5.11. xml:lang
Since XML documents are written in Unicode, XML is an excellent choice for multilingual documents, such as an Arabic commentary on a Greek text (something that couldn't be done with almost any other character set). In such multilingual documents, it's useful to identify in which language a particular section of text is written. For instance, a spellchecker that only knows English shouldn't try to check a French quote.
Each XML element may have an xml:lang attribute that specifies the language in which the content of that element is written. For example, the previous maxim might look like this:
<maxim xml:lang="el"> σόC6;BF;C2; έB1;C5;C4;όν γιγνώσκει </maxim>
This identifies it as Greek. The specific code used,
el, comes from the Greek word for Greek, 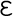
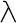
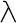
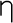
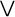
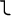
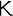
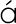 .
.
5.11.1. Language Codes
The value of the xml:lang language attribute should be one of the two-letter language codes defined in ISO-639, Codes for the Representation of Names of Languages, found at http://lcweb.loc.gov/standards/iso639-2/langhome.html, if such a code exists for the language in question.
For languages that aren't listed in ISO-639, you can use a language identifier registered with IANA; currently, about 20 of these identifiers exist, including i-navajo, i-klingon, and i-lux. The complete list can be found at ftp://ftp.isi.edu/in-notes/iana/assignments/languages/tags. All identifiers begin with i-. For example:
<maxim xml:lang="i-klingon">Heghlu'meH QaQ jajvam</maxim>
If the language you need still isn't present in these two lists, you can create your own language tag, as long as it begins with the prefix x- or X- to identify it as a user-defined language code. For example, the title of this journal is written in J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional Quenya language:
<journal xml:lang="x-quenya">Tyalië Tyelelliéva</journal>
5.11.2. Subcodes
For some purposes, knowing the language is not enough. You also need to know the region where the language is spoken. For instance, French has slightly different vocabulary, spelling, and pronunciation in France, Quebec, Belgium, and Switzerland. Although written identically with an ideographic character set, Mandarin and Cantonese are actually quite different, mutually unintelligible dialects of Chinese. The United States and the United Kingdom are jocularly referred to as "two countries separated by a common language."
To handle these distinctions, the language code may be followed by any number of subcodes that further specify the language. Hyphens separate the language code from the subcode and subcodes from each other. If the language code is an ISO-639 code, the first subcode should be one of the two-letter country codes defined by ISO-3166, Codes for the Representation of Names of Countries, found at http://www.ics.uci.edu/pub/ietf/http/related/iso3166.txt. This xml:lang attribute indicates Canadian French:
<p xml:lang="fr-CA">Marie vient pour le fin de semaine.</p>
The language code is usually written in lowercase, and the country code is written in uppercase. However, this is just a convention, not a requirement.
5.11.3. ATTLIST Declarations of xml:lang
Although the XML 1.0 specification defines the xml:lang attribute, you still have to declare it in the DTDs of your valid documents. For example, this information declares the maxim element used several times in this chapter:
<!ELEMENT maxim (#PCDATA)> <!ATTLIST maxim xml:lang NMTOKEN #IMPLIED>
Here I've used the NMTOKEN type, since all legal language codes are well-formed XML name tokens.
You may declare the xml:lang attribute in any convenient way. For instance, if you want to require its presence on the maxim element, you could make it #REQUIRED:
<!ATTLIST maxim xml:lang NMTOKEN #REQUIRED>
Or, if you wanted to allow only French and English text in your documents, you might specify it as an enumerated type with a default of English like this:
<!ATTLIST maxim xml:lang (en | fr) 'en'>
Unless you use an enumerated type, the parser will not check that the value you give it follows the rules outlined here. It's your responsibility to make sure you use appropriate language codes and subcodes.

Copyright © 2002 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.