13.3. Graphing Other Objects
MRTG polls and graphs the MIB variables ifInOctets and ifOutOctets by default, but it is possible to poll and graph the values of other objects, in addition to polling different kinds of devices. Let's first get MRTG collecting input and output octets from a server. To do this, run the following command:This is almost identical to the command we ran earlier in the chapter, except for the community string and target[71] (public@linuxserver). We appended the output to the mrtg.cfg file, as opposed to specifying an output file with the - -output option; this lets us add a new host to the existing configuration file, rather than starting a new file. Because the existing file already specifies a working directory, we also omitted the working directory option (- -global 'WorkDir: .. ' ). This cfgmaker command adds a number of lines like the following to the configuration file:[root][linuxserver] ~/mrtg-2.9.10> cfgmaker public@linuxserver >> \ /mrtg2/run/mrtg.cfg
[71]Make sure that your target is running an SNMP agent. See Chapter 7, "Configuring SNMP Agents" for a discussion of how to configure several SNMP agents for Unix and Windows NT.
Target[linuxserver]: 2:public@localhost
MaxBytes[linuxserver]: 1250000
Title[linuxserver]: linuxserver(linuxserver): eth0
PageTop[linuxserver]: <H1>Traffic Analysis for eth0
</H1>
<TABLE>
<TR><TD>System:</TD><TD>linuxserver</TD></TR>
<TR><TD>Maintainer:</TD><TD></TD></TR>
<TR><TD>Interface:</TD><TD>eth0 (2)</TD></TR>
<TR><TD>IP:</TD><TD>linuxserver( )</TD></TR>
<TR><TD>Max Speed:</TD>
<TD>1250.0 kBytes/s (ethernetCsmacd)</TD></TR>
</TABLE>hrSystemNumUsers OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX Gauge
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"The number of user sessions for which this host is storing state
information. A session is a collection of processes requiring a
single act of user authentication and possibly subject to collective
job control."
::= { hrSystem 5 }
hrSystemProcesses OBJECT-TYPE
SYNTAX Gauge
ACCESS read-only
STATUS mandatory
DESCRIPTION
"The number of process contexts currently loaded or running on
this system."
::= { hrSystem 6 }We've highlighted the changes and additions to the configuration file in bold. The first line specifies the device we want MRTG to poll, along with the two OIDs (hrSystemNumUsers and hrSystemProcessess) we want to graph. This statement is obviously more complex than the Target statement we looked at earlier; its syntax is OID1&OID2:community_string@device. The OIDs must be separated by an ampersand character (&). Using this syntax, you can convince MRTG to graph any two scalar-valued MIB variables. In the next line, we set MaxBytes to 512. This is the maximum value for the graph; values greater than 512 are set to 512. (Forget about bytes; MaxBytes simply defines a maximum value.) For the number of users logged in, this is a high number; there should never be this many people logged onto our system at once. The same goes for the total number of processes running on the system. You can choose values that make sense for your particular environment. If you need separate maximum values for each object, replace MaxBytes with two lines setting MaxBytes1 and MaxBytes2. The Options command is a new one; it allows you to change how MRTG treats the data it gathers. The only option we have specified is gauge. This instructs MRTG to treat the gathered data as Gauge data, not Counter data. Recall that Counter data is monotonically increasing, while Gauge data is not. Since the MIB definitions for both objects specify the Gauge datatype, this option makes sense. The YLegend, LegendI, and LegendO options are also new. YLegend simply changes the label that is placed on the Y-axis of the graph itself. Since we're graphing the number of users and processes, we set the legend to Users/Processes. It's important for the legend to be short; if it's too long, MRTG silently ignores it and doesn't print anything for the label. LegendI changes the legend used below the graph for the so-called "input variable" (in this case the number of users logged into the system -- remember that MRTG expects to be graphing input and output octets). LegendO changes the legend for the "output variable" (the total number of processes running on the system). The terminology is unfortunate; just remember that MRTG always graphs a pair of objects and that the input legend always refers to the first object, while the output legend refers to the second. Once you have added this entry to your configuration file and saved it, MRTG will start gathering data from the device every time it runs. If you have added the appropriate entry in your crontab file, you're all set. Now we'll use indexmaker to create intuitive index files for the server graphs, just as we did for the router graphs. The command to create a new index file is similar to the one we used to create the Cisco index file:Target[linuxserver.users]:1.3.6.1.2.1.25.1.5.0&1.3.6.1.2.1.25.1.6.0:public@linuxserver MaxBytes[linuxserver.users]: 512 Options[linuxserver.users]: gauge Title[linuxserver.users]: linuxserver (linuxserver): Number of users and processes YLegend[linuxserver.users]: Users/Processes LegendI[linuxserver.users]: Users: LegendO[linuxserver.users]: Processes: PageTop[linuxserver.users]: <H1>Number of users and processes</H1> <TABLE> <TR><TD>System:</TD><TD>linuxserver<TD></TR> <TR><TD>Maintainer:</TD><TD></TD></TR> <TR><TD>IP:</TD><TD>linuxserver( )</TD></TR> </TABLE>
Figure 13-3 shows the index page for the server graphs. It contains only two graphs: one shows traffic on the Ethernet interface and the other shows the number of running processes versus the number of users logged onto the system.[root][linuxserver] ~/mrtg-2.9.10> indexmaker --title "Linux Server" \ --filter name=~'linuxserver' --output /mrtg/images/linux.html /mrtg/run/mrtg.cfg
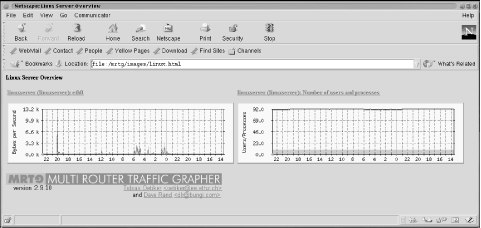
Figure 13-3. Linux Server overview graphs
Figure 13-4 shows the daily, weekly, monthly, and yearly graphs for the number of users and processes logged into the system.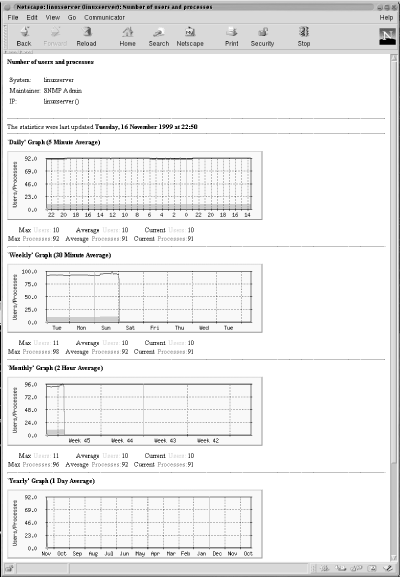
Figure 13-4. Daily, monthly, weekly, and yearly graphs for number of users and processes

Copyright © 2002 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.