Beginning with V8.12, the per-operating-system compile-time macros
were removed from the sendmail/conf.h file, and
were moved into the include/sm/conf.h file. In
addition to moving them, they were also all prefixed with the
characters SM_.
These compile-time macros are most certainly defined correctly for
your operating system. In the rare event you are porting
sendmail to a new operating system, you might
need to tune these on a selective basis:
- SM_CONF_BROKEN_SIZE_T
-
On most systems, the size_t type is defined as an
unsigned variable. When porting, if that is not
the case on your system, define this compile-time macro:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_CONF_BROKEN_SIZE_T=1')
- SM_CONF_BROKEN_STRTOD
-
The sendmail program uses
printf(3) and scanf(3) with
double-precision conversions, which will cause them to return
improper results on some operating systems. When porting, if your
operating system returns improper results, you can define this
compile-time macro:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_CONF_BROKEN_STRTOD=1')
See libsm/t-float.c to discover how to detect if
this is needed.
- SM_CONF_GETOPT
-
The sendmail program, and all its companion
programs, use the getopt(3) routine to parse
command-line arguments. When porting, if your compiler library lacks
a getopt(3) routine, define this compile-time
macro with a value of zero:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_CONF_GETOPT=0')
- SM_CONF_LDAP_MEMFREE
-
When porting, if your LDAP library includes the
ldap_memfree(3) routine, you can define this
compile-time macro:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_CONF_LDAP_MEMFREE=1')
- SM_CONF_LONGLONG
-
The 1999 ISO C-language standard defines a long
long type. When porting, if your compiler supports this
type, define this compile-time macro:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_CONF_LONGLONG=1')
- SM_CONF_MEMCHR
-
When porting, if your C-language library includes the
memchr(3) routine, define this compile-time
macro:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_CONF_MEMCHR=1')
- SM_CONF_MSG
-
When porting, if your system supports System V IPC message queues,
you can define this compile-time macro:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_CONF_MSG=1')
- SM_CONF_QUAD_T
-
When porting, if your C-language compiler lacks the long
long type, but your
/usr/include/sys/types.h file defines
quad_t as a struct, you can
define this compile-time macro:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_CONF_QUAD_T=1')
- SM_CONF_SEM
-
When porting, if your system supports System V IPC semaphores, you
can define this compile-time macro:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_CONF_SEM=1')
- SM_CONF_SETITIMER
-
When porting, if the setitimer(2) function is
missing from your C-language library, you can define this
compile-time macro with a value of zero:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_CONF_SETITIMER=0')
- SM_CONF_SHM
-
When tuning your system, if System V shared memory is available on
your machine, you can define this compile-time macro:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_CONF_SHM=1')
See SM_CONF_SHM for a full description of this
compile-time macro.
- SM_CONF_SHM_DELAY
-
This compile-time macro is defined in
libsm/config.c, but not otherwise used in the
V8.12 source.
- SM_CONF_SSIZE_T
-
When porting, if your /usr/include/sys/type.h
file lacks a definition for ssize_t, you may
define this compile-time macro to zero:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_CONF_SSIZE_T=0')
- SM_CONF_STDBOOL_H
-
When porting, if the /usr/include/stdbool.h file
exists and defines the three macros true,
false, and bool, you can define
this compile-time macro:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_CONF_STDBOOL_H=1')
- SM_CONF_STDDEF_H
-
When porting, if the /usr/include/stddef.h file
does not exist, define this compile-time macro as zero:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_CONF_STDDEF_H=0')
- SM_CONF_STRL
-
When porting, if the strlcpy(3) and
strlcat(3) C-language library routines are
available, first define this compile-time macro with a value of 1:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_CONF_STRL=1') 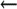 use the library routines
use the library routines
Then, compile and run the benchmark program
libsm/b-strl.c. If the benchmark
program's output shows that the
libsm-provided versions of those routines are
faster, redefine SM_CONF_STRL to zero (the default):
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_CONF_STRL=0') 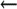 if b-strl.c shows libsm versions faster
if b-strl.c shows libsm versions faster
- SM_CONF_SYS_CDEFS_H
-
When porting, if the /usr/include/sys/cdefs.h
file exists, and if that file defines _ _P, you
should define this compile-time macro:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_CONF_SYS_CDEFS_H=1')
If you misdefine SM_CONF_SYS_CDEFS_H, you will see warnings, when
building, about _ _P being defined multiple times.
- SM_CONF_SYSEXITS_H
-
When porting, if the /usr/include/sysexits.h
file exists and defines the various EX_ macros
differently than the include/sm/sysexits.h file
does, define this compile-time macro:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_CONF_SYSEXITS_H=1')
- SM_CONF_UID_GID
-
When porting, if the file
/usr/include/sys/types.h file does not define
uid_t and gid_t, define this
compile-time macro as zero:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_CONF_UID_GID=0')
- SM_HEAP_CHECK
-
When porting or tuning, you might find it desirable to turn on
memory-leak detection by defining this compile-time macro:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_HEAP_CHECK=1')
See SM_HEAP_CHECK for a full description of this
compile-time macro.
- SM_IO_MIN_BUF, SM_IO_MAX_BUF, and SM_IO_MAX_BUF_FILE
-
The stat(3) C-language library routine returns a
structure containing the variable st_blksize. That
variable contains as its value the optimum block size to use for disk
I/O.
When porting, if that variable fails to contain a useful value, you
can define three compile-time macros as a substitute. The
SM_IO_MIN_BUF macro defines the minimum disk I/O size:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_IO_MIN_BUF=512')
The SM_IO_MAX_BUF macro defines the maximum disk I/O size:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_IO_MAX_BUF=4096')
The SM_IO_MAX_BUF macro defines the maximum file I/O size:
APPENDDEF(`confENVDEF', `-DSM_IO_MAX_BUF_FILE=2048')
To see if any of these compile-time macros are defined with your
sendmail binary, use the
-d0.12 debugging command-line switch.