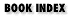15.4. The GNOME Control Center
The GNOME Control Center (Figure 15-4) is where most customization and configuration of your desktop environment takes place. Open the Control Center using the toolbox button on the panel, or from Utilities on the main menu. The Control Center contains a number of configuration applications, called capplets, that allow you to change various GNOME settings. The capplets are listed in the left pane of the Control Center window, and clicking on a name opens the capplet in the right pane.
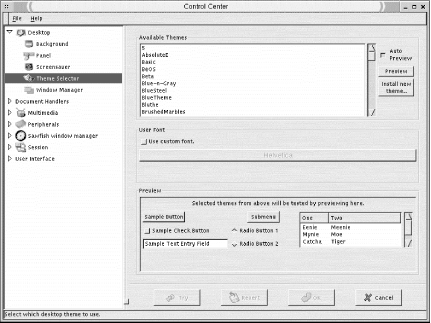
Figure 15-4. GNOME Control Center
15.4.1. Desktop Settings
These sections provide settings for the overall look of your desktop by letting you choose the background, screensaver, theme, and window manager.
15.4.1.1. Background
Here's where you set your desktop background. You can choose to use an image for wallpaper or colors. In the wallpaper section, click the Browse button to select an image file from the filesystem. You can choose to have the image tiled on the background, centered, or scaled. In the color section, select to use either a solid, single color, or a horizontal or vertical gradient of two colors. Click the boxes for primary color and secondary color to pick the color.
This capplet sets the background via GNOME. Window managers also can set the background and can sometimes conflict with the GNOME setting. To ensure that GNOME sets the background, check the box labeled Use GNOME to Set Background at the bottom of the window.
15.4.1.2. Screensaver
Contains settings for the screensaver. You can choose from a list of available screensavers (including a random setting). Input the number of minutes of inactivity before the screensaver starts and whether you, the user, will be required to give your password before going back to the desktop. Power management settings are available here if your system is configured for them.
15.4.1.3. Theme selector
Themes provide a consistent overall style to the many widgets and components used by GNOME. A number of basic themes are included with the gtk-engines package, and you can download and install additional themes from http://gtk.themes.org.
Anythemes that are installed on your system are listed in the Theme Selector. You can select one and preview it in the lower section of the window. If you click Auto Preview, a theme will preview automatically when you click on it. Otherwise, click the Preview button to see how it looks.
If you have downloaded a theme and wish to install it, click the Install New Theme button. Provide the name and location of the .tar.gz or .tgz file and click OK. The new theme will be installed in the /usr/share/themes directory and be available for you to use on your desktop.
15.4.1.4. Window manager
This section allows you to select the window manager that GNOME will use and configure its properties if it has a configuration tool. By default, GNOME runs with the Enlightenment window manager. Other window managers may be used, but make sure that they are compliant with the GNOME architecture so as not to create problems for your applications.
The listing shows installed window managers that you can use. You can add a new window manager to the list by clicking the Add button. Type the window manager's name in the dialog box. If it has its own configuration tool, supply the tool name and location, too. A button underneath the list will be enabled stating Run the Configuration Tool for wm-name. Clicking this button will open the configuration application for that window manager.
15.4.2. Panel
Panels can be configured individually or globally. For individual configuration, right-click on the panel and select This Panel's Properties.
Most of the panel settings are made in the global panel configuration tool shown in Figure 15-5. To open this tool, select Global Preferences from the Panel menu.
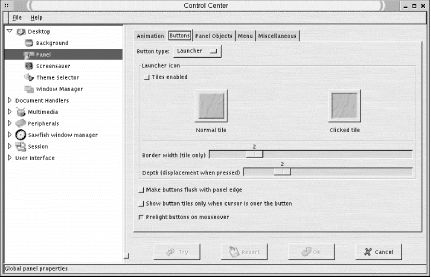
Figure 15-5. Panel configuration settings
The global panel configuration section of the Control Center opens. It contains the following sections:
15.4.2.1. Animation
This tab controls the animated movements of the panel, such as when the panel is hidden or a drawer is opened. At the top of the tab is a radio button to enable or disable animation entirely. The rest of the settings are done with slider bars. The first two sliders to determine how fast or slow the panel will collapse when it minimizes under autohide and when you explicitly hide the panel with the arrow buttons. The next slider sets the speed of the opening and closing of drawers. For autohide panels, there are additional sliders for the amount of time before the panel minimizes and the size (in pixels) of the hidden panel.
15.4.2.2. Buttons
This tab controls the look of the various types of buttons on a panel (See Figure 15-5). Select which type of button you want to configure from the drop-down box.
Tiles provide a square background for a panel icon instead of the icon being displayed directly on the panel background. If you enable tiles (using the radio button at the top), you can select an image to use for the background of all buttons on the menu. Tiles also are used to create 3D-style buttons on the panel. You can choose the images for the up position and the down position (i.e., on a mouse-down). To select the image files, click the tile images, and the image file selection dialog opens for you to choose from.
Two slider controls allow you to set the number of pixels used for the border width around tiles and the depth of the icon when pressed.
The following additional settings are available:
- Make buttons flush with panel edge
This setting causes buttons to be placed at the edges of the panel. There is no visible space between the button and the desktop background, although there is still spacing between panel buttons.
- Show button tiles only when cursor is over them
This setting causes tiles to be unseen until the mouse pointer is over the button.
- Prelight buttons on mouse-over
This setting causes buttons to "light up" when the pointer is over them.
15.4.2.3. Panel objects
This tab allows you to select among three methods of icon placement: Switched Movement makes icons switch places with the icon you are moving. This is the default behavior. Free Movement locks the current icons in place as you move another icon. Icons can be moved only to empty areas of the panel when this method is selected. Push Movement causes moving icons to push the others around but not move over them.
The Padding slider sets the amount of space (in pixels) separating objects on the panel.
15.4.2.4. Menu
This tab contains the global menu settings.
The first radio button enables large icons to be used for each menu item, indicating whether it is a folder, file, or application.
The second radio button, Show ... Buttons, toggles the cascading display of submenus off and on. If this button is selected, buttons containing ... are displayed for each menu item that contains a submenu. The submenu is displayed only when you press the ... button. Automatic display of cascading menus is used if this button is not selected.
The Show Pop-Up Menus Outside of Panels button controls the relative placement of pop-up menus to the panel. If this is enabled, pop-up menus are displayed on the desktop so that they don't overlap the panel. The Keep Menus in Memory button allows you to cache recently opened menus in memory, providing faster response from your desktop environment.
The remainder of this tab configures which sections of the menu you want to display. You have a choice of placing the sections directly on the main menu, placing them in a submenu, or not showing the sections.
15.4.2.5. Miscellaneous
The Miscellaneous tab provides a number of panel configuration settings:
- Tooltips enabled
Enables tooltips to be displayed for launcher icons.
- Close drawer if launcher inside it is pressed
Causes a drawer to close after one of its items is selected. Otherwise, it will remain open until you click on its closing arrow.
- Raise panels on mouse-over
Causes the panel to come to the foreground on mouse-over if it is covered by another window.
- Keep panel below windows
Allows GNOME-compliant applications to display over the panel (normally they would not cover the panel).
- Confirm the removal of panels with a dialog
A pop-up window will ask you if you really want to remove a panel.
15.4.3. Document Handlers
This section configures the default programs used to run specific files based on their content type or URL.
15.4.3.1. Default editor
This section sets the text editor to be used by default when you open an editable file or choose the Edit menu command on a file within the file manager. A drop-down list of available editors is displayed. Click the Run in Terminal Window button if your chosen editor must be run in a terminal.
15.4.3.2. Mime types
This section allows you to set or edit mime types. Click the Add button to add a new type. A dialog will open asking for the category/type listing for the mime type and the extensions to associate with it. Optionally, you can supply up to two regular expressions to identify the mime type. To edit a mime type, select it in the listing and click the Edit button. You will see a dialog box in which you can choose an icon to be used for the file type, add or remove file extensions, and supply commands that will open, view, and edit this type of file. To delete a type, select it from the list and click the Delete button.
15.4.3.3. URL handlers
This page allows you to adjust the settings for special URL launchers used by the GNOME help system. The defaults for protocols such as HTTP, FTP, and Mail are already set and likely handled by your default web browser (for example, Netscape). The special URLs are ghelp, info, and man, corresponding to GNOME help files, command info files, and man files. The defaults use the help browser for these types of files. It is best to leave these settings as they are.
15.4.4. Multimedia
This section adjusts the settings for system sounds.
15.4.4.1. Sound
This page sets up a sound scheme for various actions. You can enable or disable all sounds on the General tab. The Sound Events tab displays a listing of available events and the sound files used for them. Select an event from the listing and click Play to hear its assigned sound. Use the textbox to input the name of the sound file to assign to an action, or use the Browse button to locate a sound file on the filesystem.
15.4.5. Peripherals
This section provides configuration settings for the keyboard and mouse.
15.4.5.1. Keyboard
Contains settings for keyboard autorepeat and sounds. You can set the repeat rate of a pressed key and the delay before it starts. You also can enable keyboard clicks and their volume. Settings can be previewed by typing in the Test Settings textbox.
Three sliders adjust the volume, pitch, and duration of the keyboard bell. Click the Test button to hear the the bell's new settings.
15.4.6. Session
This section contains settings for programs loaded at the start of each session.
15.4.6.1. Startup hint
The Startup Hint is a program that displays a message every time you log in. Hints can provide a useful tip for a GNOME function that the user might not yet know about. You also can use this program to display a fortune or a message of the day.
15.4.6.2. Startup programs
Since GNOME is session-aware, applications that are open when you log off are remembered and reopened the next time you log in. Not all applications are compliant with the GNOME session state, however. If you would like to set up programs to automatically start at login, you can configure them here. You can add, edit, or delete startup programs and view the currently running programs.
At the top of the window, there is an option button to show the splash screen on login. Two additional buttons give you the option either to be prompted to save session changes on logout or to automatically save the changes.
15.4.7. User Interface
This section sets various properties for application window components such as menus, toolbars, status bars, and dialog boxes.
15.4.7.1. Applications
The settings available in the applications section control the behavior of menus, toolbars, and status bars for GNOME applications.
Menu bars in GNOME applications can be detached from windows and placed anywhere on the desktop. This is the default behavior.
A detachable menu will have a small bar placed on its left edge. Click on this bar and drag to move the menu bar to another part of the desktop. To redock the menu bar, drag it back to the titlebar of its application window, and it will reattach.
For unmovable menu bars, unselect the the radio button labeled Can Detach and Move Menus.
The same detachable functionality is applied to submenus by default. To disable this behavior, unselect the radio button labeled Submenus Can Be Torn Off.
Three settings allow you to display menus, toolbars, and buttons on toolbars with a relieved border. The relieved border gives a three-dimensional visual appearance to the components; otherwise, they appear very flat.
Two options are available for status bars displayed at the bottom of windows. If a progress meter is used in a status bar, you can configure it to always appear on the right side of the statusbar. If this setting is disabled, the application will determine the progress meter placement.
Some statusbars may have user functionality defined by the application. You can enable statusbar interactivity with the supplied setting.
15.4.7.2. Dialogs
This page is divided into sections for the look of dialog windows and the positioning of dialog windows.
The Dialog Layout section allows you to configure the position of dialog buttons with the following options: Default, Spread Buttons Out, Put Buttons on Edges, Left-justify Buttons, and Right-justify Buttons. You also can enable or disable icons for dialog buttons and choose to use a window's statusbar instead of a dialog, when possible.
The Dialog Behavior section allows you to set the position of dialog windows with the following options: Let Window Manager Decide, Center of the Screen, and At the Mouse Pointer. You also can configure dialog hints and enable the automatic placement of a dialog over the application window from which it was launched.
15.4.7.3. MDI
MDI (Multiple Document Interface) describes the way multiple open documents are displayed in an application window. There are three styles available: Modal, Toplevel, and Notebook. Modal is the default setting. If you choose the Notebook style, you can set the document tab position to either left, right, top, or bottom.
15.4.8. Sawfish Window Manager Configuration
The Sawfish window manager is the default window manager used by the Helix GNOME Desktop used in the figures in this chapter. Sawfish is GNOME-compliant, working well not to overlap the GNOME desktop settings. The Helix version of the GNOME Control Center integrates the Sawfish configuration settings instead of using a separate configuration tool. The Sawfish section of the Control Center is shown in Figure 15-6.
Figure 15-6. Sawfish configuration settings
The following sections describe the Sawfish configuration settings contained in the Helix GNOME Control Center.
15.4.8.1. Appearance
This section sets the default appearance of windows, including the style of the window frame, fonts, and movement style.
The drop-down box contains a list of frame styles. The frame style determines how the titlebars of windows are displayed by customizing the buttons and background of the title.
Some pop-up windows are configured to be displayed without the window titlebar. To force the display of the title bar for all windows, click the button labeled Decorate Transient Windows Similarly to Top-level Windows.
The default window animation mode determines the display of windows when they are being minimized. You can choose from solid or wireframe modes or None for no animation.
The font button allows you to select the default desktop font. The default font is set by the GNOME desktop theme and Sawfish is aware of the setting so that they match.
15.4.8.2. Focus behavior
This section contains settings that determine how windows receive the input focus.
The selection box at the top determines how the mouse pointer sets focus. The default is to focus when the mouse clicks on the window. The other choices are to focus only when the pointer is in the window ("enter-exit") and focus stays with the last window entered ("enter-only").
Three checkboxes are used to enable the following focus policies: focus each window when first displayed, transient windows inherit focus from their parent, and raise windows when they are focused. You can set the delay (in milliseconds) between focus and the time the window is raised (brought to the foreground).
The advanced section contains the following additional settings:
Give focus to windows even when they haven't asked for it.
Offset from left window edge when warping.
Offset from top window edge when warping.
Does click-to-focus mode pass the click through to the window?
The Shade Hover section contains settings for the behavior of shaded windows. A shaded window is effectively rolled up, like a window shade, into its titlebar, usually by double-clicking on the titlebar. If you check the button to enable shade hover, a shaded window will temporarily unshade when the mouse pointer is placed on its titlebar. The next box allows you to select the delay (in milliseconds) before unshading occurs. The final setting in this section enables windows to be raised automatically when they are unshaded.
15.4.8.3. Minimizing and maximizing
This window contains settings for minimizing and maximizing windows. The settings for minimizing windows are as follows:
- Windows are uniconified onto the current workspace
Minimized windows are opened on the current desktop workspace when they are clicked in the tasklist. You will usually have only one workspace in GNOME, which is divided into a grid of separate screens called viewports.
- Windows are raised after being uniconified
Minimized windows are opened in the foreground when they are clicked in the tasklist.
- Windows are focused after being uniconified
Minimized windows receive keyboard focus when they are clicked in the tasklist.
- Iconifying a window that's a member of a group removes the whole group
If you minimize a window that is part of a group (e.g., an application may spawn several child windows from the main window), the whole group of windows will be minimized.
- Uniconifying a window that's a member of a group restarts the whole group
In conjunction with the previous setting, a minimized window group will reopen if one of its members is raised.
- Windows are uniconified to the current viewport
Minimized windows will reopen in the current screen, regardless of where they were before. In Sawfish, each screen of a desktop is referred to as a viewport.
The settings for maximizing windows are as follows:
- Maximizing a window dimension always increases the size of that dimension
A window maximized vertically or horizontally will increase to that size even if it fills the screen.
- Raise windows when they're maximized
Maximized windows automatically come to the foreground and receive focus.
- Let ignored windows be overlapped when filling windows
If a window is set to be ignored (via the window menu), it will be overlapped by a fill command.
- Lock window geometry while the window is maximized
No resizing of a window can occur if it is maximized.
15.4.8.4. Miscellaneous
This section contains some miscellaneous window settings, including settings for the display of tooltips.
- Windows selected (normally by the Windows menu) are raised
A selected window, either by keyboard shortcut or the desktop window menu, will be raised with focus.
- Unshade selected windows
If a shaded window is selected, it will automatically unshade.
- Warp the mouse pointer to selected windows
The pointer is automatically moved to a selected window.
- Keep transient windows stacked above
This listbox selects how transient windows are placed. Choose from None, Parents, or All.
- Update all windows when the default frame style is changed
If you change the window frame style, all windows will be automatically updated.
- Automatically reload themes when they are updated
If a theme is edited, the changes are made immediately.
- Group transient windows with their parents
Transient windows such as dialogs are automatically placed in the window group of their parents.
- Raise windows when they are unshaded
Windows receive focus and come to the top when unshaded.
To enable window manager tooltips, click the button labeled Display Tooltips for Window Frames.
Tooltips will be displayed until the pointer leaves the item. You can set them to automatically disappear by enabling Remove Tooltips After a Period of Time. The amount of time before displaying and before removing tooltips is set by two input boxes.
You also can set the font used in tooltips, as well as the background and foreground colors.
15.4.8.5. Moving and resizing
The method for drawing windows when they are being moved can be set to opaque or box. The same options are available for the drawing of windows being resized.
You also can toggle the following settings:
Raise windows being moved or resized interactively.
Show the current position while moving windows interactively.
Show the current dimensions while resizing windows interactively.
15.4.8.6. Placement
This section contains settings for the default placement of new windows. There are placement policy options for both normal windows and transient windows. Each setting contains a listbox with the following options:
Randomly (transient default)
Interactively
Centered
Centered-on-parent
Under-pointer
None
First-fit
Best-fit (window default)
First-fit-or-interactive
If you don't want to allow applications any control over placement, check the box Ignore Program-specific Window Positions. This setting is disabled by default.
For a first-fit or best-fit policy, you can set an amount of space in pixels to leave between window edges.
15.4.8.7. Workspaces
Sawfish manages the desktop work area by creating workspaces that can be divided into a number of different viewable screens, referred to by the GNOME Desk Guide applet as viewports. Workspaces can be thought of as desktops stacked on top of one another. Viewports are configured by a grid of rows and columns.
The first option in this window sets the number of workspaces. To define the grid of viewports, select the numbers of columns and rows you want each workspace divided into from the available settings.
By default, transient (pop-up) windows will be opened in the same workspace as the window that spawned them.
The Advanced section contains settings for moving between workspaces. When moving through workspaces or moving a window, choose the following options for movement at the ends of workspaces: stop, wrap around, or keep going.
The easiest way to move among viewports is by using the Desk Guide applet in the GNOME panel. If you would like to move through screens when moving the pointer on the screen, you can enable edge flipping. Two checkbox options set up edge flipping:
Flip to next viewport/workspace when pointer hits screen edge.
Flip only when interactively moving a window.
You can specify whether edge flipping takes you to the next viewport (the default) or the next workspace. If you want to set a delay for edge flipping when the pointer hits the screen edge, input a number in milliseconds.
15.4.9. Configuring the Enlightenment Window Manager
The Enlightenment window manager is the most common window manager used with GNOME. Configuring the window manager allows you to adjust the most general behavior of the desktop, such as mouse behavior, window placement, border styles, and the number of virtual desktops. You can access the Enlightenment configuration editor from the GNOME Control Center. Go to the window manager page, select Enlightenment from the list, and click the Run Configuration Tool for Enlightenment button. This opens the configuration window shown in Figure 15-7. The Enlightenment configuration tool is composed of the following sections:
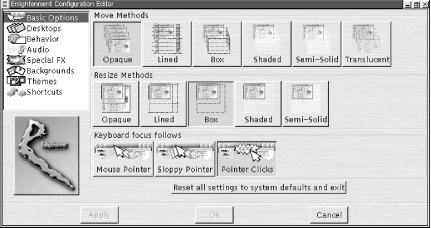
Figure 15-7. Enlightenment configuration tool
15.4.9.1. Basic options
The options on this page set styles of window movement and window focus.
- Move methods
These buttons select how the window is drawn when it is moved. The following styles are available: Opaque, Lined, Box, Shaded, Semi-Solid, and Translucent.
- Resize methods
These buttons select how the window is drawn when it is resized. The following styles are available: Opaque, Lined, Box, Shaded, and Semi-Solid.
- Keyboard focus follows
These buttons determine how "focus" is selected by the actions of the mouse. The available settings are Mouse Pointer (focus follows mouse), Sloppy Pointer (focus follows mouse after a delay), and Pointer Clicks (focus is given to window on which a mouse clicks).
15.4.9.2. Desktops
This section configures your desktop space. You can create a number of virtual desktops, each using its own screen and switch from one to another as needed. Two sliders allow you to create the column and row grid of a virtual desktop. Enabling Edge Flip will cause you to move to the adjacent desktop when the pointer moves across the edge of the current screen. The delay for the edge flip can be set in milliseconds. The Separate Desktops setting allows you to set a number of layered desktops (instead of multiscreen panes). Note that the GNOME Desk Guide applet does not support layered desktops.
15.4.9.3. Behavior
This section contains options for setting additional keyboard focus properties on new windows and miscellaneous options such as tooltips and placement of pop-up windows. The Advanced Focus tab contains the following settings:
- All new windows that appear get the keyboard focus
New windows automatically receive the keyboard focus.
- All new pop-up windows get the keyboard focus
New pop-ups automatically receive the keyboard focus.
- Only new pop-up windows whose owner is focused get the keyboard focus
Only pop-ups generated by the window with the current focus receive the keyboard focus.
- Raise windows when switching focus with keyboard
Minimized windows open when receiving focus.
- Send the pointer to windows when switching focus with the keyboard
Mouse pointer moves automatically to windows that receive keyboard focus.
The Miscellaneous tab contains the following settings:
- Tooltips
Click the Enable button to allow tooltips to appear when the pointer is over an icon. You can set the amount of time in seconds for the tooltip to display with the slider control.
- Transient pop-up windows appear together with leader
Displays additional pop-up windows with the window that generated them.
- Switch to where pop-up window appears
Automatically switches to the desktop screen where a new pop-up appears.
- Display icons when windows are iconified
Displays a small icon on the screen when a window is minimized. Leave this option disabled as GNOME will handle this functionality with the panel.
- Place windows manually
When a new window is opened, the pointer is automatically switched to the activated move bar of the window. Move the window to the desired location and click to place it.
15.4.9.4. Audio
This page is used to enable sounds in Enlightenment. Sounds for specific actions can be set manually or set as a group from a theme.
15.4.9.5. Special FX
This section contains settings for the motion of desktop components, with the following options:
- Window Sliding Methods
The same window drawing options as on the Basic Options page appear here for sliding window animations, in addition to the following settings:
-- Windows slide in when they appear.
-- Windows slide about during window cleanup.
-- Desktops slide in when changing desktops.
-- Window shading speed (pixels/sec).
- Drag bar
Click the button to enable, and set the location to left, right, top, or bottom.
- Animate menus
Select this button to enable sliding menu animation.
- Reduce Refresh
Select this button to reduce the rate at which the contents of the desktop are refreshed.
15.4.9.6. Backgrounds
This section lets you set the background for each virtual desktop you have. Select the specific desktop and then choose an image file from the list of available images. You also have an option button to select No Background. To add an image to the background list, click the Add New... button and specify the file.
The High Quality Rendering for Background button enables background images to be displayed at the full resolution and color depth that your display is set to.
Background for desktops that have not recently been viewed can be removed from memory by enabling the Minutes After Which to Expunge Unviewed Backgrounds from Memory button. Set the number of minutes to keep them in memory with the slider.
Note that setting a background image in Enlightenment will override the background settings you have made with GNOME.
15.4.9.7. Themes
This section allows you to select a theme to apply to the window manager. Themes create a distinctive and consistent look for windowing components and the background. Enlightenment themes are installed in the /usr/share/enlightenment/themesdirectory. You can download any number of user-created themes from http://e.themes.org.If you use a desktop theme in GNOME, use a basic window manager theme so you don't create any unwanted conflicts in your desktop style.
15.4.9.8. Shortcuts
This section allows you to set up keyboard shortcuts for Enlightenment functions. This section displays a list of predefined shortcuts. You can edit a shortcut by selecting it in the list, choosing a key modifier, and clicking the Change... button. A pop-up will ask you to press the key button to use for the shortcut.

Copyright © 2001 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.