9.5 Example: Generating an XML Invoice from Oracle
Like HTML, XML is stored in plain ASCII documents. Consequently, we can use the PL/SQL toolkit to generate almost any XML document. In this section we'll write a package called XML_INVOICE_PKG to generate the XML invoice we've been discussing.
9.5.1 Specification
We'll start, as always, with the package specification. For this particular application, we'll need just one procedure: print_invoice. The procedure will accept the invoice number for a particular invoice and generate the corresponding XML invoice. Here's the code:
/* Formatted by PL/Formatter v.1.1.13 */
CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE xml_invoice_pkg
IS
PROCEDURE print_invoice (
i_invoice_number IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL
);
END;
9.5.2 Body
The next step is to define the package body, as follows:
/* Formatted by PL/Formatter v.1.1.13 */ CREATE OR REPLACE PACKAGE BODY xml_invoice_pkg IS -- Include code annotated below END;
In addition to the print_invoice procedure defined in the specification, we'll need a private function, get_attribute, and two private procedures, print_xml_tags and print_items. The first two items are needed to format the output to the XML specification, since the PL/SQL toolkit doesn't have functions or procedures specifically for XML. The other local procedure fetches the invoice items from the database and prints them to the web browser. Table 9.2 lists the procedures and functions required in the package body.
|
Procedure/Function |
Parameters |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
attr_name IN VARCHAR2 attr_val IN VARCHAR2 |
Private function that returns a well-formed attribute tag:
|
|
|
tag_name IN VARCHAR2 tag_value IN VARCHAR2 tag_attr IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL |
Private procedure that prints a well-formed XML tag:
|
|
|
i_invoice_id IN NUMBER o_invoice_total OUT NUMBER |
Private procedure to print the individual items on the invoice. The OUT parameter returns the total dollar value for all items. |
|
|
i_invoice_number IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL |
Public procedure, called from the Web, that generates the XML invoice. |
The get_attribute function accepts an attribute and a value. It formats this information to the XML specification (
attr_name
=
"attr_val"
) and returns a string. Here's the function:
/* || Function to return an attribute tag */ FUNCTION get_attribute ( attr_name IN VARCHAR2, attr_val IN VARCHAR2 ) RETURN VARCHAR2 IS BEGIN RETURN attr_name || '=' || '"' || attr_val || '"'; END;
The print_xml_tag procedure has a similar purpose. It accepts a tag name, a tag value, and an optional string for tag attributes. The procedure then formats these parameters into a well-formed XML element. The HTP.PRINT procedure sends this element back to the browser. Here's the procedure:
/*
|| Simple wrapper procedure to print a tag
*/
PROCEDURE print_xml_tag (
tag_name IN VARCHAR2,
tag_value IN VARCHAR2,
tag_attr IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL
)
IS
xml_str VARCHAR2(5000);
BEGIN
IF tag_attr IS NULL
THEN
xml_str := '<' || tag_name || '>';
ELSE
xml_str := '<' || tag_name || ' ' || tag_attr || ' >';
END IF;
xml_str := xml_str || tag_value;
xml_str := xml_str || '</' || tag_name || '>';
HTP.print (xml_str);
END;
The last local procedure, print_items, uses the previous function and procedure to generate the
<INVOICE_ITEMS>
section of the XML invoice. Like the other HTML procedures we've seen, it simply opens a cursor, loops, and prints each row by calling print_xml_tag. In addition, the procedure uses an OUT parameter to keep a running total of the dollar amount of each item. The value is passed back to the caller when the procedure completes. Here's the code:
/*
|| Print the items for the selected invoice. Return
|| the total of the invoice item using an OUT parameter.
*/
PROCEDURE print_items (
i_invoice_id IN NUMBER,
o_invoice_total OUT NUMBER
)
IS
CURSOR item_cur
IS
SELECT p.part_num, p.part_name, i.quantity, i.unit_cost
FROM xml_invoice_items i, xml_parts p
WHERE i.part_id = p.part_id
AND i.invoice_id = i_invoice_id;
item_rec item_cur%ROWTYPE;
part_num_attr VARCHAR2(500);
BEGIN
o_invoice_total := 0;
OPEN item_cur;
HTP.print ('<INVOICE_ITEMS>');
LOOP
FETCH item_cur INTO item_rec;
EXIT WHEN item_cur%notfound;
-- Accumulate costs
o_invoice_total :=
o_invoice_total +
item_rec.quantity * item_rec.unit_cost;
-- Generate XML tags
HTP.print ('<ITEM>');
part_num_attr :=
get_attribute ('ITEM_NUM', item_rec.part_num);
print_xml_tag (
'ITEM_NAME',
item_rec.part_name,
part_num_attr
);
print_xml_tag ('QUANTITY', item_rec.quantity);
print_xml_tag ('PRICE', item_rec.unit_cost);
HTP.print ('</ITEM>');
END LOOP;
CLOSE item_cur;
HTP.print ('</INVOICE_ITEMS>');
END;
The main public procedure, print_invoice, uses the local procedure to actually create the invoice. Here is the implementation:
/*
|| Main procedure to print the invoice.
*/
PROCEDURE print_invoice (
i_invoice_number IN VARCHAR2 DEFAULT NULL
)
IS
CURSOR inv_cur
IS
SELECT i.invoice_id, i.invoice_date, c.customer_name
FROM xml_invoice i, xml_customers c
WHERE i.customer_id = c.customer_id
AND i.invoice_number = i_invoice_number;
inv_rec inv_cur%ROWTYPE;
inv_total NUMBER DEFAULT 0;
BEGIN
-- Set MIME type to XML
OWA_UTIL.mime_header('text/xml', TRUE);
inv_total := 0;
OPEN inv_cur;
HTP.print ('<?xml version="1.0"?>');
-- Note: the DTD is defined in a file stored on server
-- The URL has been omitted for space
HTP.print ('<!DOCTYPE INVOICE SYSTEM "invoice.dtd">');
HTP.print ('<INVOICE>');
FETCH inv_cur INTO inv_rec;
IF NOT inv_cur%notfound
THEN
print_xml_tag ('INVOICE_NUMBER', i_invoice_number);
print_xml_tag ('DATE', inv_rec.invoice_date);
print_xml_tag ('CUSTOMER', inv_rec.customer_name);
print_items (inv_rec.invoice_id, inv_total);
print_xml_tag ('TOTAL', inv_total);
END IF;
CLOSE inv_cur;
HTP.print ('</INVOICE>');
END;
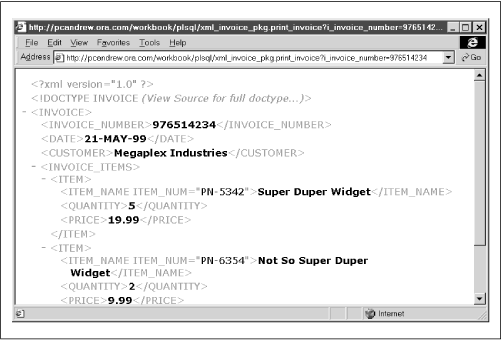
Figure 9.3 shows the XML output of the procedure.
NOTE: You must use an XML-compliant browser such as Microsoft Internet Explorer version 5 to view XML documents.
Figure 9.3: Output of XML_INVOICE_PKG.print_invoice
The XML_INVOICE_PKG is a very simple example of how to link XML and Oracle. In the next section, we'll look at a set of packages that really illustrate XML's potential.
Copyright (c) 2000 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.