
11.4. JavaScript API Reference
The rest of this chapter contains a quick-reference for the core and client-side JavaScript APIs. It documents the complete core JavaScript API, covers the legacy (Level 0) DOM API, and presents a simplified view of the W3C Level 2 DOM API. Portions of that API not relevant to JavaScript programmers working with HTML documents have been omitted. The upper-right corner of the title block for each reference entry contains information that states whether a feature is part of the core or client-side API, and further indicates which version of JavaScript, which browsers, or which version of the DOM introduced the feature.
Because JavaScript is a loosely-typed language, there is not an official set of class names for the classes and objects of the JavaScript API, and they sometimes appear under different names in different references. The following table summarizes the reference entries that follow, and allows you to quickly scan for the class or object you are interested in.
|
Anchor |
A named position in a document |
|
Applet |
A Java applet |
|
Arguments |
The arguments of a function |
|
Array |
Array creation and manipulation |
|
Attr |
An attribute of a document element |
|
Boolean |
A wrapper object for boolean values |
|
Comment |
An HTML comment |
|
DOMException |
Signals DOM errors |
|
DOMImplementation |
Creates documents, checks DOM features |
|
Date |
Manipulates dates and times |
|
Document |
An HTML document |
|
DocumentFragment |
Nodes to be manipulated together |
|
Element |
An HTML tag in a document |
|
Error |
Predefined exception types |
|
Event |
Event details |
|
Form |
An HTML input form |
|
Function |
A JavaScript function |
|
Global |
Global properties and functions |
|
History |
Browsing history |
|
Image |
An HTML image |
|
Input |
A form input element |
|
Layer |
An independent document layer |
|
Link |
An <a> or <area> link |
|
Location |
Current browser location |
|
Math |
Mathematical functions and constants |
|
Navigator |
Information about the browser |
|
Node |
A node in a document tree |
|
Number |
Support for numbers |
|
Object |
The superclass of all JavaScript objects |
|
Option |
A selectable option |
|
RegExp |
Regular expressions for pattern matching |
|
Screen |
Information about the display |
|
Select |
A graphical selection list |
|
String |
String manipulation |
|
Style |
Inline CSS properties of an element |
|
Text |
A run of text in a document |
|
Textarea |
Multiline text input |
|
Window |
Browser window or frame |
| Anchor | Client-Side JavaScript 1.2 |
| A named position in a document | Inherits From: Element |
document.anchors[index] document.anchors[name]
Description
An Anchor object represents an <a> tag with a name attribute, which serves to create a named position in a document.
Properties
- name
- The value of the name attribute of the <a> tag.
See Also
| Applet | Client-Side JavaScript 1.1 |
| A Java applet |
document.applets[i] document.applets[appletName] document.appletName
Properties & Methods
The properties and methods of an Applet object are the same as the public fields and methods of the Java applet it represents. JavaScript code can query and set the Java fields and invoke the Java methods of the applet.
| Arguments | Core JavaScript 1.1; JScript 2.0; ECMA v1 |
| The arguments of a function |
arguments[n] arguments.length
Description
The Arguments object is defined only within a function body, and within every function body, the local variable arguments refers to the Arguments object for that function. The Arguments object is an array whose elements are the values that were passed as arguments to the function. Element 0 is the first argument, element 1 is the second argument, and so on. All values passed as arguments become array elements of the Arguments object, whether or not those arguments are given names in the function declaration.
Properties
- callee
- A reference to the function that is currently executing. Useful for recursion in unnamed functions. JS 1.2; JScript 5.5; ECMA v1; only defined within a function body.
- length
- The number of arguments passed to the function. JS 1.1; JScript 2; ECMA v1; only defined within a function body.
See Also
| Array | Core JavaScript 1.1; JScript 2.0; ECMA v1 |
| Array creation and manipulation |
Constructor
new Array( ) // empty new Array(n) // n undefined elements new Array(e0, e1,...) // specified elements
Literal Syntax
In JavaScript 1.2, JScript 3.0, and ECMA v3, you can create and initialize an array by placing a comma-separated list of expressions within square brackets. The values of these expressions become the elements of the array. For example:
var a = [1, true, 'abc']; var b = [a[0], a[0]*2, f(x)];
Properties
- length
- A read/write integer specifying the number of elements in the array, or, when the array does not have contiguous elements, a number one larger than the index of the last element in the array. Changing the value of this property truncates or extends the array.
Methods
- concat(value, ...)
- Returns a new array, which is formed by concatenating each of the specified arguments to this one. If any arguments to concat( ) are themselves arrays, their elements are concatenated, rather than the arrays themselves. JS 1.2; JScript 3.0; ECMA v3.
- join(separator)
- Returns the string that results from converting each element of an array to a string and then concatenating the strings together, with the separator string between elements.
- pop( )
- Removes and returns the last element of the array, decrementing the array length. JS 1.2; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- push(value, ...)
- Appends the specified value or values to the end of the array, and returns the new length of the array. JS 1.2; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- reverse( )
- Reverses the order of the elements of an array. Returns nothing.
- shift( )
- Removes and returns the first element of the array, shifting subsequent elements down one and decrementing the array length. JS 1.2; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- slice(start, end)
- Returns a new array that contains the elements of the array from the element numbered start, up to, but not including, the element numbered end. JS 1.2; JScript 3.0; ECMA v3.
- sort(orderfunc)
- Sorts the elements of an array, and returns a reference to the array. Note that the array is sorted in place and no copy is made. The optional orderfunc argument may specify a function that defines the sorting order. The function should expect two arguments and should return a value that is less than 0 if the first argument is less than the second, 0 if they are equal, and a value greater that 0 if the first is greater than the second.
- splice(start, deleteCount, value,...)
- Deletes the specified number of elements from the array starting at the specified index, then inserts any remaining arguments into the array at that location. Returns an array containing the deleted elements. JS 1.2; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- toLocaleString( )
- Returns a localized string representation of the array. JS 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v1.
- toString( )
- Returns a string representation of array.
- unshift(value, ...)
- Inserts the argument or arguments as new elements at the beginning of an array, shifting existing array elements up to make room. Returns the new length of the array. JS 1.2; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
| Attr | DOM Level 1 |
| An attribute of a document element | Inherits From: Node |
Properties
- name
- The name of the attribute. Read-only.
- ownerElement
- The Element object that contains this attribute. Read-only. DOM Level 2.
- specified
- true if the attribute was explicitly specified in the document source or set by a script. false otherwise. Read-only.
- value
- The value of the attribute as a string. Read/write.
See Also
Document.createAttribute( ), Element.getAttributeNode( ), Element.setAttributeNode( )
| Boolean | Core JavaScript 1.1; JScript 2.0; ECMA v1 |
| A wrapper object for boolean values |
Constructor
new Boolean(value) Boolean(value)
Invoked as a function, without the new operator, Boolean( ) converts value to a boolean value (not a Boolean object) and returns it. All values convert to true except for 0, NaN, null, undefined, and the empty string, "". When invoked with the new operator, the Boolean( ) constructor performs the same conversion and wraps the result in a Boolean object.
Methods
| Comment | DOM Level 1 |
| An HTML comment | Inherits From: Node |
Properties
Comment nodes have exactly the same properties as Text nodes.
Methods
Comment nodes support all of the methods of Text nodes except for splitText( ).
See Also
| DOMException | DOM Level 1 |
| Signals DOM errors |
Properties
- code
- An error code that provides some detail about what caused the exception. Some possible values (and their meanings) for this property are defined by the constants listed below.
Constants
The following constants define the code values that may be encountered by when working with HTML documents. Note that these constants are static properties of DOMException, not properties of individual exception objects.
- DOMException.INDEX_SIZE_ERR = 1
- Out-of-bounds error for an array or string index.
- DOMException.HIERARCHY_REQUEST_ERR = 3
- An attempt was made to place a node somewhere illegal in the document tree hierarchy.
- DOMException.WRONG_DOCUMENT_ERR = 4
- An attempt was made to use a node with a document other than the document that created the node.
- DOMException.INVALID_CHARACTER_ERR = 5
- An illegal character was used (in an element name, for example).
- DOMException.NOT_FOUND_ERR = 8
- A node was not found where it was expected.
- DOMException.NOT_SUPPORTED_ERR = 9
- A method or property is not supported in the current DOM implementation.
- DOMException.INUSE_ATTRIBUTE_ERR = 10
- An attempt was made to associate an Attr with an Element when that Attr node was already associated with a different Element node.
- DOMException.SYNTAX_ERR = 12
- A syntax error occurred, such as in a CSS property specification.
| DOMImplementation | DOM Level 1 |
| Creates documents, checks DOM features |
document.implementation
Methods
- createHTMLDocument(title)
- Creates and returns a new HTML Document object and populates it with <html>, <head>, <title>, and <body> elements. title is the text to appear in the <title> element. DOM Level 2.
- hasFeature(feature, version)
- Returns true if the implementation supports the specified version of the specified feature, or false otherwise. If no version number is specified, the method returns true if the implementation completely supports any version of the specified feature. Both feature and version are strings; for example, "core", "1.0" or "html", "2.0".
| Date | Core JavaScript 1.0; JScript 1.0; ECMA v1 |
| Manipulates dates and times |
Constructor
new Date( ); // current time new Date(milliseconds) // from timestamp new Date(datestring); // parse string new Date(year, month, day, hours, minutes, seconds, ms)
With no arguments, the Date( ) constructor creates a Date object set to the current date and time. When one numeric argument is passed, it is taken as the internal numeric representation of the date in milliseconds, as returned by the getTime( ) method. When one string argument is passed, it is taken as a string representation of a date. Otherwise, the constructor is passed between two and seven numeric arguments that specify the individual fields of the local date and time. All but the first two arguments—the year and month fields—are optional. See the static Date.UTC( ) method for an alternative that uses universal time instead of local time.
When called as a function without the new operator, Date( ) ignores any arguments passed to it and returns a string representation of the current date and time.
Methods
The Date object has no properties; instead, all access to date and time values is done through methods. Most methods come in two forms: one that operates using local time, and one that has "UTC" in its name and operates using universal (UTC or GMT) time. These pairs of methods are listed here. Note that the return values and optional arguments described below for most set( ) methods are not supported prior to ECMA standardization. See the various get( ) methods for the legal ranges of each of the various date fields.
- get[UTC]Date( )
- Returns the day of the month, in local or universal time. Return values are between 1 and 31.
- get[UTC]Day( )
- Returns the day of the week, in local or universal time. Return values are between 0 (Sunday) and 6 (Saturday).
- get[UTC]FullYear( )
- Returns the year in full four-digit form, in local or universal time. JS 1.2; JScript 3.0; ECMA v1.
- get[UTC]Hours( )
- Returns the hours field, in local or universal time. Return values are between 0 (midnight) and 23 (11 p.m.).
- get[UTC]Milliseconds( )
- Returns the milliseconds field, in local or universal time. JS 1.2; JScript 3.0; ECMA v1.
- get[UTC]Minutes( )
- Returns the minutes field, in local or universal time. Return values are between 0 and 59.
- get[UTC]Month( )
- Returns the month field, in local or universal time. Return values are between 0 (January) and 11 (December).
- get[UTC]Seconds( )
- Returns the seconds field, in local or universal time. Return values are between 0 and 59.
- getTime( )
- Returns the internal millisecond representation of the date; that is, returns the number of milliseconds between midnight (UTC) of January 1st, 1970 and the date and time represented by the Date object. Note that this value is independent of time zone.
- getTimezoneOffset( )
- Returns the difference, in minutes, between the local and UTC representations of this date. Note that the value returned depends on whether daylight savings time is or would be in effect at the specified date.
- getYear( )
- Returns the year field minus 1900. Deprecated in favor of getFullYear( ).
- set[UTC]Date(day_of_month)
- Sets the day of the month field, using local or universal time. Returns the millisecond representation of the adjusted date.
- set[UTC]FullYear(year, month, day)
- Sets the year (and optionally the month and day), using local or universal time. Returns the millisecond representation of the adjusted date. JS 1.2; JScript 3.0; ECMA v1.
- set[UTC]Hours(hours, mins, secs, ms)
- Sets the hour (and optionally the minutes, seconds, and milliseconds fields), using local or universal time. Returns the millisecond representation of the adjusted date.
- set[UTC]Milliseconds(millis)
- Sets the milliseconds field of a date, using local or universal time. Returns the millisecond representation of the adjusted date. JS 1.2; JScript 3.0; ECMA v1.
- set[UTC]Minutes(minutes, seconds, millis)
- Sets the minutes field (and optionally the seconds and milliseconds fields) of a date, using local or universal time. Returns the millisecond representation of the adjusted date.
- set[UTC]Month(month, day)
- Sets the month field (and optionally the day of the month) of a date using local or universal time. Returns the millisecond representation of the adjusted date.
- set[UTC]Seconds(seconds, millis)
- Sets the seconds field (and optionally the milliseconds field) of a date, using local or universal time. Returns the millisecond representation of the adjusted date.
- setTime(milliseconds)
- Sets the internal millisecond date representation. Returns the milliseconds argument.
- setYear(year)
- Sets the 2-digit year field. Deprecated in favor of set[UTC]FullYear( ).
- toDateString( )
- Returns a string that represents the date portion of the date, expressed in the local timezone. JS 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- toGMTString( )
- Converts a Date to a string, using the GMT timezone, and returns the string. Deprecated in favor of toUTCString( ).
- toLocaleDateString( )
- Returns a string that represents the date portion of the date, expressed in the local time zone, using the local date formatting conventions. JS 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- toLocaleString( )
- Converts a Date to a string, using the local timezone and the local date formatting conventions.
- toLocaleTimeString( )
- Returns a string that represents the time portion of the date, expressed in the local time zone, using the local time formatting conventions. JS 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- toString( )
- Returns a string representation of the date using the local time zone.
- toTimeString( )
- Returns a string that represents the time portion of the date, expressed in the local time zone. JS 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- toUTCString( )
- Converts a Date to a string, using universal time, and returns the string. JS 1.2; JScript 3.0; ECMA v1.
- valueOf( )
- Returns the millisecond representation of the date, exactly as getTime( ) does. JS 1.1; ECMA v1.
Static Functions
In addition to the previously listed instance method, the Date object defines two static methods. These methods are invoked through the Date( ) constructor itself, not through individual Date objects:
| Document | Client-Side JavaScript 1.0; DOM Level 1 |
| An HTML document | Inherits From: Node (in DOM Level 1) |
window.document document
Description
The Document object represents an HTML document and is one of the most important objects in client-side JavaScript. It was introduced in JavaScript 1.0, and a number of methods and properties were added in JavaScript 1.1. Netscape and Internet Explorer each add nonstandard methods and properties to the Document object, and the W3C DOM standardizes additional properties and methods.
Common Properties
All implementations of the Document object support the following properties. This list is followed by separate lists of properties defined by the W3C DOM Document object and by the IE 4 and Netscape 4 Document objects.
- alinkColor
- A string that specifies the color of activated links. Deprecated.
- anchors[ ]
- An array of Anchor objects, one for each anchor that appears in the document. JS 1.2.
- applets[ ]
- An array of Applet objects, one for each applet that appears in the document. JS 1.1.
- bgColor
- A string that specifies the background color of the document. Deprecated.
- cookie
- A string-valued property with special behavior that allows the cookies associated with this document to be queried and set.
- domain
- A string that specifies the Internet domain the document is from. Used for security purposes. JS 1.1.
- embeds[ ]
- An array of objects that represent data embedded in the document with the <embed> tag. A synonym for plugins[ ]. Some plugins and ActiveX controls can be controlled with JavaScript code. The API depends on the specific control. JS 1.2.
- fgColor
- A string that specifies the default text color for the document. Deprecated.
- forms[ ]
- An array of Form objects, one for each HTML form that appears in the document.
- images[ ]
- An array of Image objects, one for each image that is embedded in the document with the HTML <img> tag. JS 1.1.
- lastModified
- A read-only string that specifies the date of the most recent change to the document (as reported by the web server). JS 1.0.
- linkColor
- A string that specifies the color of unvisited links. Deprecated.
- links[ ]
- An array of Link objects, one for each hypertext link that appears in the document.
- location
- The URL of the document. Deprecated in favor of the URL property.
- plugins[ ]
- A synonym for the embeds[ ] array. JS 1.1.
- referrer
- A read-only string that contains the URL of the document, if any, from which the current document was linked.
- title
- The text contents of the <title> tag. Read-only prior to DOM Level 1.
- URL
- A read-only string that specifies the URL of the document. JS 1.1.
- vlinkColor
- A string that specifies the color of visited links. Deprecated.
W3C DOM Properties
In DOM-compliant browsers, the Document object inherits the properties of Node, and defines the following additional properties.
- body
- A reference to the Element object that represents the <body> tag of this document.
- defaultView
- The Window in which the document is displayed. Read-only. DOM Level 2.
- documentElement
- A read-only reference to the <html> tag of the document.
- implementation
- The DOMImplementation object that represents the implementation that created this document. Read-only.
IE 4 Properties
The following nonstandard (and nonportable) properties are defined by Internet Explorer 4 and later versions.
- activeElement
- A read-only property that refers to the input element that is currently active (i.e., has the input focus).
- all[ ]
- An array of all Element objects within the document. This array may be indexed numerically to access elements in source order, or it may be indexed by element id or name.
- charset
- The character set of the document.
- children[ ]
- An array that contains the HTML elements that are direct children of the document. Note that this is different than the all[ ] array that contains all elements in the document, regardless of their position in the containment hierarchy.
- defaultCharset
- The default character set of the document.
- expando
- This property, if set to false, prevents client-side objects from being expanded. That is, it causes a runtime error if a program attempts to set the value of a nonexistent property of a client-side object. Setting expando to false can sometimes help to catch bugs caused by property misspellings, which can otherwise be difficult to detect. This property can be particularly helpful for programmers who are switching to JavaScript after becoming accustomed to case-insensitive languages. Although expando only works in IE, it can be safely (but ineffectively) set in Netscape.
- parentWindow
- The window that contains the document.
- readyState
-
Specifies the loading status of a document. It has one of the
following four string values:
- uninitialized
- The document has not started loading.
- loading
- The document is loading.
- interactive
- The document has loaded sufficiently for the user to interact with it.
- complete
- The document is completely loaded.
Netscape 4 Properties
The following nonstandard (and nonportable) properties are defined by Netscape 4.
- height
- The height, in pixels, of the document.
- layers[ ]
- An array of Layer objects that represents the layers contained within a document. This property is only available in Netscape 4; it is discontinued as of Netscape 6.
- width
- The width, in pixels, of the document.
Common Methods
All implementations of the Document object support the following methods. This list is followed by separate lists of methods defined by the W3C DOM standard and by the IE 4 and Netscape 4 Document objects.
- clear( )
- Erases the contents of the document and returns nothing. This method is deprecated in JavaScript 1.1. JS 1.0; deprecated.
- close( )
- Closes a document stream opened with the open( ) method and returns nothing. JS 1.0.
- open( )
- Deletes existing document content and opens a stream to which new document contents may be written. Returns nothing. JS 1.0.
- write(value, ...)
- Inserts the specified string or strings into the document currently being parsed or appends to document opened with open( ). Returns nothing. JS 1.0.
- writeln(value, ...)
- Identical to write( ), except that it appends a newline character to the output. Returns nothing. JS 1.0
W3C DOM Methods
In DOM-compliant browsers, the Document object inherits the methods of Node, and defines the following additional methods.
- createAttribute(name)
- Returns a newly-created Attr node with the specified name.
- createComment(text)
- Creates and returns a new Comment node containing the specified text.
- createDocumentFragment( )
- Creates and returns an empty DocumentFragment node.
- createElement(tagName)
- Creates and returns a new Element node with the specified tag name.
- createTextNode(text)
- Creates and returns a new Text node that contains the specified text.
- getElementById(id)
- Returns the Element of this document that has the specified value for its id attribute, or null if no such Element exists in the document.
- getElementsByName(name)
- Returns an array of nodes of all elements in the document that have a specified value for their name attribute. If no such elements are found, returns a zero-length array.
- getElementsByTagName(tagname)
- Returns an array of all Element nodes in this document that have the specified tag name. The Element nodes appear in the returned array in the same order they appear in the document source.
- importNode(importedNode, deep)
- Creates and returns a copy of a node from some other document that is suitable for insertion into this document. If the deep argument is true, it recursively copies the children of the node too. DOM Level 2.
Netscape 4 Methods
IE 4 Methods
Event Handlers
In DOM-compliant browsers and IE 4, the Document object supports the same list of generic event handlers that the Element object does. Although the onload and onunload handlers logically belong to the Document object, they are implemented as properties of the Window object.
See Also
| DocumentFragment | DOM Level 1 |
| Nodes to be manipulated together | Inherits From: Node |
Description
DocumentFragment inherits the methods and properties of Node, and defines no new method or properties of its own. It has one important behavior, however: when a DocumentFragment is inserted into a document tree, it is not the DocumentFragment node itself that is inserted, but the children of the DocumentFragment. This makes DocumentFragment useful as a temporary placeholder for nodes you want to insert, all at once, into a document.
See Also
| Element | DOM Level 1, IE 4 |
| An HTML tag in a document | Inherits From: Node (in DOM Level 1) |
Description
The Element object represents an HTML element or tag. IE 4 and later, DOM-compliant browsers such as IE 5 and later, and Netscape 6 and later allow access to every element of a document. They also define the properties and methods listed here on each of those elements. Unfortunately, the methods and properties defined by the IE 4 DOM are not the same as the methods and properties defined by the W3C DOM standard. Because of this incompatibility, they are grouped separately in the following lists.
W3C DOM Properties
In web browsers that support the W3C DOM, all elements in an HTML document have properties that correspond to their HTML attributes, including such universal attributes such as dir, id, lang, and title. When an HTML attribute name consists of multiple words, the corresponding JavaScript property name uses mixed case. Otherwise the JavaScript property is in lowercase (e.g., id and href, but tagIndex and accessKey). Two HTML attributes have names that are reserved words in JavaScript or Java, and special property names are required. JavaScript uses the property className to refer to the class attribute of all HTML tags and uses htmlFor to refer to the for attribute of <label> and <script> tags. In addition to their HTML attributes, all elements define the following properties. Remember also that in DOM-compliant browsers, all HTML elements inherit the properties of the Node object.
- className
- The string value of the class attribute of the element, which specifies one or more CSS classes. Note that this property is not named "class" because that name is a reserved word in JavaScript.
- style
- A Style object that represents the style attribute of the HTML element.
- tagName
- The read-only tag name of the element. For HTML documents, the tag name is returned in uppercase, regardless of its capitalization in the document source. In XHTML documents, the value is in lowercase.
IE DOM Properties
Internet Explorer 4 and later versions define a proprietary DOM. In the IE 4 DOM, as in the W3C DOM, each HTML element has JavaScript properties that correspond to its HTML attributes. In addition, the IE 4 DOM defines the following properties for each element:
- all[ ]
- An array of all Element objects that are descendants of this element. This array may be indexed numerically to access elements in source order. Or it may be indexed by element id or name. See also Document.all[ ].
- children[ ]
- An array of Element objects that are direct children of this element. Note that the IE 4 DOM has no equivalent of the Text or Comment nodes, so the children of an element can only be other Element objects.
- className
- A read/write string that specifies the value of the class attribute of an element.
- document
- A reference to the containing Document object.
- innerHTML
- The HTML text contained within the element, not including the opening and closing tags of the element itself. Setting this property replaces the content of the element. Because this nonstandard property is powerful and widely used, it has been implemented by other browsers including Netscape 6 and later and Mozilla.
- innerText
- The plain text contained within the element, not including the opening and closing tags of the element itself. Setting this property replaces the content of the element with unparsed plain text.
- offsetHeight
- The height, in pixels, of the element and all its content.
- offsetLeft
- The X-coordinate of the element relative to the offsetParent container element.
- offsetParent
- Specifies the container element that defines the coordinate system in which offsetLeft and offsetTop are measured. For most elements, offsetParent is the Document object that contains them. However, if an element has a dynamically positioned ancestor, that ancestor is the offsetParent. Table cells are positioned relative to the row in which they are contained.
- offsetTop
- The Y-coordinate of the element, relative to the offsetParent container element.
- offsetWidth
- The width, in pixels, of the element and all its content.
- outerHTML
- The HTML text of an element, including its start tags, end tags, and content. Setting this property completely replaces the element and its content.
- outerText
- The plain text of an element, including its start and end tags. Setting this property replaces the element and its contents with unparsed plain text.
- parentElement
- The element that is the direct parent of this one. This property is read-only.
- sourceIndex
- The index of the element in the Document.all[ ] array of the document that contains it.
- style
- A Style object that represents the inline CSS style attributes for this element. Setting properties of this object changes the display style of the element.
- tagName
- A read-only string that specifies the name of the HTML tag that this element represents.
W3C DOM Methods
In web browsers that support the W3C DOM, all elements in an HTML document support the following methods, and also inherit the methods of Node. Many of these methods are used to get and set attribute values, and are rarely used because Element objects have properties that mirror all their HTML attributes.
- getAttribute(name)
- Returns the value of a named attribute as a string.
- getAttributeNode(name)
- Returns the value of a named attribute as an Attr node.
- getElementsByTagName(name)
- Returns an array of all descendants of this element that have the specified tag name, in the order in which they appear in the document.
- hasAttribute(name)
- Returns true if this element has an attribute with the specified name, or false if it does not. DOM Level 2.
- removeAttribute(name)
- Deletes the named attribute from this element and returns nothing.
- removeAttributeNode(oldAttr)
- Removes the specified Attr node from the list of attributes for this element. Returns the Attr node that was removed.
- setAttribute(name, value)
- Sets the named attribute to the specified string value and returns nothing.
- setAttributeNode(newAttr)
- Adds the specified Attr node to the list of attributes for this element. If an attribute with the same name already exists, its value is replaced. Returns the Attr node that was replaced by newAttr, or null if no attribute was replaced.
IE DOM Methods
Internet Explorer 4 and later versions support the following nonstandard methods for all document elements.
- contains(target)
- Returns true if this element contains the Element target, or false if it does not.
- getAttribute(name)
- Returns the value of the named attribute of this element as a string, or null if there is no such attribute.
- insertAdjacentHTML(where, text)
- Inserts the HTML text into the document near this element at a position specified by where. where must be one of the strings "BeforeBegin", "AfterBegin", "BeforeEnd" or "AfterEnd". Returns nothing.
- insertAdjacentText(where, text)
- Inserts plain text text into the document near this element, at the position specified by where. Returns nothing.
- removeAttribute(name)
- Deletes the named attribute and its value from the element. Returns true on success; false on failure.
- scrollIntoView(top)
- Scrolls the document so this element is visible at the top or bottom of the window. If top is true or is omitted, the element appears at the top of the window. If false, the element appears at the bottom.
- setAttribute(name, value)
- Sets the named attribute to the specified string value and returns nothing.
Event Handlers
Elements of an HTML document define the following event handlers to respond to raw mouse and keyboard events. Particular types of elements (such as the Form and Input objects) may define more specialized event handlers (such as onsubmit and onchange) that impose an interpretation upon the raw input events.
- onclick
- Invoked when the user clicks on the element.
- ondblclick
- Invoked when the user double-clicks on the element.
- onhelp
- Invoked when the user requests help. IE only.
- onkeydown
- Invoked when the user presses a key.
- onkeypress
- Invoked when the user presses and releases a key.
- onkeyup
- Invoked when the user releases a key.
- onmousedown
- Invoked when the user presses a mouse button.
- onmousemove
- Invoked when the user moves the mouse.
- onmouseout
- Invoked when the user moves the mouse off the element.
- onmouseover
- Invoked when the user moves the mouse over an element.
- onmouseup
- Invoked when the user releases a mouse button.
See Also
| Error | Core JavaScript 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3 |
| Predefined exception types | Inherits From: Object |
Constructor
new Error(message) new EvalError(message) new RangeError(message) new ReferenceError(message) new SyntaxError(message) new TypeError(message) new URIError(message)
These constructors create an instance of the Error class or of one of its subclasses. The message argument is optional.
Properties
Error and all of its subclasses define the same two properties:
- message
- An error message that provides details about the exception. This property holds the string passed to the constructor, or an implementation-defined default string.
- name
- A string that specifies the type of the exception. This property is always the name of the constructor used to create the exception object.
Methods
| Event | DOM Level 2, IE 4, Netscape 4 |
| Event details |
Description
The Event object serves to provide both details about an event and control over the propagation of an event. DOM Level 2 defines a standard Event object, but Internet Explorer 4, 5, and 6 use a proprietary object instead. Netscape 4 has its own proprietary object that is different from the other two. DOM Level 2 does not standardize keyboard events, so the Netscape 4 Event object may be still useful to programmers interested in key events in Netscape 6 and later. The properties of the DOM, IE, and Netscape 4 Event objects are listed in separate sections below.
In the DOM and Netscape event models, an Event object is passed as an argument to the event handler. In the IE event model, the Event object that describes the most recent event is instead stored in the event property of the Window object.
DOM Constants
These constants are the legal values of the eventPhase property; they represent the current phase of event propagation for this event.
- Event.CAPTURING_PHASE = 1
- The event is in its capturing phase.
- Event.AT_TARGET = 2
- The event is being handled by its target node.
- Event.BUBBLING_PHASE = 3
- The event is bubbling.
DOM Properties
All properties of this object are read-only.
- altKey
- true if the Alt key was held down when an event occurred. Defined for mouse events.
- bubbles
- true if the event is of a type that bubbles; false otherwise. Defined for all events.
- button
- Specifies which mouse button changed state during a mousedown, mouseup, or click event. 0 indicates the left button, 1 indicates the middle button, and 2 indicates the right button. Note that this property is only defined when a button changes state: it is not used to report whether a button is held down during a mousemove event, for example. Also, this property is not a bitmap: it cannot tell you if more than one button is held down. Netscape 6.0 uses the values 1, 2, and 3 instead of 0, 1, and 2. This is fixed in Netscape 6.1.
- cancelable
- true if the default action associated with the event can be canceled with preventDefault( ), false otherwise. Defined for all events.
- clientX, clientY
- These properties specify the X and Y coordinates of the mouse pointer, relative to the client area of the browser window. Note that these coordinates do not take document scrolling into account. Defined for mouse events.
- ctrlKey
- true if the Ctrl key was held down when the event occurred. Defined for mouse events.
- currentTarget
- The document node that is currently handling this event. During capturing and bubbling, this is different than target. Defined for all events.
- detail
- The click count: 1 for a single click, 2 for a double-click, 3 for a triple click, and so on. Defined for click, mousedown and mouseup events.
- eventPhase
- The current phase of event propagation. The constants above define the three legal values for this property. Defined for all events.
- metaKey
- true if the Meta key was held down when the event occurred. Defined for mouse events.
- relatedTarget
- For mouseover events, this is the document node that the mouse left when it moved over the target. For mouseout events, it is the node that the mouse entered when leaving the target. It is undefined for other types of events.
- screenX, screenY
- These properties specify the X and Y coordinates of the mouse pointer relative to the upper-left corner of the user's screen. Defined for mouse events.
- shiftKey
- true if the Shift key was held down when the event occurred. Defined for mouse events.
- target
- The target for this event; the document node that generated the event. Note that this may be any node, including Text nodes; it is not restricted to Element nodes. Defined for all events.
- timeStamp
- A Date object that specifies the date and time at which the event occurred. Defined for all events, but implementations are not required to provide a valid timestamp.
- type
- The type of event that occurred. This is the name of the event handler property with the leading "on" removed. For example, "click", "load", or "mousedown". Defined for all events.
- view
- The Window object in which the event was generated.
DOM Methods
- preventDefault( )
- Tells the web browser not to perform the default action (if there is one) associated with this event. If the event is not of a type that is cancelable, this method has no effect. Returns nothing.
- stopPropagation( )
- Stops the event from propagating any further through the capturing, target, or bubbling phases of event propagation. Returns nothing.
IE 4 Properties
- altKey
- A boolean value that specifies whether the Alt key was held down when the event occurred.
- button
- For mouse events, button specifies which mouse button or buttons were pressed. This read-only integer is a bitmask: the 1 bit is set if the left button was pressed. The 2 bit is set if the right button was pressed. The 4 bit is set if the middle button (of a three button mouse) was pressed.
- cancelBubble
- If an event handler wants to stop an event from being propagated up to containing objects, it must set this property to true.
- clientX, clientY
- The X and Y coordinates, relative to the web browser page, at which the event occurred.
- ctrlKey
- A boolean value that specifies whether the Ctrl key was held down when the event occurred.
- fromElement
- For mouseover and mouseout events, fromElement refers to the object from which the mouse pointer is moving.
- keyCode
- For keyboard events, keyCode specifies the Unicode character code generated by the key that was struck.
- offsetX, offsetY
- The X and Y coordinates at which the event occurred, within the coordinate system of the event's source element (see srcElement).
- returnValue
- If this property is set, its value takes precedence over the value actually returned by an event handler. Set this property to false to cancel the default action of the source element on which the event occurred.
- screenX, screenY
- The X and Y coordinates, relative to the screen, at which the event occurred.
- shiftKey
- A boolean value that specifies whether the Shift key was held down when the event occurred.
- srcElement
- The Window, Document, or Element object that generated the event.
- toElement
- For mouseover and mouseout events, toElement refers to the object into which the mouse pointer is moving.
- type
- A string property that specifies the type of the event. Its value is the name of the event handler, minus the "on" prefix. So, when the onclick( ) event handler is invoked, the type property of the Event object is "click".
- x, y
- The X and Y coordinates at which the event occurred. These properties specify coordinates relative to the innermost containing element that is dynamically positioned using CSS.
Netscape 4 Properties
- height
- Set only in resize events. Specifies the new height of the window or frame that was resized.
- layerX, layerY
- Specify the X and Y coordinates, relative to the enclosing layer, at which an event occurred.
- modifiers
- Specifies which keyboard modifier keys were held down when the event occurred. This numeric value is a bitmask consisting of any of the constants Event.ALT_MASK, Event.CONTROL_MASK, Event.META_MASK, or Event.SHIFT_MASK. Due to a bug, this property is not defined in Netscape 6 or 6.1.
- pageX, pageY
- The X and Y coordinates, relative to the web browser page, at which the event occurred. Note that these coordinates are relative to the top-level page, not to any enclosing layers.
- screenX, screenY
- The X and Y coordinates, relative to the screen, at which the event occurred.
- target
- The Window, Document, Layer, or Element object on which the event occurred.
- type
- A string property that specifies the type of the event. Its value is the name of the event handler, minus the "on" prefix. So, when the onclick( ) event handler is invoked, the type property of the Event object is "click".
- which
- For keyboard and mouse events, which specifies which key or mouse button was pressed or released. For keyboard events, this property contains the character encoding of the key that was pressed. For mouse events, it contains 1, 2, or 3, indicating the left, middle, or right buttons.
- width
- Set only in resize events. Specifies the new width of the window or frame that was resized.
- x, y
- The X and Y coordinates at which the event occurred. These properties are synonyms for layerX and layerY and specify the position relative to the containing layer (if any).
| Form | Client-Side JavaScript 1.0 |
| An HTML input form | Inherits From: Element |
document.forms[form_number] document.forms[form_name] document.form_name
Properties
The Form object defines properties for each of the attributes of the HTML <form> element, such as action, encoding, method, name, and target. In addition, it defines the following properties:
- elements[ ]
- A read-only array of Input objects representing the elements that appear in the form. The array can be indexed numerically, or by element name for elements that have HTML name attributes defined.
- length
- The number of elements in the form. Equivalent to elements.length.
Methods
- reset( )
- Resets each of the input elements of the form to their default values. Returns nothing. JS 1.1.
- submit( )
- Submits the form, but does not trigger the onsubmit event handler. Returns nothing.
Event Handlers
- onreset
- Invoked just before the elements of the form are reset. Return false to prevent reset.
- onsubmit
- Invoked just before the form is submitted. This event handler allows form entries to be validated before being submitted. Return false to prevent submission.
See Also
| Function | Core JavaScript 1.0; JScript 1.0; ECMA v1 |
| A JavaScript function |
Constructor
new Function(argument_names..., body)
This constructor was introduced in JavaScript 1.1, and has been obsoleted by the function literal syntax of JavaScript 1.2.
Properties
- length
- The number of named arguments specified when the function was declared. See Arguments.length for the number of argument actually passed. JS 1.1; JScript 2.0; ECMA v1.
- prototype
- An object which, for a constructor function, defines properties and methods shared by all objects created with that constructor function. JS 1.1; JScript 2.0; ECMA v1.
Methods
- apply(thisobj, args)
- Invokes the function as a method of thisobj, passing the elements of the array args as arguments to the function. Returns whatever value is returned by the invocation of the function. JS 1.2; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- call(thisobj, args...)
- Invokes the function as a method of thisobj, using any subsequent arguments as arguments to the function. Returns the value that is returned by the invocation of the function. JS 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- toString( )
- Returns a string representation of the function. In some implementations, this is the actual source code of the function. JS 1.0; JScript 2.0; ECMA v1.
See Also
| Global | Core JavaScript 1.0; JScript 1.0; ECMA v1 |
| Global properties and functions |
this
Description
The Global object holds the global properties and methods listed. These properties and methods do not need to be referenced or invoked through any other object. Any variables and functions you define in your own top-level code become properties of the Global object. The Global object has no name, but you can refer to it in top-level code (i.e., outside of methods) with the this keyword. In client-side JavaScript, the Window object serves as the Global object. It has quite a few additional properties and methods, and can be referred to as window.
Global Properties
- Infinity
- A numeric value that represents positive infinity. JS 1.3; JScript 3.0; ECMA v1.
- NaN
- The not-a-number value. JS 1.3; JScript 3.0; ECMA v1.
- undefined
- The undefined value. JS 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
Global Functions
- decodeURI(uri)
- Returns a decoded copy of uri, with any hexadecimal escape sequences replaced with the characters they represent. JS 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- decodeURIComponent(s)
- Returns a decoded copy of s, with any hexadecimal escape sequences replaced with the characters they represent. JS 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- encodeURI(uri)
- Returns an encoded copy of uri, with certain characters replaced by hexadecimal escape sequences. Does not encode characters such as #, ?, and @ that are used to separate the components of a URI. JS 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- encodeURIComponent(s)
- Returns an encoded copy of s, with certain characters replaced by hexadecimal escape sequences. Encodes any punctuation characters that could be used to separate components of a URI. JS 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- escape(s)
- Returns an encoded copy of s in which certain characters have been replaced by hexadecimal escape sequences. JS 1.0; JScript 1.0; ECMA v1; deprecated in ECMA v3: use encodeURI( ) and encodeURIComponent( ) instead.
- eval(code)
- Evaluates a string of JavaScript code and returns the result.
- isFinite(n)
- Returns true if n is (or can be converted to) a finite number. Returns false if n is (or converts to) NaN (not a number) or positive or negative infinity. JS 1.2; JScript 3.0; ECMA v1.
- isNaN(x)
- Returns true if x is (or can be converted to) the not-a-number value. Returns false if x is (or can be converted to) any numeric value. JS 1.1; JScript 1.0; ECMA v1.
- parseFloat(s)
- Converts the string s (or a prefix of s) to a number and returns that number. Returns NaN (0 in JS 1.0) if s does not begin with a valid number. JS 1.0; JScript 1.1; ECMA v1.
- parseInt(s, radix)
- Converts the string s (or a prefix of s) to an integer and returns that integer. Returns NaN (0 in JS 1.0) if s does not begin with a valid number. The optional radix argument specifies the radix (between 2 and 36) to use. If omitted, base 10 is the default or base 16 if s begins with the hexadecimal prefix "0x" or "0X". JS 1.0; JScript 1.1; ECMA v1.
- unescape(s)
- Decodes a string encoded with escape( ). Returns a decoded copy of s. JS 1.0; JScript 1.0; ECMA v1; deprecated in ECMA v3; use decodeURI( ) and decodeURIComponent( ) instead.
See Also
| History | Client-Side JavaScript 1.0 |
| Go back or forward in browsing history |
window.history history
Methods
- back( )
- Goes back to a previously visited URL in the browsing history. Returns nothing.
- forward( )
- Goes forward in the browsing history. Returns nothing.
- go(n)
- Goes to the nth URL relative to the currently displayed URL. Calling this method with -1 is the same as calling the back( ) method. Returns nothing.
| Image | Client-Side JavaScript 1.1 |
| An HTML image | Inherits From: Element |
document.images[i] document.images[image-name] document.image-name
Constructor
new Image(width, height);
This constructor creates an off-screen Image object that cannot be displayed. The width and height arguments are optional. Setting the src attribute of the resulting object causes the browser to preload an image into its cache.
Properties
The Image object defines properties for each of the attributes of the HTML <img> element, such as src, border, width, height, vspace, and hspace. In addition, it defines or provides special behavior for the following properties:
- complete
- false if the image is still loading. true if it has finished loading or if there was an error while loading. Read-only.
- src
- A read/write string that specifies the URL of the image to be displayed by the browser. This property simply mirrors the src attribute of the <img> tag, but is detailed here because many important DHTML effects are created by dynamically setting the src property of an Image object, to replace one image with another.
Event Handlers
Image inherits event handlers from Element and also defines the following:
- onabort
- Invoked if the user aborts the download of an image.
- onerror
- Invoked if an error occurs while downloading the image.
- onload
- Invoked when the image successfully finishes loading.
| Input | Client-Side JavaScript 1.0 |
| A form input element | Inherits From: Element |
form.elements[i] form.elements[name] form.name
Properties
The Input object defines properties for each of the attributes of the HTML <input> tag, such as maxLength, readOnly, size, and tabIndex. In addition, it defines the following properties:
- checked
- A read/write boolean that specifies whether an input element of type "checkbox" or "radio" is checked (true) or not (false).
- defaultChecked
- A boolean that specifies whether an input element of type "checkbox" or "radio" is checked when first created or when it is reset to its initial state.
- defaultValue
- A string that specifies the text that appears in an input element of type "text" or "password" when it is first created or when it is reset to its initial state. For security reasons, this property does not affect input elements of type file.
- form
- A read-only reference to the Form object that contains the element. This property is defined for input elements of all types.
- name
- The name of this input element, as specified by the HTML name attribute. This property is defined for input elements of all types.
- type
-
A string that specifies the type of the form element. This property
mirrors the HTML type attribute. Legal values are
listed in the following table; the default is text. Submit and
Textarea objects also have a type property, with
possible values select-one, select-multiple, and textarea. JS 1.1.
Type
Description
"button"
Push button
"checkbox"
Checkbox element
"file"
File upload element
"hidden"
Hidden element
"image"
Graphical form submit button
"password"
Masked text entry field
"radio"
Mutually-exclusive radio button
"reset"
Form reset button
"text"
Single-line text entry field
"submit"
Form submission button
- value
- The string value that is sent when the form is submitted. For input elements of type "text", "password", and "file", this is the editable text displayed in the element. You can set this property to change that displayed text. For input elements of type "button", "submit", and "reset", value is the label that appears in the button. For other types, the value string is not displayed. Note that for security reasons, the value property of elements of type "file" is usually read-only.
Methods
- blur( )
- Yields the keyboard focus and returns nothing. Defined for all element types except "hidden".
- click( )
- Simulates a mouse click on the form element and returns nothing. Defined for button element types: "button", "checkbox", "radio", "reset", and "submit".
- focus( )
- Takes the keyboard focus and returns nothing. Defined for all element types except "hidden".
- select( )
- Selects the text that appears in the element and returns nothing. Works for elements of type "text", "password", and "file". Also defined by the Textarea object.
Event Handlers
- onblur
- Invoked when the element loses keyboard focus. Defined for all element types except "hidden".
- onchange
- For text-entry elements of type "text", "password", and "file", this event handler is invoked when the user changes the displayed text and then transfers keyboard focus away from the element, signaling that text entry is complete. It is not invoked for each keystroke.
- onclick
- For button elements of type "button", "checkbox", "radio", "reset", and "submit", this event handler is invoked when the user clicks the button. Return false to prevent form submission or reset for elements of type "submit" and "reset", respectively.
- onfocus
- Invoked the element gains keyboard focus. Defined for all element types except "hidden".
See Also
| Layer | Client-Side Netscape 4 only |
| An independent document layer |
document.layers[i] document.layers[layer-name] document.layer-name
Constructor
new Layer(width, parent_layer)
Description
The Layer object is supported only in Netscape 4 and was discontinued in Netscape 6. It is entirely nonstandard, but is documented here because it provides the only way to work with dynamically positioned objects in Netscape 4. Any HTML element with a CSS position attribute of absolute is represented by a Layer object in JavaScript. You can also create layers with the nonstandard <layer> tag, or with the Layer( ) constructor.
Properties
- above
- The layer above this one, if any. Read-only.
- background
- The background image of the layer.
- below
- The layer below this one, if any. Read-only.
- bgColor
- The background color of the layer.
- clip.bottom
- The Y-coordinate of the bottom edge of the layer's clipping area, relative to top.
- clip.height
- The height of the layer's clipping area. Setting this property also sets the value of clip.bottom.
- clip.left
- The X-coordinate of the left edge of the layer's clipping area, relative to left.
- clip.right
- The X-coordinate of the right edge of the layer's clipping area, relative to left.
- clip.top
- The Y-coordinate of the top edge of the layer's clipping area, relative to top.
- clip.width
- The width of the layer's clipping area. Setting this property also sets the value of clip.right.
- document
- A read-only reference to the Document object contained within the layer.
- hidden
- Specifies whether a layer is hidden or visible. Setting this property to true hides the layer, and setting it to false makes the layer visible.
- layers[ ]
- An array that contains any child Layer objects of this layer. It is the same as the document.layers[ ] array of a layer.
- left
- The X-coordinate of this layer, relative to the containing layer or document. Setting this property moves the layer to the left or right. left is a synonym for x.
- name
- The name attribute of the HTML tag represented by this layer.
- pageX, pageY
- The X and Y-coordinates of this layer relative to the top-level document. Note that these coordinates are relative to the top-level page, not relative to any containing layer.
- parentLayer
- A read-only reference to the Layer or Window object that contains (is the parent of) this layer.
- siblingAbove, siblingBelow
- These properties refer to the sibling Layer object (i.e., a child of the same parent Layer) immediately above or below this layer in the stacking order. If there is no such layer, these properties are null.
- src
- A read/write string that specifies the URL, if any, of the contents of a layer. Setting this property to a new URL causes the browser to read the contents of that URL and display them in the layer.
- top
- The Y-coordinate of this layer relative to the containing layer or document. Setting this property moves the layer up or down. top is a synonym for y.
- visibility
- A read/write string that specifies the visibility of the layer. The three legal values are: "show", "hide", and "inherit".
- window
- The Window object that contains the layer, regardless of how deeply nested the layer is within other layers.
- x, y
- The X and Y-coordinates of the layer. x is a synonym for the left property and y is a synonym for the top property.
- zIndex
- The position of the layer in the z-order, or stacking order, of layers. When two layers overlap, the one with the higher zIndex appears on top and obscures the one with the lower zIndex. If two sibling layers have the same zIndex, the one that appears later in the layers[ ] array of the containing document is displayed later and overlaps the one that appears earlier.
Methods
- load(src, width)
- Loads a new URL into the layer, sets the layer width, and returns nothing.
- moveAbove(other_layer)
- Moves this layer above another and returns nothing.
- moveBelow(other_layer)
- Moves this layer below another and returns nothing.
- moveBy(dx, dy)
- Moves the layer relative to its current position and returns nothing.
- moveTo(x, y)
- Moves the layer to the point (x,y) relative to its containing layer or window and returns nothing.
- moveToAbsolute(x, y)
- Moves the layer to a position relative to the page and returns nothing.
- resizeBy(dw, dh)
- Resizes the layer by the specified amounts and returns nothing.
- resizeTo(width, height)
- Resizes the layer to the specified size returns nothing.
| Link | Client-Side JavaScript 1.0 |
| An <a> or <area> link | Inherits From: Element |
document.links[i]
Properties
Many of the properties of a Link object represent portions of its URL. For each such property below, the example given is a portion of the following (fictitious) URL:
http://www.oreilly.com:1234/catalog/search.html ?q=JavaScript&m=10#results
- hash
- A read/write string property that specifies the anchor portion of the Link's URL, including the leading hash (#) mark. For example: "#result".
- host
- A read/write string property that specifies the hostname and port portions of a Link's URL. For example: "www.oreilly.com:1234".
- hostname
- A read/write string property that specifies the hostname portion of a Link's URL. For example: "www.oreilly.com".
- href
- A read/write string property that specifies the complete text of the Link's URL.
- pathname
- A read/write string property that specifies the pathname portion of a Link's URL. For example: "/catalog/search.html".
- port
- A read/write string (not a number) property that specifies the port portion of a Link's URL. For example: "1234".
- protocol
- A read/write string property that specifies the protocol portion of a Link's URL, including the trailing colon. For example: "http:".
- search
- A read/write string property that specifies the query portion of a Link's URL, including the leading question mark. For example: "?q=JavaScript&m=10".
- target
- A read/write string property that specifies the name of a Window object (i.e., a frame or a top-level browser window) in which the linked document should be displayed. This property is the standard target HTML attribute. The special names "_blank", "_top", "_parent", and "_self" are allowed.
Event Handlers
- onclick
- Invoked when the user clicks on the link. In JavaScript 1.1, this event handler may prevent the link from being followed by returning false.
- onmouseout
- Invoked when the user moves the mouse off the link. JS 1.1.
- onmouseover
- Invoked when the user moves the mouse over the link. The status property of the current window may be set here. Return true to tell the browser not to display the URL of the link in the status line.
See Also
| Location | Client-Side JavaScript 1.0 |
| Current browser location |
location window.location
Properties
The Location object defines the same URL-related properties that the Link object does, with the exception of the target. See the Link object for a description of the hash, host, hostname, href, pathname, port, protocol, and search properties. Setting any of these properties causes the browser to load and display the document from the new URL. As a shortcut, you can also load a new document by assigning a URL string to the location property of the Window.
Methods
- reload( force)
- Reloads the current document from the cache or the server. The force argument is optional. If true, it forces a complete reload, even if the document has not been modified. Returns nothing. JS 1.1.
- replace(url)
- Replaces the current document with a new one, without generating a new entry in the browsing history. Returns nothing. JS 1.1.
See Also
| Math | Core JavaScript 1.0; JScript 1.0; ECMA v1 |
| Mathematical functions and constants |
Math.constant Math.function( )
Description
The Math object is a placeholder for grouping mathematical constants and functions. It does not define a class of objects as Date and String do. There is no Math( ) constructor, and functions like Math.sin( ) are simply functions, not methods that operate on an object.
Constants
- Math.E
- The constant e, the base of the natural logarithm.
- Math.LN10
- The natural logarithm of 10.
- Math.LN2
- The natural logarithm of 2.
- Math.LOG10E
- The base-10 logarithm of e.
- Math.LOG2E
- The base-2 logarithm of e.
- Math.PI
-
The constant
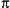 .
.
- Math.SQRT1_2
- 1 divided by the square root of 2.
- Math.SQRT2
- The square root of 2.
Functions
- Math.abs(x)
- Returns the absolute value of x.
- Math.acos(x)
-
Returns the arc cosine of x; the return
value is between 0 and
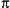 radians.
radians.
- Math.asin(x)
-
Returns the arc sine of x; the return
value is between -
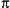 /2 and
/2 and 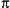 /2 radians.
/2 radians.
- Math.atan(x)
-
Returns the arc tangent of x; the return
value is between -
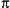 /2 and
/2 and 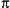 /2 radians.
/2 radians.
- Math.atan2(y, x)
-
Returns a value between -
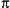 and
and 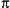 radians that
specifies the counterclockwise angle between the positive X-axis and
the point (x,
y). Note the order of the arguments to
this function.
radians that
specifies the counterclockwise angle between the positive X-axis and
the point (x,
y). Note the order of the arguments to
this function.
- Math.ceil(x)
- Returns the nearest integer greater than or equal to x.
- Math.cos(x)
- Returns the cosine of the specified value x.
- Math.exp(x)
- Returns the constant e raised to the power of x.
- Math.floor(x)
- Returns the nearest integer less than or equal to x.
- Math.log(x)
- Returns the natural logarithm of x.
- Math.max(args...)
- Returns the largest of the arguments. Returns -Infinity if there are no arguments. Returns NaN if any of the arguments is NaN or is a non-numeric value that cannot be converted to a number. Prior to ECMA v3, this function requires exactly 2 arguments.
- Math.min(args...)
- Returns the smallest of the arguments. Returns Infinity if there are no arguments. Returns NaN if any argument is NaN or is a non-numeric value that cannot be converted to a number. Prior to ECMA v3, this function requires exactly 2 arguments.
- Math.pow(x, y)
- Returns x to the power of y.
- Math.random( )
- Returns a pseudorandom number between 0.0 and 1.0. JS 1.1; JScript 1.0; ECMA v1.
- Math.round(x)
- Returns the integer closest to x.
- Math.sin(x)
- Returns the sine of x.
- Math.sqrt(x)
- Returns the square root of x. Returns NaN if x is less than zero.
- Math.tan(x)
- Returns the tangent of x.
See Also
| Navigator | Client-Side JavaScript 1.0 |
| Information about the browser |
navigator
Properties
- appCodeName
- A read-only string that specifies a nickname for the browser. In all Netscape browsers, this is "Mozilla". For compatibility, this property is "Mozilla" in Microsoft browsers as well.
- appName
- A read-only string property that specifies the name of the browser. For Netscape, the value of this property is "Netscape". In IE, the value of this property is "Microsoft Internet Explorer".
- appVersion
- A read-only string that specifies version and platform information for the browser. The first part of this string is a version number. Pass the string to parseInt( ) to obtain the major version number only or to parseFloat( ) to obtain the major and minor version numbers as a floating-point value. The remainder of the string value of this property provides other details about the browser version, including the operating system it is running on. Unfortunately, however, the format of this information varies widely from browser to browser.
- cookieEnabled
- A read-only boolean that is true if the browser has cookies enabled, and false if they are disabled. IE 4, Netscape 6.
- language
- A read-only string that specifies the default language of the browser version. The value of this property is a standard two-letter language code such as "en" for English or "fr" for French. It can also be a five-letter string indicating a language and a regional variant, such as "fr_CA" for French, as spoken in Canada. Netscape 4; note that IE 4 provides two different language-related properties.
- platform
- A read-only string that specifies the operating system and/or hardware platform the browser is running under. Although there is not standard set of values for this property, some typical values are "Win32", "MacPPC", and "Linux i586". JS 1.2.
- systemLanguage
- A read-only string that specifies the default language of the operating system using the same standard codes used by the Netscape-specific language property. IE 4.
- userAgent
- A read-only string that specifies the value the browser uses for the user-agent header in HTTP requests. Typically, this is the value of navigator.appCodeName followed by a slash and the value of navigator.appVersion.
- userLanguage
- A read-only string that specifies the preferred language of the user using the same standard codes used by the Netscape-specific language property. IE 4.
Methods
- javaEnabled( )
- Returns true if Java is supported and enabled in the current browser, or false if it is not. JS 1.1.
See Also
| Node | DOM Level 1 |
| A node in a document tree |
Subclasses
Attr, Comment, Document, DocumentFragment, Element, Text
Constants
All nodes in an HTML document are instances of one of the Node subclasses listed above. Every Node object has a nodeType property that specifies which of the subclasses it is an instance of. The following constants are the legal values for nodeType. Note that these are static properties of Node, not properties of individual Node objects. They are not defined in Internet Explorer 4, 5, or 6; in those browsers you must use the corresponding integer literals.
Node.ELEMENT_NODE = 1; // Element Node.ATTRIBUTE_NODE = 2; // Attr Node.TEXT_NODE = 3; // Text Node.COMMENT_NODE = 8; // Comment Node.DOCUMENT_NODE = 9; // Document Node.DOCUMENT_FRAGMENT_NODE=11; // DocumentFragment
Properties
- attributes[ ]
- If this Node is an Element, the attributes property is a read-only array of Attr objects that represent the attributes of the element. The array can be indexed by number or by attribute name. All HTML attributes have corresponding Element properties, however, so it is uncommon to use the attributes[ ] array.
- childNodes[ ]
- This read-only array of Node objects contains the children of this node. If the node has no children, this property is a zero-length array.
- firstChild
- This read-only property refers to the first child Node of this node, or null if the node has no children.
- lastChild
- This read-only property refers to the last child Node of this node, or null if the node has no children.
- nextSibling
- The sibling Node that immediately follows this one in the childNodes[ ] array of the parentNode, or null if there is no such node. Read-only.
- nodeName
- The name of the node. For Element nodes, this property specifies the tag name of the element, which can also be retrieved with the tagName property of Element. For Attr nodes, this property specifies the attribute name. For other types of nodes, the value is a constant string that specifies the node type. Read-only.
- nodeType
- The type of the node. The legal values for this property are defined by the constants listed above.
- nodeValue
- The string value of a node. For Text and Comment nodes, this property holds the text content. For Attr nodes, it holds the attribute value. This property is read/write.
- ownerDocument
- The Document object of which this Node is a part. For Document nodes, this property is null. Read-only.
- parentNode
- The parent or container Node of this node, or null if there is no parent. Note that Document and Attr nodes never have parent nodes. Nodes that have been removed from the document or are newly created and have not yet been inserted into the document tree have a parentNode of null. Read-only.
- previousSibling
- The sibling Node that immediately precedes this one in the childNodes[ ] array of the parentNode, or null, if there is no such node.
Methods
- addEventListener(type, listener, useCapture)
- Registers an event listener for this node. type is a string that specifies the event type minus the "on" prefix (e.g., "click" or "submit"). listener is the event handler function. When triggered, it is invoked with an Event object as its argument. If useCapture is true, this is a capturing event handler. If false or omitted, it is a regular event handler. Returns nothing. DOM Level 2; not supported in IE 4, 5, or 6.
- appendChild(newChild)
- Adds the newChild Node to the document tree by appending it to the childNodes[ ] array of this node. If the node is already in the document tree, it is first removed before being reinserted at its new position. Returns the newChild argument.
- cloneNode(deep)
- Returns a copy of this node. If deep is true, the descendents of the node are recursively copied as well.
- hasAttributes( )
- Returns true if this node is an Element and has any attributes. DOM Level 2.
- hasChildNodes( )
- Returns true if this node has any children.
- insertBefore(newChild, refChild)
- Inserts the newChild Node into the document tree immediately before the refChild Node, which must be a child of this node. If the node being inserted is already in the tree, it is first removed. Returns newChild.
- isSupported(feature, version)
- Returns true if the specified version number of a named feature is supported by this node. See also DOMImplementation.hasFeature( ). DOM Level 2.
- normalize( )
- Normalizes all Text node descendants of this node by deleting empty Text nodes and merging adjacent Text nodes. Returns nothing.
- removeChild(oldChild)
- Removes the oldChild Node from the document tree. oldChild must be a child of this node. Returns oldChild.
- removeEventListener(type, listener, useCapture)
- Removes the specified event listener. Returns nothing. DOM Level 2; not supported in IE 4, 5, or 6.
- replaceChild(newChild, oldChild)
- Replaces the oldChild Node (which must be a child of this node) with the newChild Node. If newChild is already in the document tree, it is first removed from its current location. Returns oldChild.
See Also
| Number | Core JavaScript 1.1; JScript 2.0; ECMA v1 |
| Support for numbers |
Constructor
new Number(value) Number(value)
With the new operator, the Number( ) constructor converts its argument to a numeric value and returns a new Number object wrapped around that value. Without new, Number( ) is a conversion function that converts its argument to a number and returns that value.
Constants
These constants are properties of Number itself, not of individual Number objects.
- Number.MAX_VALUE
- The largest representable number. Approximately 1.79E + 308.
- Number.MIN_VALUE
- The smallest representable number. Approximately 5E - 324.
- Number.NaN
- Not-a-number value. Same as the global NaN.
- Number.NEGATIVE_INFINITY
- Negative infinite value.
- Number.POSITIVE_INFINITY
- Infinite value. Same as global Infinity.
Methods
- toExponential(digits)
- Returns a string representation of the number, in exponential notation, with one digit before the decimal place and digits digits after the decimal place. The fractional part of the number is rounded, or padded with zeros so that it has the specified length. digits must be between 0 and 20, and if omitted, as many digits as necessary are used. JS 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- toFixed(digits)
- Returns a string representation of the number that does not use exponential notation, and has exactly digits digits after the decimal place. digits must be between 0 and 20. The number is rounded or padded with zeros if necessary. JS 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- toLocaleString( )
- Returns an implementation-dependent string representation of the number, formatted according to local conventions. This may affect things such as the punctuation characters used for the decimal point and the thousands separator. JS 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- toPrecision(precision)
- Returns a string representation of number that contains precision significant digits. precision must be between 1 and 21. The returned string uses fixed-point notation where possible, or exponential notation otherwise. The number is rounded or padded with zeros if necessary. JS 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- toString(radix)
- Converts a number to a string, using a specified radix (base), and returns the string. radix must be between 2 and 36. If omitted, base 10 is used.
See Also
| Object | Core JavaScript 1.0; JScript 1.0; ECMA v1 |
| The superclass of all JavaScript objects |
Constructor
new Object( );
This constructor creates an empty object to which you can add arbitrary properties.
Properties
All JavaScript objects, however they are created, have the following properties.
- constructor
- A reference to the JavaScript function that was the constructor for the object. JS 1.1; JScript 2.0; ECMA v1.
Methods
All JavaScript objects, however they are created, have the following methods.
- hasOwnProperty(propname)
- Returns true if the object has a non-inherited property with the specified name. Returns false if the object does not have a property with the specified name, or if it inherits that property from its prototype object. JS 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- isPrototypeOf(o)
- Returns true if this object is the prototype of o. Returns false if o is not an object or if this object is not its prototype. JS 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- propertyIsEnumerable(propname)
- Returns true if this object has a non-inherited enumerable property with the specified name, and returns false otherwise. Enumerable properties are those that are enumerated by for/in loops. JS 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- toLocaleString( )
- Returns a localized string representation of the object. The default implementation of this method simply calls toString( ), but subclasses may override it to provide localization. JS 1.5; JScript 5.5; ECMA v3.
- toString( )
- Returns a string representation of the object. The implementation of this method provided by the Object class is quite generic and does not provide much useful information. Subclasses of Object typically override this method by defining their own toString( ) method that produces more useful output. JS 1.0; JScript 2.0; ECMA v1.
- valueOf( )
- Returns the primitive value of the object, if any. For objects of type Object, this method simply returns the object itself. Subclasses of Object, such as Number and Boolean, override this method to return the primitive value associated with the object. JS 1.1; JScript 2.0; ECMA v1.
See Also
| Option | Client-Side JavaScript 1.0 |
| A selectable option | Inherits From: Element |
select.options[i]
Constructor
In JavaScript 1.1 and later, Option objects can be created dynamically with the Option( ) constructor:
new Option(text, value, defaultSelected, selected)
Properties
- defaultSelected
- A read/write boolean that specifies whether the option is initially selected when the Select object that contains it is created or reset.
- index
- A read-only integer that specifies the index of the option within the options[ ] array of the Select object that contains it.
- selected
- A read/write boolean value that specifies whether an option is currently selected. You can use this property to test whether a given option is selected. You can also set it to select or deselect an option. Note that when you select or deselect an option in this way, the Select.onchange( ) event handler is not invoked.
- text
- A read/write string that specifies the text that appears to the user for the option.
- value
- A read/write string that specifies the text that is passed to the web server if the option is selected when the form is submitted.
See Also
| RegExp | Core JavaScript 1.2; JScript 3.0; ECMA v3 |
| Regular expressions for pattern matching |
/pattern/attributes
Constructor
new RegExp(pattern, attributes)
Regular expression patterns are expressed using a complex grammar that is summarized earlier in this chapter (Section 11.2.12).
Instance Properties
- global
- A read-only boolean that specifies whether the RegExp has the g attribute and therefore performs global matching.
- ignoreCase
- A read-only boolean that specifies whether the RegExp has the i attribute and therefore performs case-insensitive matching.
- lastIndex
- For global RegExp objects, this read/write property specifies the character position immediately following the last match; this is the first character examined for the next match.
- multiline
- A read-only boolean that specifies whether the RegExp has the m attribute and therefore performs multi-line matching.
- source
- A read-only string that holds the source text of the regular expression pattern, excluding slashes and attributes.
Methods
- exec(string)
- Matches string against this RegExp and returns an array containing the results of the match, or null if no match was found. Element 0 of the array is the matching text. Subsequent elements of the array contain the substrings that matched the subexpressions within the RegExp. The returned array also has an index property that specifies the start position of the match.
- test(string)
- Returns true if string contains text matching this RegExp, or false otherwise.
See Also
| Screen | Client-Side JavaScript 1.2 |
| Information about the display |
screen
Properties
- availHeight
- The available height, in pixels, of the screen.
- availWidth
- Specifies the available width, in pixels, of the screen.
- colorDepth
- The depth of the browser's color palette, or the number of bits-per-pixel for the screen.
- height
- Specifies the total height, in pixels, of the screen.
- width
- Specifies the total width, in pixels, of the screen.
See Also
| Select | Client-Side JavaScript 1.0 |
| A graphical selection list | Inherits From: Element |
form.elements[i] form.elements[element_name] form.element_name
Properties
The Select object defines properties for each of the attributes of the HTML <select> tag, such as disabled, multiple, name, and size. In addition, it defines the following properties:
- form
- The Form object that contains this Select object. Read-only.
- length
- A read-only integer that specifies the number of elements in the options[ ] array. The value of this property is the same as options.length.
- options[ ]
- An array of Option objects, each describing one of the options displayed within the Select element. You can shorten the set of options by setting the options.length property to a smaller value (or remove all options by setting it to zero). You can remove individual options by setting an element of the array to null—this shifts the elements above it down, shortening the array. You can append options to the Select object by using the Option( ) constructor to create a new Option and assigning it to options[options.length].
- selectedIndex
- A read/write integer that specifies the index of the selected option within the Select object. If no option is selected, selectedIndex is -1. If more than one option is selected, selectedIndex specifies the index of the first one only. Setting this property causes all other options to become deselected. Setting it to -1 causes all options to be deselected.
- type
- A read-only string property that specifies the type of the element. If the Select object allows only a single selection (i.e., if the multiple attribute does not appear in the object's HTML definition), this property is "select-one". Otherwise, the value is "select-multiple". See also Input.type. JS 1.1.
Methods
- add(new, old)
- Inserts the Option object new into the options[ ] array at the position immediately before the Option object old. If old is null, the new Option is appended to the array. Returns nothing. DOM Level 1.
- blur( )
- Yields the keyboard focus and returns nothing.
- focus( )
- Grabs the keyboard focus and returns nothing.
- remove(n)
- Removes the nth element from the options[ ] array. Returns nothing. DOM Level 1.
Event Handlers
- onblur
- Invoked when input focus is lost.
- onchange
- Invoked when the user selects or deselects an item.
- onfocus
- Invoked when input focus is gained.
See Also
| String | Core JavaScript 1.0; JScript 1.0; ECMA v1 |
| String manipulation | Inherits From: Object |
Constructor
String(s) new String(s)
Without the new operator, the String( ) function converts its argument to a string. With the new operator, it is a constructor that wraps the converted value in a String object.
Properties
- length
- The number of characters in the string. Read-only.
Methods
- charAt(n)
- Returns the character at position n in the string.
- charCodeAt(n)
- Returns the Unicode encoding of the character at position n in the string. JS 1.2; JScript 5.5; ECMA v1.
- concat(value, ...)
- Returns a new string that results from converting each of the arguments to a string and concatenating the resulting strings. JS 1.2; JScript 3.0; ECMA v3.
- indexOf(substring, start)
- Returns the position of the first occurrence of substring within this string that appears at or after the start position or -1 if no such occurrence is found. If start is omitted, 0 is used.
- lastIndexOf(substring, start)
- Returns the position of the last occurrence of substring within string that appears before the start position, or -1 if no such occurrence is found. If start is omitted, the string length is used.
- match(regexp)
- Matches this string against the specified regular expression and returns an array containing the match results or null if no match is found. If regexp is not a global regular expression, the returned array is the same as for the RegExp.exec( ) method. If regexp is global (has the "g" attribute), the elements of the returned array contain the text of each match found. JS 1.2; JScript 3.0; ECMA v3.
- replace(regexp, replacement)
- Returns a new string, with text matching regexp replaced with replacement. regexp may be a regular expression or a plain string. replacement may be a string, containing optional regular expression escape sequences (such as $1) that are replaced with portions of the matched text. It may also be a function that computes the replacement string based on match details passed as arguments. JS 1.2; JScript 3.0; ECMA v3.
- search(regexp)
- Returns the position of the start of the first substring of this string that matches regexp, or -1 if no match is found. JS 1.2; JScript 3.0; ECMA v3.
- slice(start, end)
- Returns a new string that contains all the characters of string from and including the position start and up to but not including end. If end is omitted, the slice extends to the end of the string. Negative arguments specify character positions measured from the end of the string. JS 1.2; JScript 3.0; ECMA v3.
- split(delimiter, limit)
- Returns an array of strings, created by splitting string into substrings at the boundaries specified by delimiter. delimiter may be a string or a RegExp. If delimiter is a RegExp with a parenthesized subexpression, the delimiter text that matches the subexpression is included in the returned array. See also Array.join( ). JS 1.1; JScript 3.0; ECMA v1.
- substring(from, to)
- Returns a new string that contains characters copied from positions from to to-1 of string. If to is omitted, the substring extends to the end of the string. Negative arguments are not allowed.
- substr(start, length)
- Returns a copy of the portion of this string starting at start and continuing for length characters, or to the end of the string, if length is not specified. JS 1.2; JScript 3.0; nonstandard: use slice( ) or substring( ) instead.
- toLowerCase( )
- Returns a copy of the string, with all uppercase letters converted to their lowercase equivalent, if they have one.
- toUpperCase( )
- Returns a copy of the string, with all lowercase letters converted to their uppercase equivalent, if they have one.
Static Functions
| Style | DOM Level 2; IE 4 |
| Inline CSS properties of an element |
element.style
Properties
The Style object defines a large number of properties: one property for each CSS attribute defined by the CSS2 specification. The property names correspond closely to the CSS attribute names, with minor changes required to avoid syntax errors in JavaScript. Multiword attributes that contain hyphens, such as font-family are written without hyphens in JavaScript, and each word after the first is capitalized: fontFamily. Also, the float attribute conflicts with the reserved word float, so it translates to the property cssFloat.
The visual CSS properties are listed in the following table. Since the properties correspond directly to CSS attributes, no individual documentation is given for each property. See a CSS reference (such as Cascading Style Sheets: The Definitive Guide by Eric A. Meyer, published by O'Reilly) for the meaning and legal values of each. Note that current browsers do not implement all of these properties.
All of the properties are strings, and care is required when working with properties that have numeric values. When querying such a property, you must use parseFloat( ) to convert the string to a number. When setting such a property you must convert your number to a string, which you can usually do by adding the required units specification, such as "px".
background |
counterIncrement |
orphans |
backgroundAttachment |
counterReset |
outline |
backgroundColor |
cssFloat |
outlineColor |
backgroundImage |
cursor |
outlineStyle |
backgroundPosition |
direction |
outlineWidth |
backgroundRepeat |
display |
overflow |
border |
emptyCells |
padding |
borderBottom |
font |
paddingBottom |
borderBottomColor |
fontFamily |
paddingLeft |
borderBottomStyle |
fontSize |
paddingRight |
borderBottomWidth |
fontSizeAdjust |
paddingTop |
borderCollapse |
fontStretch |
page |
borderColor |
fontStyle |
pageBreakAfter |
borderLeft |
fontVariant |
pageBreakBefore |
borderLeftColor |
fontWeight |
pageBreakInside |
borderLeftStyle |
height |
position |
borderLeftWidth |
left |
quotes |
borderRight |
letterSpacing |
right |
borderRightColor |
lineHeight |
size |
borderRightStyle |
listStyle |
tableLayout |
borderRightWidth |
listStyleImage |
textAlign |
borderSpacing |
listStylePosition |
textDecoration |
borderStyle |
listStyleType |
textIndent |
borderTop |
margin |
textShadow |
borderTopColor |
marginBottom |
textTransform |
borderTopStyle |
marginLeft |
top |
borderTopWidth |
marginRight |
unicodeBidi |
borderWidth |
marginTop |
verticalAlign |
bottom |
markerOffset |
visibility |
captionSide |
marks |
whiteSpace |
clear |
maxHeight |
widows |
clip |
maxWidth |
width |
color |
minHeight |
wordSpacing |
content |
minWidth |
zIndex |
| Text | DOM Level 1 |
| A run of text in a document | Inherits From: Node |
Description
A Text object represents a run of plain text without markup in a DOM document tree. Do not confuse it with the single-line text input element of HTML, which is represented by the Input object.
Properties
- data
- The string of text contained by this node.
- length
- The number of characters contained by this node. Read-only.
Methods
- appendData(text)
- Appends the specified text to this node and returns nothing.
- deleteData(offset, count)
- Deletes text from this node, starting with the character at the specified offset, and continuing for count characters. Returns nothing.
- insertData(offset, text)
- Inserts the specified text into this node at the specified character offset. Returns nothing.
- replaceData(offset, count, text)
- Replaces the characters starting at the specified offset and continuing for count characters with the specified text. Returns nothing.
- splitText(offset)
- Splits this Text node into two at the specified character position, inserts the new Text node into the document after the original, and returns the new node.
- substringData(offset, count)
- Returns a string that consists of the count characters starting with the character at position offset.
See Also
| Textarea | Client-Side JavaScript 1.0 |
| Multiline text input | Inherits From: Element |
form.elements[i] form.elements[name] form.name
Description
The Textarea object is very similar to the Input object.
Properties
The Textarea object defines properties for each of the attributes of the HTML <textarea> tag, such as cols, defaultValue, disabled, name, readOnly, and rows. In addition, it defines the following properties:
- form
- The Form object that contains this Textarea object. Read-only.
- type
- A read-only string property that specifies the type of the element. For Textarea objects, this property is always "textarea".
- value
- A read/write string that specifies the text contained in the Textarea. The initial value of this property is the same as the defaultValue property.
Methods
- blur( )
- Yields the keyboard focus and returns nothing.
- focus( )
- Grabs the keyboard focus and returns nothing.
- select( )
- Selects the entire contents of the text area. Returns nothing.
Event Handlers
- onblur
- Invoked when input focus is lost.
- onchange
- Invoked when the user changes the value in the Textarea element and moves the keyboard focus elsewhere. This event handler is invoked only when the user completes an edit in the Textarea element.
- onfocus
- Invoked when input focus is gained.
See Also
| Window | Client-Side JavaScript 1.0 |
| Browser window or frame |
self window window.frames[i]
Properties
The Window object defines the following properties. Nonportable, browser-specific properties are listed separately after this list. Note that the Window object is the Global object for client-side JavaScript; therefore, the Window object also has the properties listed on the Global reference page.
- closed
- A read-only boolean value that specifies whether the window has been closed.
- defaultStatus
- A read/write string that specifies a persistent message to appear in the status line whenever the browser is not displaying another message.
- document
- A read-only reference to the Document object contained in this window or frame. See Document.
- frames[ ]
- An array of Window objects, one for each frame contained within the this window. Note that frames referenced by the frames[ ] array may themselves contain frames and may have a frames[ ] array of their own.
- history
- A read-only reference to the History object of this window or frame. See History.
- length
- Specifies the number of frames contained in this window or frame. Same as frames.length.
- location
- The Location object for this window or frame. See Location. This property has special behavior: if you assign a URL string to it, the browser loads and displays that URL.
- name
- A string that contains the name of the window or frame. The name is specified with the Window.open( ) method, or with the name attribute of a <frame> tag. Read-only in JS 1.0; read/write in JS 1.1.
- navigator
- A read-only reference to the Navigator object, which provides version and configuration information about the web browser. See Navigator.
- opener
- A read/write reference to the Window that opened this window. JS 1.1.
- parent
- A read-only reference to the Window object that contains this window or frame. If this window is a top-level window, parent refers to the window itself.
- screen
- A read-only reference to the Screen object that specifies information about the screen the browser is running on. See Screen. JS 1.2.
- self
- A read-only reference to this window itself. This is a synonym for the window property.
- status
- A read/write string that can be set to display a transient message in the browser's status line.
- top
- A read-only reference to the top-level window that contains this window. If this window is a top-level window, top refers to the window itself.
- window
- The window property is identical to the self property; it contains a reference to this window.
Netscape 4 Properties
- innerHeight, innerWidth
- Read/write properties that specify the height and width, in pixels, of the document display area of this window. These dimensions do not include the height of the menubar, toolbars, scrollbars, and so on.
- outerHeight, outerWidth
- Read/write integers that specify the total height and width, in pixels, of the window. These dimensions include the height and width of the menubar, toolbars, scrollbars, window borders, and so on.
- pageXOffset, pageYOffset
- Read-only integers that specify the number of pixels that the current document has been scrolled to the right (pageXOffset) and down (pageYOffset).
- screenX, screenY
- Read-only integers that specify the X and Y-coordinates of the upper-left corner of the window on the screen. If this window is a frame, these properties specify the X and Y-coordinates of the top-level window that contains the frame.
IE 4 Properties
- clientInformation
- An IE-specific synonym for the navigator property. Refers to the Navigator object.
- event
- The event property refers to an Event object that contains the details of the most recent event to occur within this window. In the IE event model, the Event object is not passed as an argument to the event handler, and is instead assigned to this property.
Methods
The Window object has the following portable methods. Since the Window object is the Global object in client-side JavaScript, it also defines the methods listed on the Global reference page.
- alert(message)
- Displays message in a dialog box. Returns nothing. JS 1.0.
- blur( )
- Yields the keyboard focus and returns nothing. JS 1.1.
- clearInterval(intervalId)
- Cancels the periodic execution of code specified by intervalId. See setInterval( ). Returns nothing. JS 1.2.
- clearTimeout(timeoutId)
- Cancels the pending timeout specified by timeoutId. See setTimeout( ). Returns nothing. JS 1.0.
- close( )
- Closes a window and returns nothing. JS 1.0.
- confirm(question)
- Displays question in a dialog box and waits for a yes-or-no response. Returns true if the user clicks the OK button, or false if the user clicks the Cancel button. JS 1.0.
- focus( )
- Requests keyboard focus; this also brings the window to the front on most platforms. Returns nothing. JS 1.1.
- getComputedStyle(elt)
- Returns a read-only Style object that contains all CSS styles (not just inline styles) that apply to the specified document element elt. Positioning attributes such as left, top, and width queried from this computed style object are always returned as pixel values. DOM Level 2.
- moveBy(dx, dy)
- Moves the window the specified distances from its current position and returns nothing. JS 1.2.
- moveTo(x, y)
- Moves the window to the specified position and returns nothing. JS 1.2
- open(url, name, features)
- Displays the specified url in the named window. If the name argument is omitted or if there is no window by that name, a new window is created. The optional features argument is a string that specifies the size and decorations of the new window as a comma-separated list of features. Feature names commonly supported on all platforms are: width=pixels, height=pixels, location, menubar, resizable, status, and toolbar. In IE, set the position of the window with left=x and top=y. In Netscape, use screenX=x and screenY=y. Returns the existing or new Window object. JS 1.0.
- print( )
- Simulates a click on the browser's Print button and returns nothing. Netscape 4; IE 5.
- prompt(message, default)
- Displays message in a dialog box and waits for the user to enter a text response. Displays the optional default as the default response. Returns the string entered by the user, or the empty string if the user did not enter a string, or null if the user clicked Cancel. JS 1.0.
- resizeBy(dw, dh)
- Resizes the window by the specified amount and returns nothing. JS 1.2.
- resizeTo(width, height)
- Resizes the window to the specified size and returns nothing. JS 1.2.
- scroll(x, y)
- Scrolls the window to the specified coordinates and returns nothing. JS 1.1; deprecated in JS 1.2 in favor of scrollTo( ).
- scrollBy(dx, dy)
- Scrolls the window by a specified amount and returns nothing. JS 1.2.
- scrollTo(x, y)
- Scrolls the window to a specified position and returns nothing. JS 1.2.
- setInterval(code, interval, args...)
- Evaluates the string of JavaScript code every interval milliseconds. In Netscape 4 and IE 5, code may be a reference to a function instead of a string. In that case, the function is invoked every interval milliseconds. In Netscape, any arguments after interval are passed to the function when it is invoked, but this feature is not supported by IE. Returns an interval ID value that can be passed to clearInterval( ) to cancel the periodic executions. JS 1.2.
- setTimeout(code, delay)
- Evaluates the JavaScript code in the string code after delay milliseconds have elapsed. In Netscape 4 and IE5, code may be a function rather than a string; see the discussion under setInterval( ). Returns a timeout ID value that can be passed to clearTimeout( ) to cancel the pending execution of code. Note that this method returns immediately; it does not wait for delay milliseconds before returning. JS 1.0.
Event Handlers
Event handlers for a Window object are defined by attributes of the <body> tag of the document.
- onblur
- Invoked when the window loses focus.
- onerror
- Invoked when a JavaScript error occurs. This is a special event handler that is invoked with three arguments that specify the error message, the URL of the document that contained the error, and the line number of the error, if available.
- onfocus
- Invoked when the window gains focus.
- onload
- Invoked when the document (or frameset) is fully loaded.
- onresize
- Invoked when the window is resized.
- onunload
- Invoked when the browser leaves the current document.
See Also

Copyright © 2003 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.



