13.3. Generating PNGs with GD
The GD module was created and is maintained by Lincoln Stein, who is also the author of CGI.pm. GD provides a Perl port of the gd graphics library created by Thomas Boutell for the C programming language. The gd library was originally created for creating and editing GIFs. As a result of the Unisys patent issue, however, it was rewritten for PNG (incidentally, Thomas Boutell was a co-author and the editor for the PNG specification). Current versions of the gd library and the GD module no longer support GIFs, and older versions are no longer distributed. If you have an older version of these modules (for example, an older version was included with your system) that does support GIFs, you should probably contact Unisys for licensing terms and/or an attorney familiar with patent issues before using them.
13.3.1. Installation
You can install GD just like other CPAN modules, except that you should ensure that you have the latest version of gd. GD contains C code that must be compiled with gd, and if you have an older version of gd, or if gd is missing, you will get errors during compilation.
The gd library is available at http://www.boutell.com/. This site also has instructions for building gd plus references to other optional packages that gd uses if available, such as the FreeType engine, which enables gd (and thus GD) to support TrueType fonts. Note that gd requires the latest versions of libpng and zlib; you can find links to these libraries at http://www.boutell.com/ too.
13.3.2. Using GD
In this section, we'll develop an application that uses the uptime Unix system command to plot the system load average (see Figure 13-1). As we will see in the next section, there are modules to help us generate graphs more easily, but let's first see gd 's graphics primitives in action.
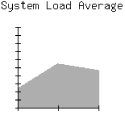
Figure 13-1. Sample graph generated by loads.cgi
The application itself is rather straightforward. First, we invoke the uptime command, which returns three values, representing the load averages for the previous 5, 10 and 15 minutes, respectively -- though this may differ among the various Unix implementations. Here is the output of an uptime command:
2:26pm up 11:07, 12 users, load average: 4.63, 5.29, 2.56
Then, we use gd's various drawing primitives, such as lines and polygons to draw the axes and scale and to plot the load values.
Example 13-2 shows the code.
Example 13-2. loads.cgi
#!/usr/bin/perl -wT
use strict;
use CGI;
use GD;
BEGIN {
$ENV{PATH} = '/bin:/usr/bin:/usr/ucb:/usr/local/bin';
delete @ENV{ qw( IFS CDPATH ENV BASH_ENV ) };
}
use constant LOAD_MAX => 10;
use constant IMAGE_SIZE => 170; # height and width
use constant GRAPH_SIZE => 100; # height and width
use constant TICK_LENGTH => 3;
use constant ORIGIN_X_COORD => 30;
use constant ORIGIN_Y_COORD => 150;
use constant TITLE_TEXT => "System Load Average";
use constant TITLE_X_COORD => 10;
use constant TITLE_Y_COORD => 15;
use constant AREA_COLOR => ( 255, 0, 0 );
use constant AXIS_COLOR => ( 0, 0, 0 );
use constant TEXT_COLOR => ( 0, 0, 0 );
use constant BG_COLOR => ( 255, 255, 255 );
my $q = new CGI;
my @loads = get_loads( );
print $q->header( -type => "image/png", -expires => "-1d" );
binmode STDOUT;
print area_graph( \@loads );
# Returns a list of the average loads from the system's uptime command
sub get_loads {
my $uptime = `uptime` or die "Error running uptime: $!";
my( $up_string ) = $uptime =~ /average: (.+)$/;
my @loads = reverse
map { $_ > LOAD_MAX ? LOAD_MAX : $_ }
split /,\s*/, $up_string;
@loads or die "Cannot parse response from uptime: $up_string";
return @loads;
}
# Takes a one-dimensional list of data and returns an area graph as PNG
sub area_graph {
my $data = shift;
my $image = new GD::Image( IMAGE_SIZE, IMAGE_SIZE );
my $background = $image->colorAllocate( BG_COLOR );
my $area_color = $image->colorAllocate( AREA_COLOR );
my $axis_color = $image->colorAllocate( AXIS_COLOR );
my $text_color = $image->colorAllocate( TEXT_COLOR );
# Add Title
$image->string( gdLargeFont, TITLE_X_COORD, TITLE_Y_COORD,
TITLE_TEXT, $text_color );
# Create polygon for data
my $polygon = new GD::Polygon;
$polygon->addPt( ORIGIN_X_COORD, ORIGIN_Y_COORD );
for ( my $i = 0; $i < @$data; $i++ ) {
$polygon->addPt( ORIGIN_X_COORD + GRAPH_SIZE / ( @$data - 1 ) * $i,
ORIGIN_Y_COORD - $$data[$i] * GRAPH_SIZE / LOAD_MAX );
}
$polygon->addPt( ORIGIN_X_COORD + GRAPH_SIZE, ORIGIN_Y_COORD );
# Add Polygon
$image->filledPolygon( $polygon, $area_color );
# Add X Axis
$image->line( ORIGIN_X_COORD, ORIGIN_Y_COORD,
ORIGIN_X_COORD + GRAPH_SIZE, ORIGIN_Y_COORD,
$axis_color );
# Add Y Axis
$image->line( ORIGIN_X_COORD, ORIGIN_Y_COORD,
ORIGIN_X_COORD, ORIGIN_Y_COORD - GRAPH_SIZE,
$axis_color );
# Add X Axis Ticks Marks
for ( my $x = 0; $x <= GRAPH_SIZE; $x += GRAPH_SIZE / ( @$data - 1 ) ) {
$image->line( $x + ORIGIN_X_COORD, ORIGIN_Y_COORD - TICK_LENGTH,
$x + ORIGIN_X_COORD, ORIGIN_Y_COORD + TICK_LENGTH,
$axis_color );
}
# Add Y Axis Tick Marks
for ( my $y = 0; $y <= GRAPH_SIZE; $y += GRAPH_SIZE / LOAD_MAX ) {
$image->line( ORIGIN_X_COORD - TICK_LENGTH, ORIGIN_Y_COORD - $y,
ORIGIN_X_COORD + TICK_LENGTH, ORIGIN_Y_COORD - $y,
$axis_color );
}
$image->transparent( $background );
return $image->png;
}
After importing our modules, we use a BEGIN block to make the environment safe for taint. We have to do this because our script will use the external uptime command (see Section 8.4, "Perl's Taint Mode").
Then we set a large number of constants. The UPPER_LIMIT constant sets the upper limit on the load average. If a load average exceeds the value of 10, then it is set to 10, so we don't have to worry about possibly scaling the axes. Remember, the whole point of this application is not to create a highly useful graphing application, but one that will illustrate some of GD's drawing primitives.
Next, we choose a size for our graph area, GRAPH_SIZE, as well as for the image itself, IMAGE_SIZE. Both the image and the graph are square, so these sizes represent length as well as width. TICK_LENGTH corresponds to the length of each tick mark (this is actually half the length of the tick mark once it's drawn).
ORIGIN_X_COORD and ORIGIN_Y_COORD contain the coordinates of the origin of our graph (its lower left-hand corner). TITLE_TEXT, TITLE_X_COORD, and TITLE_Y_COORD contain values for the title of our graph. Finally, we set AREA_COLOR, AXIS_COLOR, TEXT_COLOR, and BG_COLOR to an array of three numbers containing red, green, and blue values, respectively; these values range from 0 to 255.
The system's load is returned by get_loads. It takes the output of uptime , parses out the load averages, truncates any average greater than the value specified by UPPER_LIMIT, and reverses the values so they are returned from oldest to newest. Thus, our graph will plot from left to right the load average of the system over the last 15, 10, and 5 minutes.
Returning to the main body of our CGI script, we output our header, enable binary mode, then fetch the data for our PNG from area_graph and print it.
The area_graph function contains all of our image code. It accepts a reference to an array of data points, which it assigns to $data. We first create a new instance of GD::Image, passing to it the dimensions of the canvas that we want to work with.
Next, we allocate four colors that correspond to our earlier constants. Note that the first color we allocate automatically becomes the background color. In this case, the image will have a white background.
We use the string method to display our title using the gdLarge font. Then, we draw two lines, one horizontal and one vertical from the origin, representing the x and y axes. Once we draw the axes, we iterate through the entire graph area and draw the tick marks on the axes.
Now, we're ready to plot the load averages on the graph. We create a new instance of the GD::Polygon class to draw a polygon with the vertices representing the three load averages. Drawing a polygon is similar in principle to creating a closed path with several points.
We use the addPt method to add a point to the polygon. The origin is added as the first point. Then, each load average coordinate is calculated and added to the polygon. We add a final point on the x axis. GD automatically connects the final point to the first point.
The filledPolygon method fills the polygon specified by the $polygon object with the associated color. And finally, the graph is rendered as a PNG and the data is returned.
GD supports many methods beyond those listed here, but we do not have space to list them all here. Refer to the GD documentation or Programming Web Graphics for full usage.

Copyright © 2001 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.