23. Managing Code in the Database
Contents:
Executing Stored Code
Transaction Integrity and Execute Authority
Module Validation and Dependency Management
Remote Procedure Calls
Managing Stored Objects with SQL*Plus
Using SQL to Examine Stored Objects
Encrypting Stored Code
You will either embed PL/SQL programs in your client-side application, as happens in the Oracle Developer/2000 tools, or you will store your code in the Oracle database.
The term stored procedure commonly refers to code that is stored in the database. Along with procedures, you can also store functions and packages, which can contain variables, cursors, record structures, etc. Whenever you hear the term stored procedures, you should think "stored objects."
There are a number of benefits to storing an object in the database:
-
The database manages dependencies between your stored objects. For example, if a stored function relies on a certain table and that table's structure is changed, the status of that function is automatically set to INVALID and recompilation takes place, again automatically, when someone tries to execute that function.
-
Any session with EXECUTE authority can execute the stored object. Whether you are in an Oracle Forms application, a database trigger, or a batch process, that stored object is accessible as long as the database is accessible. The compiled code for the object is made available from the shared memory of the database instance.
-
You can execute a module stored in another (remote) database. This is known as a remote procedure call, or RPC. The ability to execute code on a different database means that you do not have to distribute application code to multiple databases in order to support distributed applications.
-
Stored modules offer transaction-level security, which goes well beyond the table- and column-level data and referential integrity offered by the database. With a stored module you can make sure that transactions involving multiple tables and different steps are always performed properly. This was actually one of the original motivations for the development of the PL/SQL language.
-
Execution of a stored object shifts CPU load to the server. Rather than run your code locally in a form or report, the stored object executes on the database server. Assuming that the server is sized to handle the load, this shift could improve overall application performance. This feature could be less of a benefit, of course, if the server is already heavily burdened.
Stored objects play an important role in today's client-server applications. The information in this chapter will help you make the best possible use of stored objects.
23.1 Executing Stored Code
To execute a stored program unit, you must first store this program in the database. I'll explain this CREATE OR REPLACE step later in this chapter. For now, let's take a look at what happens when you run a stored PL/SQL program.
23.1.1 Executing Procedures
If you are working in SQL*Plus, you can execute programs directly from the command line. Use the EXECUTE command to run procedures as follows:
SQL> execute calc_totals
Notice that you do not have to provide a semicolon. In fact, if you are going to use the EXECUTE command, the entire PL/SQL procedure call must fit on one physical line. As soon as you press the Enter key, the program executes.
You can also save a few microseconds (but accumulated over a whole year...) by providing only the minimum number of characters for the EXECUTE command:
SQL> exec calc_totals
When you are executing a procedure within a PL/SQL block, you do not use the EXECUTE syntax. You simply call the procedure, passing all necessary parameters within parentheses, and then terminate the line of code with a semicolon. Here is the syntax for calling the calc_totals procedure within a PL/SQL block:
BEGIN calc_totals; END;
You can also execute PL/SQL procedures in various "front-end" tools, such as Oracle Forms, PowerBuilder, and many 3GL languages like C and COBOL. The syntax for calling procedures (and functions) will vary from tool to tool. Within the Oracle Developer/2000 environment, you can call stored programs from within a "native," albeit outdated, version of PL/SQL (see Appendix B, Calling Stored Procedures from PL/SQL Version 1.1 , for more information). From a language like C, you will actually use a precompiler called Pro*C (from Oracle) and embed calls to PL/SQL programs within a SQL execution block like this:
EXEC SQL EXECUTE
BEGIN
calc_totals;
END;
END-EXEC;
23.1.2 Executing Functions
The situation with functions is a little bit different. A function returns a value, so you can't just execute it directly. If you try to run a function as if it is a procedure, you will get the following error:
SQL> exec total_sales (1997) begin total_sales (1997); end; * ERROR at line 1: ORA-06550: line 1, column 7: PLS-00221: 'TOTAL_SALES' is not a procedure or is undefined ORA-06550: line 1, column 7: PL/SQL: Statement ignored
If you want to run a function simply to view its return value, you can execute it within a call to DBMS_OUTPUT. PUT_LINE as follows:
SQL> exec DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE (total_sales (1997))
Of course, this only works if the datatype of the return value of the function matches one of the datatypes supported by DBMS_OUTPUT: number, string and date. For anything else, you will need to execute the function within an anonymous block and then convert the value as necessary for display. In the following example, I declare a PL/SQL table of strings to retrieve the value from a function that returns all the foreign key information for a table. I then use a FOR loop to display that information:
/* Employs PL/SQL 2.3 syntax for PL/SQL tables. */
DECLARE
TYPE strtabtype IS TABLE OF VARCHAR2(100) INDEX BY BINARY_INTEGER;
strtab strtabtype;
BEGIN
strtab := primary_keys.for_table (`emp');
IF strtab.COUNT > 0
THEN
FOR tabrow IN strtab.FIRST .. strtab.LAST
LOOP
DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE (strtab.column_name);
END LOOP;
END IF;
END;
/
If I have saved this block in a file called myscript.sql, I can then execute this program and verify my function's behavior as follows:
SQL> @myscript
NOTE: You might wonder why I placed my FOR loop inside an IF statement. Surely, if there were no rows, the strtab.FIRST method would return NULL and the loop would not execute. Yes and no. The FIRST and LAST methods do return NULL if the PL/SQL table is empty, but oddly enough, if your numeric FOR loop range evaluates to:
FOR tabrow IN NULL .. NULLthen the PL/SQL runtime engine does enter the loop and try to process the body contents immediately. Then it raises an ORA-06502 VALUE_ERROR exception. So you really want to put some conditional logic around those FOR loops if you think the range endpoints might evaluate to NULL.1
Now that you've seen how to execute programs "from the outside," let's move inside and take a look at the architecture Oracle employs to deliver that code to you for execution.
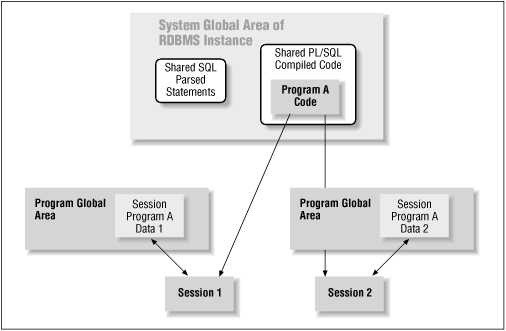
23.1.3 Memory-Based Architecture of PL/SQL Code
Whenever you start up an Oracle instance, a chunk (usually a rather large chunk) of memory is set aside for the System Global Area or SGA. Various Oracle processes manage this area of memory to do any of the following and more:
-
Retrieve data from the database and deliver it to user processes (a PL/SQL procedure executing an explicit cursor, an Oracle Forms application querying records through a base table block, an Internet HTML page utilizing the Oracle WebServer interface, and so on).
-
Change data and then manage the transaction processing (commits and rollbacks) based on those changes.
-
Provide access to PL/SQL programs for execution in the server itself.
-
Transfer information between Oracle sessions using database pipes and database alerts.
When you use a stored program element (by executing a procedure or function or by making reference to a nonexecutable part of a package like a constant or cursor), it must be accessible from the SGA. So when you reference a program element, its compiled version is loaded into the SGA's shared pool, if it is not already present. Then any program data associated with that element is instantiated in your Program Global Area (PGA). At that point, the code can be executed or otherwise used in your session.
The next time a session with execute authority on that program element references it, it will already have been loaded and will therefore be available for execution.
When the SGA shared pool area fills up, code in the pool will be aged out (that is, room will be made for newly requested programs) on a least-recently-used basis. Programs which are used often will therefore most likely be available immediately upon request. You can also pin programs into shared memory if you want to make certain that they will not be aged out. See Chapter 25, Tuning PL/SQL Applications , for more details on pinning.
Note that even if your compiled code is aged out of the SGA, any persistent, package-based data will remain available in your PGA. In other words, code may be swapped out of the SGA, but program data remains and persists for the duration of your session (or until you explicitly request a reinitialization of your schema).
Figure 23.1 illustrates a number of the points covered in this section.
Figure 23.1: The System Global Area and Program Global Area
23.1.4 Key Concepts for Program Execution
Here are some basic principles to remember about program execution:
-
Compiled PL/SQL code is shared among all users with EXECUTE authority on that code. Usually you will set up your environment so that one account or schema owns all the code for an application. You then grant EXECUTE authority to other users on that code. When any of those schemas runs this code, they are working with the same compiled code. Again, the data instantiated and manipulated within those programs is specific to each connection.
-
When you reference any individual element in a package, the entire package is loaded into shared memory. This can be both an advantage and a disadvantage. If you group together (in a package) functionality which is usually executed in "close proximity," then you are more likely to find the program you need in shared memory. This will speed up the completion of your program.
On the other hand, suppose that you build some very large packages which contain programs covering a disparate range of functionality. My application needs just one function out of the 100 procedures, functions, and cursors defined. Too bad! My SGA and my PGA must absorb the full punishment of the package (both the room needed for the shared, compiled code and all the package data instantiated in my PGA).
-
Program data instantiated within a program is stored in PGA for each user, rather than in the SGA. This means that each user has his own copy of program data. If a procedure declares a PL/SQL table and stuffs it full of 1000 strings, every user who executes that procedure has his own copy of that table and its 1000 strings. The nice thing about this characteristic is that gives you a fair amount of flexibility in finding the delicate balance between those ever-competing resources: CPU and memory.
NOTE: The architecture in the multi-threaded server (MTS) is a bit different, but the principle is the same: different users have their own copies of their program data.
-
Stored code runs under the authority of that code's owner, not that of the schema which is executing the code. Suppose that you have stored all the code for your order entry application in the SYSTEM account (a very bad idea, as this example will illustrate). You then grant EXECUTE authority on that code to SCOTT, the traditional Oracle demonstration account, which has very little power outside of doing whatever it wants with the emp and dept tables.
Now suppose further that the delall procedure of the ordent package allows you to delete all orders from the application table. The intention is that only administrators will have the ability to do that. In fact, the only account that can delete from the orders table at all is SYSTEM. Once you have granted EXECUTE authority on ordent to SCOTT, however, all heck can very decidedly break loose. For when a user logged in as SCOTT executes the ordent.delall procedure, that user is, for that moment, acting as though she were connected to SYSTEM. All rows are removed from the orders table!
You must, consequently, very careful about (a) the authority of the schema owning your shared application code, and (b) to whom you grant EXECUTE authority on that code.
-
Even though stored code runs under the authority of that code's owner, the USER function still returns the name of the schema currently connected to Oracle. The USER function does not, in other words, return the name of the schema which owns the code in which the USER function was called.
Copyright (c) 2000 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.