boot the Micro Hub 1503. Select this option with the bootup-option bootp-download command. This command configures the hub to download an IP address and operating firmware from a file server on the same LAN as the hub. |
| collision | When two devices on an Ethernet network transmit data at the same time, the data packets from each device collide on the network cable and are damaged. |
| device | A piece of computer equipment, such as a workstation or printer, on a network that communicates with equipment on the network. Also referred to as a node. |
| Ethernet | A type of LAN that connects network devices by cable and data is broken into packets before being sent to the destination on the cable. |
| firmware | Software that is stored in read-only memory (ROM). The hub uses this type of software. Firmware controls hub operation when the hub is first powered up. |
| gateway address | An IP address for a router that is on the same network segment as the hub. The gateway address is required if the workstation used for managing the hub is on a different network segment from the hub. Configuring the hub with a gateway address enables the hub to send data throught the router, to the workstation. |
| IP | Internet Protocol--A network layer protocol in the TCP/IP stack offering a connectionless internetwork service.
An IP address identifies a device on an IP network is in the following form: xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx, where xxx is a number between 0 and 255. The actual numbers used in an IP address depend on what type of IP network the device is on (Class A, Class B, or Class C). |
| IPX
| Protocol used by Novell NetWare. A router with IPX routing can interconnect LANs so that Novell NetWare clients and servers can communicate. |
| LAN | local-area network--A geographically limited network, usually within one office or building. Ethernet is an example of a LAN standard. |
| loop | Occurs when network devices are connected to each other by more than one path. The Cisco Micro Hub detects when a loop occurs and breaks the loop by isolating one path. |
| packet | A logical unit of data. Devices on an Ethernet network send information back and forth in data packets. |
| partition | In order to maintain network efficiency, the hub partitions a malfunctioning network device from the rest of the network. The hub does this automatically in some cases, for example, if there are too many data collisions caused by packets being sent from from the device. You can use the port-operation command to manually partition any network device connected to the hub. |
| protocol | A set of rules that describes how data is transmitted between devices on a network. For example, some protocols describe electrical and physical standardst. Other protocols define how the data is formatted on a LAN and on a WAN. |
|
You can use a straight-through Ethernet cable when connecting devices to port 5 on the Cisco Micro Hub. Use the The MDI/MDI-X button on the rear panel of the hub to configure port 5 for the the following two types of connections:
|
|
SNMP | Simple Network Management Protocol--A network protocol that enables devices on a network to be managed by a management agent. Other SNMP terms are the following:
|
|
SLIP | Serial Line Internet Protocol--A network protocol that enables IP information, normally used on Ethernet, to be used over a serial line. |
| subnet mask | A bit mask used to identify which bits in an IP address correspond to the network portion of the IP address and which bits correspond to the device portions of the IP address. A subnet mask is in the form of an IP address, usually beginning with 255. |
| TCP/IP | Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol--A group of protocols that defines how data is transferred between network devices. |
| Telnet | A network protocol used for logging into a system from a remote location. |
| Terminal emulation software | Software that enables a computer to function as a terminal, for example a VT100. The computer then appears as a terminal to the device that it is connected to. |
| TFTP | Trivial File Transfer Protocol--This is an optional way to boot up the hub, using the bootup-option tftp-download command. This command configures the hub to download operating firmware from a TFTP server that is on the same LAN as the hub every time the hub is turned on. |
| WAN | wide-area network--A network that extends over a larger distance than a LAN. Devices on the network are usually connected over serial, ISDN, or analog lines. |
| XModem | A protocol used for transferring data over serial lines (for example, between modems). This is an optional way to download firmware updates to the hub using the start xmodem-download command. |
Following are the features of Cisco Micro Hubs:
| Feature | Description |
| Easy to use |
|
|
High performance |
|
|
Multiple users |
|
|
Upgradeable |
|
|
Network management features |
|
| Complete standards conformance |
|
This section describes the connectors on the rear panel of the hub.
This section describes the LEDs on the front panel of the hub.
|
|