8.3. Wrappers and Decorators
One of the most common requests that comes up about JDOM is related to interfaces. Many, many users have asked for interfaces in JDOM, and that request has been consistently denied. The reasoning is simple: no set of common methods could be arrived at for all JDOM constructs. There has been a reluctance to use the DOM approach, which provides a set of common methods for most constructs. For example, getChildren( ) is on the common DOM org.w3c.dom.Node interface; however, it returns null when it doesn't apply, such as to a Text node. The JDOM approach has been to only provide methods on a basic interface common to all JDOM classes, and no methods fulfilling this requirement have been found. Additionally, for every request to add interfaces, there has been a request to leave the API as is.
However, there are patterns that allow interface-type functionality to be used with JDOM without changing the API drastically (in fact, without changing it at all!). In this section, I want to talk about the most effective of those patterns, which involves using wrappers or decorators. I'm not going to dive into a lot of design pattern material in this book, but suffice it to say that a wrapper or decorator (I use the two interchangeably in this chapter) is on the exterior of existing classes, rather than on the interior, as a core JDOM interface would be. In other words, existing behavior is wrapped. In this section, I show you how this pattern allows you to customize JDOM (or any other API) in any way you please.
NOTE: By now, you should be fairly advanced in Java and XML. For that reason, I'm going to move through the example code in this section with a minimal amount of comment. You should be able to figure out what's going on pretty easily, and I'd rather get in more code than more talk.
8.3.1. JDOMNode
To get started, I've defined a JDOMNode interface in Example 8-5. This interface defines very simple behavior that I want accessible for all JDOM nodes, and that I want without having to perform type-casting.
Example 8-5. A node decorator interface
package javaxml2;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Iterator;
// JDOM imports
import org.jdom.Document;
public interface JDOMNode {
public Object getNode( );
public String getNodeName( );
public JDOMNode getParentNode( );
public String getQName( );
public Iterator iterator( );
public String toString( );
}The only method that may look odd is iterator( ); it will return a Java Iterator over a node's children, or return an empty list Iterator if there are no children (such as for attributes or text nodes). It's worth noting that I could have just as easily chosen to use the DOM org.w3c.dom.Node interface (if I wanted DOM and JDOM interoperability at a class level), or a different interface specific to my business needs. The sky is the limit on this core interface.
8.3.2. Implementing Classes
The next, more interesting step is to provide implementations of this interface that decorate existing JDOM constructs. These provide wrapping for the concrete classes already in JDOM, and most of the methods on the JDOMNode interface simply are passed through to the underlying (decorated) object. First up is Example 8-6, which decorates a JDOM Element.
Example 8-6. Decorator for JDOM Elements
package javaxml2;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
// JDOM imports
import org.jdom.Element;
public class ElementNode implements JDOMNode {
/** the decorated Element */
protected Element decorated;
public ElementNode(Element element) {
this.decorated = element;
}
public Object getNode( ) {
return decorated;
}
public String getNodeName( ) {
if (decorated != null) {
return decorated.getName( );
}
return "";
}
public JDOMNode getParentNode( ) {
if (decorated.getParent( ) != null) {
return new ElementNode(decorated.getParent( ));
}
return null;
}
public String getQName( ) {
if (decorated.getNamespacePrefix( ).equals("")) {
return decorated.getName( );
} else {
return new StringBuffer(decorated.getNamespacePrefix( ))
.append(":")
.append(decorated.getName()).toString( );
}
}
public Iterator iterator( ) {
List list = decorated.getAttributes( );
ArrayList content = new ArrayList(list);
// put the element's content in the list in order
Iterator i = decorated.getMixedContent().iterator( );
while (i.hasNext( )) {
content.add(i.next( ));
}
return content.iterator( );
}
public String toString( ) {
return decorated.toString( );
}
}There's nothing too remarkable here, so let's keep going. In Example 8-7, I've defined a similar class, AttributeNode, which decorates a JDOM Attribute and implements my core JDOMNode class. Notice the several no-op (no-operation) methods for things like getting the children of the attribute; this closely models the DOM approach. Again, keep in mind that these classes could just as easily implement any other interface (think org.w3c.dom.Attr in this case) without needing changes within the core JDOM API.
Example 8-7. Decorator for JDOM Attributes
package javaxml2;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Collections;
// JDOM imports
import org.jdom.Attribute;
public class AttributeNode implements JDOMNode {
/** The decorated attribute */
protected Attribute decorated;
public AttributeNode(Attribute attribute) {
this.decorated = attribute;
}
public Object getNode( ) {
return decorated;
}
public String getNodeName( ) {
if (decorated != null) {
return decorated.getName( );
}
return "";
}
public JDOMNode getParentNode( ) {
if (decorated.getParent( ) != null) {
return new ElementNode(decorated.getParent( ));
}
return null;
}
public String getQName( ) {
if (decorated.getNamespacePrefix( ).equals("")) {
return decorated.getName( );
} else {
return new StringBuffer(decorated.getNamespacePrefix( ))
.append(":")
.append(decorated.getName()).toString( );
}
}
public Iterator iterator( ) {
return Collections.EMPTY_LIST.iterator( );
}
public String toString( ) {
return decorated.toString( );
}
}Finally, I'll decorate JDOM's textual content (see Example 8-8). At the time of this writing, the JDOM Text class I talked about in the first of this chapter hadn't quite been integrated into its final form in the JDOM source tree. As a result, I'm actually wrapping a Java String in the TextNode class. When the Text node makes it in, this needs to be updated to wrap that type, which is a simple operation.
Example 8-8. Decorator for JDOM textual content
package javaxml2;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Iterator;
// JDOM imports
import org.jdom.Element;
public class TextNode implements JDOMNode {
/** The decorated String */
protected String decorated;
/** The manually set parent of this string content */
private Element parent = null;
public TextNode(String string) {
decorated = string;
}
public Object getNode( ) {
return decorated;
}
public String getNodeName( ) {
return "";
}
public JDOMNode getParentNode( ) {
if (parent == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"The parent of this String content has not been set!");
}
return new ElementNode(parent);
}
public String getQName( ) {
// text nodes have no name
return "";
}
public Iterator iterator( ) {
return Collections.EMPTY_LIST.iterator( );
}
public TextNode setParent(Element parent) {
this.parent = parent;
return this;
}
public String toString( ) {
return decorated;
}
}I'm not going to provide decorators for all the other JDOM types because you should be getting the picture by now. Note that I could also have provided a single JDOMNode implementation, ConcreteNode or something like that, that wrapped the various JDOM types all in one class. However, that would require quite a bit of special casing code that isn't suitable here. Instead, there is a one-to-one mapping between JDOM core classes and JDOMNode implementations.
8.3.3. Providing Support for XPath
Now that you've got some interface-based JDOM nodes, I will extend things a little further. This is a common business scenario, in which you need to provide specific functionality on top of an existing API. For a practical example, I tackle XPath. For any JDOMNode implementation, I'd like to be able to get the XPath expression representing that node. To allow for that functionality, I have written another wrapper class, shown in Example 8-9. This class, XPathDisplayNode , wraps an existing node (of any type, because of the interface-based logic), and provides a single public XPath method, getXPath( ) . This method returns an XPath expression for the wrapped node as a Java string of characters.
Example 8-9. Wrapper for XPath support
package javaxml2;
import java.util.Vector;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Stack;
// JDOM imports
import org.jdom.Attribute;
import org.jdom.Element;
import org.jdom.Namespace;
public class XPathDisplayNode {
/** The JDOMNode this xpath is based on */
JDOMNode node;
public XPathDisplayNode(JDOMNode node) {
this.node = node;
}
private String getElementXPath(JDOMNode currentNode) {
StringBuffer buf = new StringBuffer("/")
.append(currentNode.getQName( ));
Element current = (Element)currentNode.getNode( );
Element parent = current.getParent( );
// See if we're at the root element
if (parent == null ) {
return buf.toString( );
}
// Check for other siblings of the same name and namespace
Namespace ns = current.getNamespace( );
List siblings = parent.getChildren(current.getName( ), ns);
int total = 0;
Iterator i = siblings.iterator( );
while (i.hasNext( )) {
total++;
if (current == i.next( )) {
break;
}
}
// No selector needed if this is the only element
if ((total == 1) && (!i.hasNext( ))) {
return buf.toString( );
}
return buf.append("[")
.append(String.valueOf(total))
.append("]").toString( );
}
public String getXPath( ) {
// Handle elements
if (node.getNode( ) instanceof Element) {
JDOMNode parent = node.getParentNode( );
// If this is null, we're at the root
if (parent == null) {
return "/" + node.getQName( );
}
// Otherwise, build a path back to the root
Stack stack = new Stack( );
stack.add(node);
do {
stack.add(parent);
parent = parent.getParentNode( );
} while (parent != null);
// Build the path
StringBuffer xpath = new StringBuffer( );
while (!stack.isEmpty( )) {
xpath.append(getElementXPath((JDOMNode)stack.pop( )));
}
return xpath.toString( );
}
// Handle attributes
if (node.getNode( ) instanceof Attribute) {
Attribute attribute = (Attribute)node.getNode( );
JDOMNode parent = node.getParentNode( );
StringBuffer xpath = new StringBuffer("//")
.append(parent.getQName( ))
.append("[@")
.append(node.getQName( ))
.append("='")
.append(attribute.getValue( ))
.append("']");
return xpath.toString( );
}
// Handle text
if (node.getNode( ) instanceof String) {
StringBuffer xpath = new StringBuffer(
new XPathDisplayNode(node.getParentNode()).getXPath( ))
.append("[child::text( )]");
return xpath.toString( );
}
// Other node types could follow here
return "Node type not supported yet.";
}
}In this class, I provided special casing for each node type; in other words, I didn't implement an XPathElementNode, XPathAttributeNode, and so on. That's because the similarities in generating this XPath statement are much greater than the advantages of splitting out the code for each type. Of course, this is just the opposite of providing a type-specific node decorator for each JDOM type. You'll want to always try and figure out the difference in your applications, which results in much cleaner code (and often less code, as well).
I'm going to leave the details of working through the process followed in this code up to you. For any node, the XPath expression is calculated and assembled manually, and you should be able to follow the logic pretty easily. That expression is then returned to the calling program, which I cover next.
8.3.4. Endgame
Once you have all your various node types as well as the XPath wrapper, it's time to do something useful. In this case, I want to provide a document viewer, similar to the SAXTreeViewer class from Chapter 3, "SAX", for a JDOM tree. However, I'd also like to provide the XPath expression for each item in that tree down in the status bar. Example 8-10 shows how to do this, using the nodes and wrappers discussed in this section.
Example 8-10. The SimpleXPathViewer class
package javaxml2;
import java.awt.*;
import java.io.File;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.tree.*;
import javax.swing.event.*;
import java.util.Iterator;
// JDOM imports
import org.jdom.*;
import org.jdom.input.SAXBuilder;
public class SimpleXPathViewer extends JFrame {
/** The event handler inner class */
EventHandler eventHandler = new EventHandler( );
/** A text field for displaying the XPath for the selectected node */
private JTextField statusText;
/** The JTree used to display the nodes of the xml document */
private JTree jdomTree;
/** The selection model used to determine which node was clicked */
private DefaultTreeSelectionModel selectionModel;
/** The filename containing the xml file to view */
private String filename;
/** Temporary hack to get around the lack of a text node */
private static Element lastElement;
class EventHandler implements TreeSelectionListener {
public void valueChanged(TreeSelectionEvent e) {
TreePath path= selectionModel.getLeadSelectionPath( );
// If you are just collapsing the tree, you may not have a new path
if (path != null) {
JDOMNode selection=
(JDOMNode)((DefaultMutableTreeNode)path.getLastPathComponent( ))
.getUserObject( );
buildXPath(selection);
}
};
};
public SimpleXPathViewer(String fileName) throws Exception {
super( );
this.filename = fileName;
setSize(600, 450);
initialize( );
}
private void initialize( ) throws Exception {
setTitle("Simple XPath Viewer");
// Setup the UI
initConnections( );
// Load the JDOM Document
Document doc = loadDocument(filename);
// Create the initial JDOMNode from the Factory method
JDOMNode root = createNode(doc.getRootElement( ));
// Create the root node of the JTree and build it from the JDOM Document
DefaultMutableTreeNode treeNode =
new DefaultMutableTreeNode("Document: " + filename);
buildTree(root, treeNode);
// Add the node to the tree's model
((DefaultTreeModel)jdomTree.getModel( )).setRoot(treeNode);
}
private void initConnections( ) {
setDefaultCloseOperation(javax.swing.WindowConstants.DISPOSE_ON_CLOSE);
// Setup the JTree and a pane to display it in
jdomTree = new JTree( );
jdomTree.setName("JDOM Tree");
jdomTree.addTreeSelectionListener(eventHandler);
selectionModel = (DefaultTreeSelectionModel)jdomTree.getSelectionModel( );
getContentPane( ).add(new JScrollPane(jdomTree), BorderLayout.CENTER);
// Setup a text box for use in a status bar
statusText = new JTextField("Click on an element to view xpath");
JPanel statusBarPane= new JPanel( );
statusBarPane.setLayout(new BorderLayout( ));
statusBarPane.add(statusText, BorderLayout.CENTER );
getContentPane( ).add(statusBarPane, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
}
private Document loadDocument(String filename) throws JDOMException {
SAXBuilder builder = new SAXBuilder( );
builder.setIgnoringElementContentWhitespace(true);
return builder.build(new File(filename));
}
private JDOMNode createNode(Object node) {
if (node instanceof Element) {
lastElement = (Element)node;
return new ElementNode((Element)node);
}
if (node instanceof Attribute) {
return new AttributeNode((Attribute)node);
}
if (node instanceof String) {
return new TextNode((String)node).setParent(lastElement);
}
// All other nodes are not implemented
return null;
}
private void buildTree(JDOMNode node, DefaultMutableTreeNode treeNode) {
// If this is a whitespace node or unhandled node, ignore it
if ((node == null) || (node.toString().trim( ).equals(""))) {
return;
}
DefaultMutableTreeNode newTreeNode = new DefaultMutableTreeNode(node);
// Walk over the children of the node
Iterator i = node.iterator( );
while (i.hasNext( )) {
// Create JDOMNodes on the children and add to the tree
JDOMNode newNode = createNode(i.next( ));
buildTree(newNode, newTreeNode);
}
// After all the children have been added, connect to the tree
treeNode.add(newTreeNode);
}
private void buildXPath(JDOMNode node) {
statusText.setText(new XPathDisplayNode(node).getXPath( ));
}
public static void main(java.lang.String[] args) {
try {
if (args.length != 1) {
System.out.println("Usage: java javaxml2.SimpleXPathViewer " +
"[XML Document filename]");
return;
}
/* Create the frame */
SimpleXPathViewer viewer= new SimpleXPathViewer(args[0]);
/* Add a windowListener for the windowClosedEvent */
viewer.addWindowListener(new java.awt.event.WindowAdapter( ) {
public void windowClosed(java.awt.event.WindowEvent e) {
System.exit(0);
};
});
viewer.setVisible(true);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace( );
}
}
}
As usual, I am skipping the Swing details. You can see that once the document is loaded using SAXBuilder, though, the root element of that document is obtained (in the initialize( ) method). This element is used to create an instance of JDOMNode through the createNode( ) utility function. The function simply converts between JDOM types and JDOMNode implementations, and took about 15 seconds to code up. Use a similar method in your own programs that use decorators and wrappers.
Once I've got JDOMNode implementations, it's simple to walk the tree, creating visual objects for each node encountered. Additionally, for each node, I've set the status text of the window to the XPath expression for that node. You can compile all of these examples, and run them using this command:
C:\javaxml2\build>java javaxml2.SimpleXPathViewer
c:\javaxml2\ch08\xml\contents.xmlBe sure that JDOM and your XML parser are in your classpath. The result is the Swing UI shown in Figure 8-1. Notice how the status bar reflects the XPath expression for the currently selected node. Play around with this -- seeing four or five screenshots in a book isn't nearly as useful as your exploration of the tool.
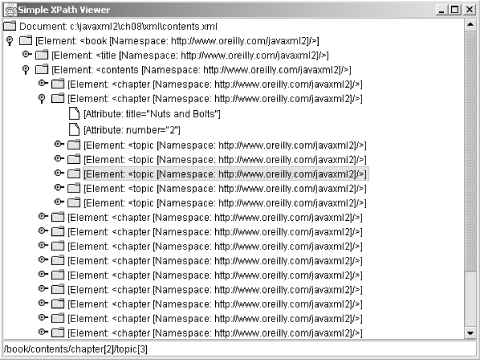
Figure 8-1. Viewing contents.xml and XPaths
And that's it! I know I've gone quickly, but the concepts involved are simple. You can think about how decorators and wrappers might help you with the interface-like functionality you need in your applications. Also check out the JDOM web site at http://www.jdom.org for contributions that may include stock wrappers (like this one, or a DOM set of decorators).
Finally, I'd like to thank Philip Nelson, who did the lion's share of the work on the decorator code shown here. Philip has really explored using decorators with JDOM, and was a great help in this section.

Copyright © 2002 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.