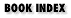Chapter 9. The java.awt Package
The java.awt package is the main package of the AWT, or Abstract Windowing Toolkit. It contains classes for graphics, including the Java 2D graphics capabilities introduced in the Java 2 platform, and also defines the basic graphical user interface (GUI) framework for Java. java.awt also includes a number of heavyweight GUI objects, many of which have been superseded by the javax.swing package. java.awt also has a number of important subpackages.
The most important graphics classes in java.awt are Graphics and its Java 2D extension, Graphics2D. These classes represent a drawing surface, maintain a set of drawing attributes, and define methods for drawing and filling lines, shapes, and text. Classes that represent graphics attributes include Color, Font, Paint, Stroke, and Composite. The Image class and Shape interface represent things that you can draw using a Graphics object and the various graphics attributes. Figure 9-1 shows the graphics classes of this package.
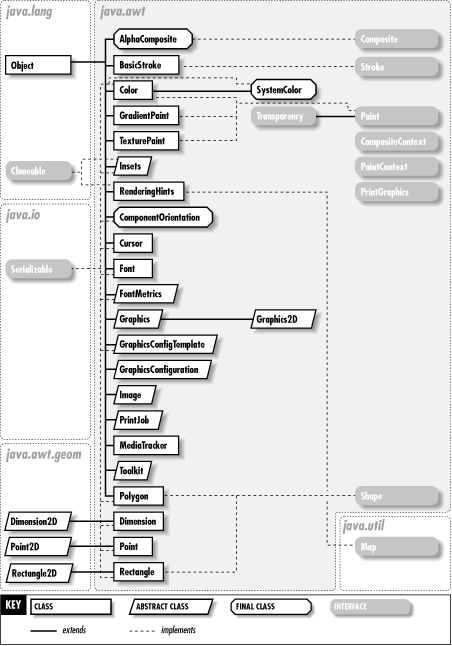
Figure 9-1. Graphics classes of the java.awt package
The most important class for GUIs is Component, which represents a single graphical element in a GUI. Container is a kind of component that can contain other components. The LayoutManager interface and its various implementations are used to position components within their containers. Figure 9-2 shows the GUI classes of this package, and Figure 9-3 shows the event, exception, and security classes.
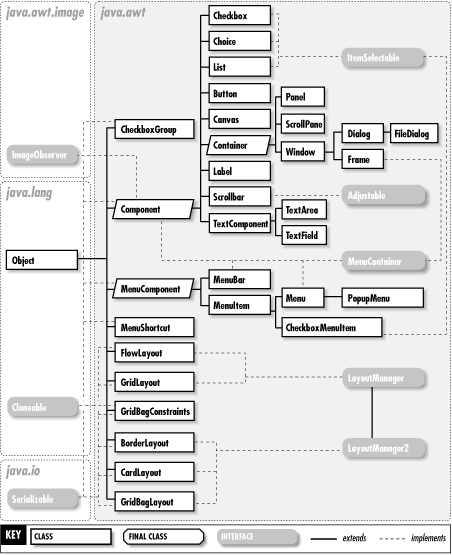
Figure 9-2. GUI classes of the java.awt package
Figure 9-3. Event, exception, and security classes of the java.awt package
See Chapter 4, "Graphics with AWT and Java 2D", for an introduction to Java graphics with AWT and Java 2D and Chapter 2, "Swing and AWTArchitecture", for an introduction to the GUI framework defined by the java.awt package.
| ActiveEvent | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | ||
This interface is implemented by events that know how to dispatch themselves. When the event dispatch system encounters an ActiveEvent on the event queue, it simply invokes the dispatch() method of the event, instead of attempting to dispatch the event on its own. This interface is implemented by java.awt.event.InvocationEvent, which is used by the invokeLater() and invokeAndWait() methods of EventQueue.
| public abstract interface ActiveEvent { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract void dispatch (); | ||
| } | ||
Implementations: java.awt.event.InvocationEvent
| Adjustable | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | PJ1.1 | |
This interface defines the methods that should be implemented by an object that maintains a user-adjustable numeric value. The adjustable value has specified minimum and maximum values, and it may be incremented or decremented either a unit at a time or a block at a time. An Adjustable object generates an AdjustmentEvent when it is adjusted and maintains a list of AdjustmentListener objects interested in being notified when such an event occurs.
This interface abstracts the essential functionality of the Scrollbar and javax.swing.JScrollBar components.
| public abstract interface Adjustable { | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int HORIZONTAL ; | =0 | |
| public static final int VERTICAL ; | =1 | |
| // | Event Registration Methods (by event name) | |
| public abstract void addAdjustmentListener (java.awt.event.AdjustmentListener l); | ||
| public abstract void removeAdjustmentListener (java.awt.event.AdjustmentListener l); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract int getBlockIncrement (); | ||
| public abstract void setBlockIncrement (int b); | ||
| public abstract int getMaximum (); | ||
| public abstract void setMaximum (int max); | ||
| public abstract int getMinimum (); | ||
| public abstract void setMinimum (int min); | ||
| public abstract int getOrientation (); | ||
| public abstract int getUnitIncrement (); | ||
| public abstract void setUnitIncrement (int u); | ||
| public abstract int getValue (); | ||
| public abstract void setValue (int v); | ||
| public abstract int getVisibleAmount (); | ||
| public abstract void setVisibleAmount (int v); | ||
| } | ||
Implementations: Scrollbar, javax.swing.JScrollBar
Passed To: java.awt.event.AdjustmentEvent.AdjustmentEvent(), java.awt.peer.ScrollPanePeer.{setUnitIncrement(), setValue()}
Returned By: ScrollPane.{getHAdjustable(), getVAdjustable()}, java.awt.event.AdjustmentEvent.getAdjustable()
| AlphaComposite | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | ||
This implementation of the Composite interface blends colors according to their levels of alpha transparency. AlphaComposite does not have a public constructor, but you can obtain a shared immutable instance by calling the static getInstance() method, specifying the desired compositing rule (one of the eight integer constants defined by the class), and specifying an alpha value. Alternatively, if you use an alpha value of 1.0, you can simply use one of the eight predefined AlphaComposite constants. Once you have obtained an AlphaComposite object, you use it by passing it to the setComposite() method of a Graphics2D object.
The most common way to use an AlphaComposite object is to specify the SRC_OVER compositing rule and an alpha value greater than 0 but less than 1. This causes the source colors you draw to be given the specified level of alpha transparency, so that they are blended with whatever colors already exist on the screen, making the destination colors appear to show through the translucent source colors. This technique allows you to achieve transparency effects using opaque colors when you are drawing onto a drawing surface, like a screen, that does not have an alpha channel.
The other compositing rules of AlphaComposite are best understood when both the source (your drawing) and the destination (the drawing surface) have alpha channels. For example, you can create translucent Color objects with the four-argument version of the Color() constructor, and you can create an off-screen image with an alpha channel by passing the constant TYPE_INT_ARGB to the java.awt.image.BufferedImage() constructor. (Once your compositing operation has been performed in an off-screen image with an alpha channel, you can view the results by copying the contents of the image to the screen, of course.) When your source and destination have alpha channels built in, you do not usually specify an alpha value for the AlphaComposite itself. If you do, however, the transparency values of the source colors are multiplied by this alpha value.
AlphaComposite supports the following compositing rules:
- SRC
-
Replace the colors of the destination with the colors of the source, ignoring the destination colors and the transparency of the source.
- SRC_OVER
-
Combine the source and destination colors combined based on the transparency of the source, so that the source appears to be drawn over the destination.
- DST_OVER
-
Combine the source and destination colors based on the transparency of the destination, so that the source appears to be drawn underneath the destination.
- SRC_IN
-
Draw the colors of the source using the transparency values of the destination, completely ignoring the colors of the destination.
- SRC_OUT
-
Draw the colors of the source using the inverse transparency values of the destination.
- DST_IN
-
Modify the colors of the destination using the alpha values of the source and ignoring the colors of the source.
- DST_OUT
-
Modify the colors of the destination using the inverted alpha values of the source and ignoring the colors of the source.
- CLEAR
-
Ignore the color and transparency of both the destination and the source. This clears the destination by making it a fully transparent black.
| public final class AlphaComposite implements Composite { | ||
| // | No Constructor | |
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final AlphaComposite Clear ; | ||
| public static final int CLEAR ; | =1 | |
| public static final int DST_IN ; | =6 | |
| public static final int DST_OUT ; | =8 | |
| public static final int DST_OVER ; | =4 | |
| public static final AlphaComposite DstIn ; | ||
| public static final AlphaComposite DstOut ; | ||
| public static final AlphaComposite DstOver ; | ||
| public static final AlphaComposite Src ; | ||
| public static final int SRC ; | =2 | |
| public static final int SRC_IN ; | =5 | |
| public static final int SRC_OUT ; | =7 | |
| public static final int SRC_OVER ; | =3 | |
| public static final AlphaComposite SrcIn ; | ||
| public static final AlphaComposite SrcOut ; | ||
| public static final AlphaComposite SrcOver ; | ||
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| public static AlphaComposite getInstance (int rule); | ||
| public static AlphaComposite getInstance (int rule, float alpha); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public float getAlpha (); | ||
| public int getRule (); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing Composite | |
| public CompositeContext createContext (java.awt.image.ColorModel srcColorModel, java.awt.image.ColorModel dstColorModel, RenderingHints hints); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public boolean equals (Object obj); | ||
| public int hashCode (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->AlphaComposite(Composite)
Returned By: AlphaComposite.getInstance()
Type Of: AlphaComposite.{Clear, DstIn, DstOut, DstOver, Src, SrcIn, SrcOut, SrcOver}
| AWTError | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable error PJ1.1 | |
Signals that an error has occurred in the java.awt package.
| public class AWTError extends Error { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public AWTError (String msg); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Throwable(Serializable)-->Error-->AWTError
| AWTEvent | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable event PJ1.1 | |
This abstract class serves as the root event type for all AWT events in Java 1.1 and supersedes the Event class that was used in Java 1.0.
Each AWTEvent has a source object, as all EventObject objects do. You can query the source of an event with the inherited getSource() method. The AWTEvent class adds an event type, or ID, for every AWT event. Use getID() to query the type of an event. Subclasses of AWTEvent define various constants for this type field.
The various _MASK constants are used by applets and custom components that call the enableEvents() method of Component to receive various event types without having to register EventListener objects.
| public abstract class AWTEvent extends java.util.EventObject { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public AWTEvent (Event event); | ||
| public AWTEvent (Object source, int id); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final long ACTION_EVENT_MASK ; | =128 | |
| public static final long ADJUSTMENT_EVENT_MASK ; | =256 | |
| public static final long COMPONENT_EVENT_MASK ; | =1 | |
| public static final long CONTAINER_EVENT_MASK ; | =2 | |
| public static final long FOCUS_EVENT_MASK ; | =4 | |
| 1.2 | public static final long INPUT_METHOD_EVENT_MASK ; | =2048 |
| public static final long ITEM_EVENT_MASK ; | =512 | |
| public static final long KEY_EVENT_MASK ; | =8 | |
| public static final long MOUSE_EVENT_MASK ; | =16 | |
| public static final long MOUSE_MOTION_EVENT_MASK ; | =32 | |
| public static final int RESERVED_ID_MAX ; | =1999 | |
| public static final long TEXT_EVENT_MASK ; | =1024 | |
| public static final long WINDOW_EVENT_MASK ; | =64 | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public int getID (); | ||
| public String paramString (); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding EventObject | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Object | |
| 1.2 | protected void finalize () throws Throwable; | |
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| protected void consume (); | ||
| protected boolean isConsumed (); | ||
| // | Protected Instance Fields | |
| protected boolean consumed ; | ||
| protected int id ; | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->java.util.EventObject(Serializable)-->AWTEvent
Subclasses: java.awt.event.ActionEvent, java.awt.event.AdjustmentEvent, java.awt.event.ComponentEvent, java.awt.event.InputMethodEvent, java.awt.event.InvocationEvent, java.awt.event.ItemEvent, java.awt.event.TextEvent, javax.swing.event.AncestorEvent, javax.swing.event.InternalFrameEvent
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Component.coalesceEvents(), EventQueue.{getNextEvent(), peekEvent()}
| AWTEventMulticaster | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | PJ1.1 | |
AWTEventMulticaster is a convenience class used when writing a custom AWT component. It provides an easy way to maintain a list of AWT EventListener objects and notify the listeners on that list when an event occurs.
AWTEventMulticaster implements each of the event listener interfaces defined in the java.awt.event package, which means that an AWTEventMulticaster object can serve as any desired type of event listener. (It also means that the class defines quite a few methods.) AWTEventMulticaster implements what amounts to a linked list of EventListener objects. When you invoke one of the EventListener methods of an AWTEventMulticaster, it invokes the same method on all of the EventListener objects in the linked list.
Rather than instantiate an AWTEventMulticaster object directly, you use the static add() and remove() methods of the class to add and remove EventListener objects from the linked list. Calling add() or remove() returns an AWTEventMulticaster with the appropriate EventListener object registered or deregistered. Using an AWTEventMulticaster is somewhat non-intuitive, so here is some example code that shows its use:
public class MyList extends Component { // a class that sends ItemEvents
// The head of a linked list of AWTEventMulticaster objects
protected ItemListener listener = null;
public void addItemListener(ItemListener l) { // add a listener
listener = AWTEventMulticaster.add(listener, l);
}
public void removeItemListener(ItemListener l) { // remove a listener
listener = AWTEventMulticaster.remove(listener, l);
}
protected void fireItemEvent(ItemEvent e) { // notify all listeners
if (listener != null) listener.itemStateChanged(e);
}
// The rest of the class goes here
}
| public class AWTEventMulticaster implements java.awt.event.ActionListener, java.awt.event.AdjustmentListener, java.awt.event.ComponentListener, java.awt.event.ContainerListener, java.awt.event.FocusListener, java.awt.event.InputMethodListener, java.awt.event.ItemListener, java.awt.event.KeyListener, java.awt.event.MouseListener, java.awt.event.MouseMotionListener, java.awt.event.TextListener, java.awt.event.WindowListener { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected AWTEventMulticaster (java.util.EventListener a, java.util.EventListener b); | ||
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| public static java.awt.event.ActionListener add (java.awt.event.ActionListener a, java.awt.event.ActionListener b); | ||
| public static java.awt.event.AdjustmentListener add (java.awt.event.AdjustmentListener a, java.awt.event.AdjustmentListener b); | ||
| public static java.awt.event.ComponentListener add (java.awt.event.ComponentListener a, java.awt.event.ComponentListener b); | ||
| public static java.awt.event.ContainerListener add (java.awt.event.ContainerListener a, java.awt.event.ContainerListener b); | ||
| public static java.awt.event.FocusListener add (java.awt.event.FocusListener a, java.awt.event.FocusListener b); | ||
| 1.2 | public static java.awt.event.InputMethodListener add (java.awt.event.InputMethodListener a, java.awt.event.InputMethodListener b); | |
| public static java.awt.event.ItemListener add (java.awt.event.ItemListener a, java.awt.event.ItemListener b); | ||
| public static java.awt.event.KeyListener add (java.awt.event.KeyListener a, java.awt.event.KeyListener b); | ||
| public static java.awt.event.MouseListener add (java.awt.event.MouseListener a, java.awt.event.MouseListener b); | ||
| public static java.awt.event.MouseMotionListener add (java.awt.event.MouseMotionListener a, java.awt.event.MouseMotionListener b); | ||
| public static java.awt.event.TextListener add (java.awt.event.TextListener a, java.awt.event.TextListener b); | ||
| public static java.awt.event.WindowListener add (java.awt.event.WindowListener a, java.awt.event.WindowListener b); | ||
| public static java.awt.event.ActionListener remove (java.awt.event.ActionListener l, java.awt.event.ActionListener oldl); | ||
| public static java.awt.event.AdjustmentListener remove (java.awt.event.AdjustmentListener l, java.awt.event.AdjustmentListener oldl); | ||
| public static java.awt.event.ComponentListener remove (java.awt.event.ComponentListener l, java.awt.event.ComponentListener oldl); | ||
| public static java.awt.event.ContainerListener remove (java.awt.event.ContainerListener l, java.awt.event.ContainerListener oldl); | ||
| public static java.awt.event.FocusListener remove (java.awt.event.FocusListener l, java.awt.event.FocusListener oldl); | ||
| 1.2 | public static java.awt.event.InputMethodListener remove (java.awt.event.InputMethodListener l, java.awt.event.InputMethodListener oldl); | |
| public static java.awt.event.ItemListener remove (java.awt.event.ItemListener l, java.awt.event.ItemListener oldl); | ||
| public static java.awt.event.KeyListener remove (java.awt.event.KeyListener l, java.awt.event.KeyListener oldl); | ||
| public static java.awt.event.MouseListener remove (java.awt.event.MouseListener l, java.awt.event.MouseListener oldl); | ||
| public static java.awt.event.MouseMotionListener remove (java.awt.event.MouseMotionListener l, java.awt.event.MouseMotionListener oldl); | ||
| public static java.awt.event.TextListener remove (java.awt.event.TextListener l, java.awt.event.TextListener oldl); | ||
| public static java.awt.event.WindowListener remove (java.awt.event.WindowListener l, java.awt.event.WindowListener oldl); | ||
| // | Protected Class Methods | |
| protected static java.util.EventListener addInternal (java.util.EventListener a, java.util.EventListener b); | ||
| protected static java.util.EventListener removeInternal (java.util.EventListener l, java.util.EventListener oldl); | ||
| protected static void save (java.io.ObjectOutputStream s, String k, java.util.EventListener l) throws java.io.IOException; | ||
| // | Methods Implementing ActionListener | |
| public void actionPerformed (java.awt.event.ActionEvent e); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing AdjustmentListener | |
| public void adjustmentValueChanged (java.awt.event.AdjustmentEvent e); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing ComponentListener | |
| public void componentHidden (java.awt.event.ComponentEvent e); | ||
| public void componentMoved (java.awt.event.ComponentEvent e); | ||
| public void componentResized (java.awt.event.ComponentEvent e); | ||
| public void componentShown (java.awt.event.ComponentEvent e); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing ContainerListener | |
| public void componentAdded (java.awt.event.ContainerEvent e); | ||
| public void componentRemoved (java.awt.event.ContainerEvent e); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing FocusListener | |
| public void focusGained (java.awt.event.FocusEvent e); | ||
| public void focusLost (java.awt.event.FocusEvent e); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing InputMethodListener | |
| 1.2 | public void caretPositionChanged (java.awt.event.InputMethodEvent e); | |
| 1.2 | public void inputMethodTextChanged (java.awt.event.InputMethodEvent e); | |
| // | Methods Implementing ItemListener | |
| public void itemStateChanged (java.awt.event.ItemEvent e); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing KeyListener | |
| public void keyPressed (java.awt.event.KeyEvent e); | ||
| public void keyReleased (java.awt.event.KeyEvent e); | ||
| public void keyTyped (java.awt.event.KeyEvent e); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing MouseListener | |
| public void mouseClicked (java.awt.event.MouseEvent e); | ||
| public void mouseEntered (java.awt.event.MouseEvent e); | ||
| public void mouseExited (java.awt.event.MouseEvent e); | ||
| public void mousePressed (java.awt.event.MouseEvent e); | ||
| public void mouseReleased (java.awt.event.MouseEvent e); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing MouseMotionListener | |
| public void mouseDragged (java.awt.event.MouseEvent e); | ||
| public void mouseMoved (java.awt.event.MouseEvent e); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing TextListener | |
| public void textValueChanged (java.awt.event.TextEvent e); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing WindowListener | |
| public void windowActivated (java.awt.event.WindowEvent e); | ||
| public void windowClosed (java.awt.event.WindowEvent e); | ||
| public void windowClosing (java.awt.event.WindowEvent e); | ||
| public void windowDeactivated (java.awt.event.WindowEvent e); | ||
| public void windowDeiconified (java.awt.event.WindowEvent e); | ||
| public void windowIconified (java.awt.event.WindowEvent e); | ||
| public void windowOpened (java.awt.event.WindowEvent e); | ||
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| protected java.util.EventListener remove (java.util.EventListener oldl); | ||
| protected void saveInternal (java.io.ObjectOutputStream s, String k) throws java.io.IOException; | ||
| // | Protected Instance Fields | |
| protected final java.util.EventListener a ; | ||
| protected final java.util.EventListener b ; | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->AWTEventMulticaster(java.awt.event.ActionListener(java.util.EventListener),java.awt.event.AdjustmentListener(java.util.EventListener),java.awt.event.ComponentListener(java.util.EventListener),java.awt.event.ContainerListener(java.util.EventListener),java.awt.event.FocusListener(java.util.EventListener),java.awt.event.InputMethodListener(java.util.EventListener),java.awt.event.ItemListener(java.util.EventListener),java.awt.event.KeyListener(java.util.EventListener),java.awt.event.MouseListener(java.util.EventListener),java.awt.event.MouseMotionListener(java.util.EventListener),java.awt.event.TextListener(java.util.EventListener),java.awt.event.WindowListener(java.util.EventListener))
| AWTException | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable checked PJ1.1 | |
Signals that an exception has occurred in the java.awt package.
| public class AWTException extends Exception { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public AWTException (String msg); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Throwable(Serializable)-->Exception-->AWTException
Thrown By: Cursor.getSystemCustomCursor()
| AWTPermission | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable permission | |
This class encapsulates permissions for performing various AWT-related operations; applications do not typically use it. The name, or target, of a permission should be one of the following values: "accessClipboard", "accessEventQueue", "listenToAllAWTEvents", or "showWindowWithoutWarningBanner". Alternatively, a name of "*" implies all of these values. AWTPermission does not use actions, so the actions argument to the constructor should be null.
| public final class AWTPermission extends java.security.BasicPermission { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public AWTPermission (String name); | ||
| public AWTPermission (String name, String actions); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->java.security.Permission(java.security.Guard,Serializable)-->java.security.BasicPermission(Serializable)-->AWTPermission
| BasicStroke | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | ||
This class defines properties that control how lines are drawn. By default, lines are one-pixel wide and solid. To change these attributes, pass a BasicStroke (or another implementation of Stroke) to the setStroke() method of a Graphics2D object. BasicStroke supports the following line attribute properties:
- lineWidth
-
The thickness of the line.
- endCap
-
The end cap style of the line. CAP_BUTT specifies that a line ends exactly at its end points, without caps. CAP_SQUARE causes a line to end with square caps that extend beyond the end points by a distance equal to one-half of the line width. CAP_ROUND specifies that a line ends with round caps with a radius of one-half of the line width.
- lineJoin
-
The join style when two line segments meet at the vertex of a shape. JOIN_MITER specifies that the outside edges of the two line segments are extended as far as necessary until they intersect. JOIN_BEVEL causes the outside corners of the vertex to be joined with a straight line. JOIN_ROUND specifies that the vertex is rounded with a curve that has a radius of half the line width.
- miterLimit
-
The maximum length of the miter used to connect two intersecting line segments. When two lines intersect at an acute angle and the line join style is JOIN_MITER, the length of the miter gets progressively longer as the angle between the lines gets smaller. This property imposes a maximum length on the miter; beyond this length, the miter is squared off.
- dashArray
-
The pattern of dashes and spaces that make up a dashed line. This attribute is an array, where the first element and all the additional odd elements specify the lengths of dashes. The second element and all the additional even elements specify the lengths of the spaces. When the dash pattern is complete, it starts over at the beginning of the array, of course.
- dashPhase
-
The distance into the dash pattern that line drawing begins. Note that this value is not an index into the dash array, but a distance. For example, if you've specified a dash of length 5 followed by a space of length 3 and want to begin your line with the space rather than the dash, you set this property to 5.
See Stroke for a discussion of how line drawing is performed in Java 2D.
| public class BasicStroke implements Stroke { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public BasicStroke (); | ||
| public BasicStroke (float width); | ||
| public BasicStroke (float width, int cap, int join); | ||
| public BasicStroke (float width, int cap, int join, float miterlimit); | ||
| public BasicStroke (float width, int cap, int join, float miterlimit, float[ ] dash, float dash_phase); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int CAP_BUTT ; | =0 | |
| public static final int CAP_ROUND ; | =1 | |
| public static final int CAP_SQUARE ; | =2 | |
| public static final int JOIN_BEVEL ; | =2 | |
| public static final int JOIN_MITER ; | =0 | |
| public static final int JOIN_ROUND ; | =1 | |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public float[ ] getDashArray (); | default:null | |
| public float getDashPhase (); | default:0.0 | |
| public int getEndCap (); | default:2 | |
| public int getLineJoin (); | default:0 | |
| public float getLineWidth (); | default:1.0 | |
| public float getMiterLimit (); | default:10.0 | |
| // | Methods Implementing Stroke | |
| public Shape createStrokedShape (Shape s); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public boolean equals (Object obj); | ||
| public int hashCode (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->BasicStroke(Stroke)
| BorderLayout | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable layout manager PJ1.1 | |
A LayoutManager that arranges components that have been added to their Container (using the Container.add() method) with the names "North", "South", "East", "West", and "Center". These named components are arranged along the edges and in the center of the container. The hgap and vgap arguments to the BorderLayout constructor specify the desired horizontal and vertical spacing between adjacent components.
In Java 1.1, five constants were defined to represent these strings. In Java 1.2, an additional four constants have been added to represent the four sides of the container in a way that is independent of writing direction. For example, BEFORE_LINE_BEGINS is the same as WEST in locales where text is drawn from left to right, but is the same as EAST in locales where text is drawn from right to left.
Note that an application should never call the LayoutManager methods of this class directly; the Container for which the BorderLayout is registered does this.
In Java 1.1, five constants were defined to represent these strings. In Java 1.2, an additional four constants have been added to represent the four sides of the container in a way that is independent of writing direction. For example, BEFORE_LINE_BEGINS is the same as WEST in locales where text is drawn from left to right but is the same as EAST in locales where text is drawn right to left.
| public class BorderLayout implements LayoutManager2, Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public BorderLayout (); | ||
| public BorderLayout (int hgap, int vgap); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| 1.2 | public static final String AFTER_LAST_LINE ; | ="Last" |
| 1.2 | public static final String AFTER_LINE_ENDS ; | ="After" |
| 1.2 | public static final String BEFORE_FIRST_LINE ; | ="First" |
| 1.2 | public static final String BEFORE_LINE_BEGINS ; | ="Before" |
| 1.1 | public static final String CENTER ; | ="Center" |
| 1.1 | public static final String EAST ; | ="East" |
| 1.1 | public static final String NORTH ; | ="North" |
| 1.1 | public static final String SOUTH ; | ="South" |
| 1.1 | public static final String WEST ; | ="West" |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.1 | public int getHgap (); | default:0 |
| 1.1 | public void setHgap (int hgap); | |
| 1.1 | public int getVgap (); | default:0 |
| 1.1 | public void setVgap (int vgap); | |
| // | Methods Implementing LayoutManager | |
| public void layoutContainer (Container target); | ||
| public Dimension minimumLayoutSize (Container target); | ||
| public Dimension preferredLayoutSize (Container target); | ||
| public void removeLayoutComponent (Component comp); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing LayoutManager2 | |
| 1.1 | public void addLayoutComponent (Component comp, Object constraints); | |
| 1.1 | public float getLayoutAlignmentX (Container parent); | |
| 1.1 | public float getLayoutAlignmentY (Container parent); | |
| 1.1 | public void invalidateLayout (Container target); | empty |
| 1.1 | public Dimension maximumLayoutSize (Container target); | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public void addLayoutComponent (String name, Component comp); | Implements:LayoutManager |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->BorderLayout(LayoutManager2(LayoutManager),Serializable)
| Button | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1 | |
This class represents a GUI push button that displays a specified textual label. Use setActionCommand() to specify an identifying string that is included in the ActionEvent events generated by the button.
| public class Button extends Component { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Button (); | ||
| public Button (String label); | ||
| // | Event Registration Methods (by event name) | |
| 1.1 | public void addActionListener (java.awt.event.ActionListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void removeActionListener (java.awt.event.ActionListener l); | synchronized |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.1 | public String getActionCommand (); | default:"" |
| 1.1 | public void setActionCommand (String command); | |
| public String getLabel (); | default:"" | |
| public void setLabel (String label); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Component | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Component | |
| protected String paramString (); | ||
| 1.1 | protected void processEvent (AWTEvent e); | |
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| 1.1 | protected void processActionEvent (java.awt.event.ActionEvent e); | |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Component(java.awt.image.ImageObserver,MenuContainer,Serializable)-->Button
Passed To: Toolkit.createButton()
| Canvas | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1 | |
A Component that does no default drawing or event handling on its own. You can subclass it to display any kind of drawing or image and handle any kind of user input event. Canvas inherits the event-handling methods of its superclass. In Java 1.1, you can also subclass Component directly to create a lightweight component, instead of having to subclass Canvas.
| public class Canvas extends Component { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Canvas (); | ||
| 1.2 | public Canvas (GraphicsConfiguration config); | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Component | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| public void paint (Graphics g); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Component(java.awt.image.ImageObserver,MenuContainer,Serializable)-->Canvas
Passed To: Toolkit.createCanvas()
| CardLayout | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable layout manager PJ1.1 | |
A LayoutManager that makes each of the components it manages as large as the container and ensures that only one is visible at a time. The standard LayoutManager methods are called by the Container object and should not be called directly by applet or application code. first(), last(), next(), previous(), and show() make a particular Component in the Container visible. The names with which the components are added to the container are used only by the show() method.
| public class CardLayout implements LayoutManager2, Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public CardLayout (); | ||
| public CardLayout (int hgap, int vgap); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.1 | public int getHgap (); | default:0 |
| 1.1 | public void setHgap (int hgap); | |
| 1.1 | public int getVgap (); | default:0 |
| 1.1 | public void setVgap (int vgap); | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void first (Container parent); | ||
| public void last (Container parent); | ||
| public void next (Container parent); | ||
| public void previous (Container parent); | ||
| public void show (Container parent, String name); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing LayoutManager | |
| public void layoutContainer (Container parent); | ||
| public Dimension minimumLayoutSize (Container parent); | ||
| public Dimension preferredLayoutSize (Container parent); | ||
| public void removeLayoutComponent (Component comp); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing LayoutManager2 | |
| 1.1 | public void addLayoutComponent (Component comp, Object constraints); | |
| 1.1 | public float getLayoutAlignmentX (Container parent); | |
| 1.1 | public float getLayoutAlignmentY (Container parent); | |
| 1.1 | public void invalidateLayout (Container target); | empty |
| 1.1 | public Dimension maximumLayoutSize (Container target); | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public void addLayoutComponent (String name, Component comp); | Implements:LayoutManager |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->CardLayout(LayoutManager2(LayoutManager),Serializable)
| Checkbox | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1 | |
This class represents a GUI checkbox with a textual label. The Checkbox maintains a boolean state--whether it is checked or not. The checkbox may optionally be part of a CheckboxGroup that enforces radio button behavior.
| public class Checkbox extends Component implements ItemSelectable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Checkbox (); | ||
| public Checkbox (String label); | ||
| 1.1 | public Checkbox (String label, boolean state); | |
| public Checkbox (String label, CheckboxGroup group, boolean state); | ||
| 1.1 | public Checkbox (String label, boolean state, CheckboxGroup group); | |
| // | Event Registration Methods (by event name) | |
| 1.1 | public void addItemListener (java.awt.event.ItemListener l); | Implements:ItemSelectable synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void removeItemListener (java.awt.event.ItemListener l); | Implements:ItemSelectable synchronized |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public CheckboxGroup getCheckboxGroup (); | default:null | |
| public void setCheckboxGroup (CheckboxGroup g); | ||
| public String getLabel (); | default:"" | |
| public void setLabel (String label); | ||
| 1.1 | public Object[ ] getSelectedObjects (); | Implements:ItemSelectable default:null |
| public boolean getState (); | default:false | |
| public void setState (boolean state); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing ItemSelectable | |
| 1.1 | public void addItemListener (java.awt.event.ItemListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public Object[ ] getSelectedObjects (); | default:null |
| 1.1 | public void removeItemListener (java.awt.event.ItemListener l); | synchronized |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Component | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Component | |
| protected String paramString (); | ||
| 1.1 | protected void processEvent (AWTEvent e); | |
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| 1.1 | protected void processItemEvent (java.awt.event.ItemEvent e); | |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Component(java.awt.image.ImageObserver,MenuContainer,Serializable)-->Checkbox(ItemSelectable)
Passed To: CheckboxGroup.{setCurrent(), setSelectedCheckbox()}, Toolkit.createCheckbox()
Returned By: CheckboxGroup.{getCurrent(), getSelectedCheckbox()}
| CheckboxGroup | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable PJ1.1 | |
A CheckboxGroup object enforces mutual exclusion (also known as radio button behavior) among any number of Checkbox buttons. A Checkbox component can specify a CheckboxGroup object when created or with its setCheckboxGroup() method. If a Checkbox within a CheckboxGroup object is selected, the CheckboxGroup ensures that the previously selected Checkbox becomes unselected.
| public class CheckboxGroup implements Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public CheckboxGroup (); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.1 | public Checkbox getSelectedCheckbox (); | default:null |
| 1.1 | public void setSelectedCheckbox (Checkbox box); | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public Checkbox getCurrent (); | default:null |
| # | public void setCurrent (Checkbox box); | synchronized |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->CheckboxGroup(Serializable)
Passed To: Checkbox.{Checkbox(), setCheckboxGroup()}, java.awt.peer.CheckboxPeer.setCheckboxGroup()
Returned By: Checkbox.getCheckboxGroup()
| CheckboxMenuItem | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1(opt) | |
This class represents a checkbox with a textual label in a GUI menu. It maintains a boolean state--whether it is checked or not. See also MenuItem.
| public class CheckboxMenuItem extends MenuItem implements ItemSelectable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| 1.1 | public CheckboxMenuItem (); | |
| public CheckboxMenuItem (String label); | ||
| 1.1 | public CheckboxMenuItem (String label, boolean state); | |
| // | Event Registration Methods (by event name) | |
| 1.1 | public void addItemListener (java.awt.event.ItemListener l); | Implements:ItemSelectable synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void removeItemListener (java.awt.event.ItemListener l); | Implements:ItemSelectable synchronized |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.1 | public Object[ ] getSelectedObjects (); | Implements:ItemSelectable synchronized default:null |
| public boolean getState (); | default:false | |
| public void setState (boolean b); | synchronized | |
| // | Methods Implementing ItemSelectable | |
| 1.1 | public void addItemListener (java.awt.event.ItemListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public Object[ ] getSelectedObjects (); | synchronized default:null |
| 1.1 | public void removeItemListener (java.awt.event.ItemListener l); | synchronized |
| // | Public Methods Overriding MenuItem | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| public String paramString (); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding MenuItem | |
| 1.1 | protected void processEvent (AWTEvent e); | |
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| 1.1 | protected void processItemEvent (java.awt.event.ItemEvent e); | |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->MenuComponent(Serializable)-->MenuItem-->CheckboxMenuItem(ItemSelectable)
Passed To: Toolkit.createCheckboxMenuItem()
| Choice | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1 | |
This class represents an option menu or dropdown list. The addItem() method adds an item with the specified label to a Choice menu. getSelectedIndex() returns the numerical position of the selected item in the menu, while getSelectedItem() returns the label of the selected item.
| public class Choice extends Component implements ItemSelectable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Choice (); | ||
| // | Event Registration Methods (by event name) | |
| 1.1 | public void addItemListener (java.awt.event.ItemListener l); | Implements:ItemSelectable synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void removeItemListener (java.awt.event.ItemListener l); | Implements:ItemSelectable synchronized |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.1 | public int getItemCount (); | default:0 |
| public int getSelectedIndex (); | default:-1 | |
| public String getSelectedItem (); | synchronized default:null | |
| 1.1 | public Object[ ] getSelectedObjects (); | Implements:ItemSelectable synchronized default:null |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| 1.1 | public void add (String item); | |
| public void addItem (String item); | ||
| public String getItem (int index); | ||
| 1.1 | public void insert (String item, int index); | |
| 1.1 | public void remove (String item); | |
| 1.1 | public void remove (int position); | |
| 1.1 | public void removeAll (); | |
| public void select (String str); | synchronized | |
| public void select (int pos); | synchronized | |
| // | Methods Implementing ItemSelectable | |
| 1.1 | public void addItemListener (java.awt.event.ItemListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public Object[ ] getSelectedObjects (); | synchronized default:null |
| 1.1 | public void removeItemListener (java.awt.event.ItemListener l); | synchronized |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Component | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Component | |
| protected String paramString (); | ||
| 1.1 | protected void processEvent (AWTEvent e); | |
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| 1.1 | protected void processItemEvent (java.awt.event.ItemEvent e); | |
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public int countItems (); | |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Component(java.awt.image.ImageObserver,MenuContainer,Serializable)-->Choice(ItemSelectable)
Passed To: Toolkit.createChoice()
| Color | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable PJ1.1 | |
This class describes a color in terms of the individual components of that color. These components are either float values that range between 0 and 1 or 8-bit integers that range from 0 to 255. Prior to Java 1.2, only the RGB (red, green, blue) color space was supported. With the advent of Java 2D, the Color class has been extended to support alpha transparency and arbitrary java.awt.color.ColorSpace objects. In addition, the Java 1.2 Color class implements the Paint interface and is used to perform Java 2D drawing and filling operations that use solid colors.
Color objects can be obtained in a number of ways. The Color() constructors allow color components to be directly specified. The class also defines several color constants. The SystemColor subclass defines other useful Color constants that are related to standard colors used on the system desktop. The static methods HSBtoRGB() and RGBtoHSB() convert between the RGB color space and the HSB (hue, saturation, brightness) color space and can be used to create colors specified using the more intuitive HSB color components. brighter() and darker() return variants on the current color and are useful for creating shading effects.
An RGB color can be expressed as a 24-bit number, where the top 8 bits specifies the red component, the middle 8 bits specifies the green component, and the low 8 bits specifies the blue component. Colors are often represented using a string representation of this 24-bit number. It is particularly common to use a hexadecimal representation for a color, since it keeps the red, green, and blue components distinct. For example, the string "0xFF0000" represents a bright red color: the red component has a value of 255, and both the green and blue components are 0. The static decode() method converts color strings encoded in this way to Color objects. Each getColor() method looks up the specified key in the system properties list and then decodes the value and returns the resulting Color or the specified default color, if no color is found in the properties list.
getRGB() returns the red, green, and blue components of a color as a 24-bit number. getRed(), getBlue(), getGreen(), and getAlpha() return the individual components of a color as integers. getComponents() is a generalized method that returns the color and transparency components of a color in a float array, using an optionally specified ColorSpace. getColorComponents() is similar but returns only the color components, not the transparency component. getRGBComponents() returns the color and alpha components as float values using the RGB color space. getRGBColorComponents() does the same but does not return the alpha component. Each of these methods either fills in the elements of a float[] array you provide or allocates one of its own, if you pass null.
| public class Color implements Paint, Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Color (int rgb); | ||
| 1.2 | public Color (int rgba, boolean hasalpha); | |
| 1.2 | public Color (java.awt.color.ColorSpace cspace, float[ ] components, float alpha); | |
| public Color (float r, float g, float b); | ||
| public Color (int r, int g, int b); | ||
| 1.2 | public Color (int r, int g, int b, int a); | |
| 1.2 | public Color (float r, float g, float b, float a); | |
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final Color black ; | ||
| public static final Color blue ; | ||
| public static final Color cyan ; | ||
| public static final Color darkGray ; | ||
| public static final Color gray ; | ||
| public static final Color green ; | ||
| public static final Color lightGray ; | ||
| public static final Color magenta ; | ||
| public static final Color orange ; | ||
| public static final Color pink ; | ||
| public static final Color red ; | ||
| public static final Color white ; | ||
| public static final Color yellow ; | ||
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| 1.1 | public static Color decode (String nm) throws NumberFormatException; | |
| public static Color getColor (String nm); | ||
| public static Color getColor (String nm, Color v); | ||
| public static Color getColor (String nm, int v); | ||
| public static Color getHSBColor (float h, float s, float b); | ||
| public static int HSBtoRGB (float hue, float saturation, float brightness); | ||
| public static float[ ] RGBtoHSB (int r, int g, int b, float[ ] hsbvals); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.2 | public int getAlpha (); | |
| public int getBlue (); | ||
| 1.2 | public java.awt.color.ColorSpace getColorSpace (); | |
| public int getGreen (); | ||
| public int getRed (); | ||
| public int getRGB (); | ||
| 1.2 | public int getTransparency (); | Implements:Transparency |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public Color brighter (); | ||
| public Color darker (); | ||
| 1.2 | public float[ ] getColorComponents (float[ ] compArray); | |
| 1.2 | public float[ ] getColorComponents (java.awt.color.ColorSpace cspace, float[ ] compArray); | |
| 1.2 | public float[ ] getComponents (float[ ] compArray); | |
| 1.2 | public float[ ] getComponents (java.awt.color.ColorSpace cspace, float[ ] compArray); | |
| 1.2 | public float[ ] getRGBColorComponents (float[ ] compArray); | |
| 1.2 | public float[ ] getRGBComponents (float[ ] compArray); | |
| // | Methods Implementing Paint | |
| 1.2 | public PaintContext createContext (java.awt.image.ColorModel cm, Rectangle r, java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D r2d, java.awt.geom.AffineTransform xform, RenderingHints hints); | synchronized |
| // | Methods Implementing Transparency | |
| 1.2 | public int getTransparency (); | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public boolean equals (Object obj); | ||
| public int hashCode (); | ||
| public String toString (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Color(Paint(Transparency),Serializable)
Subclasses: SystemColor, javax.swing.plaf.ColorUIResource
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Too many methods to list.
Type Of: Too many fields to list.
| Component | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1(mod) | |
Component is the superclass of all GUI components (except menu components) in the java.awt package. You cannot instantiate a Component directly; you must use a subclass.
Component defines many methods. Some of these are intended to be implemented by subclasses, including some that are for handling events. Other methods are used internally by the AWT. And many are useful utility methods for working with GUI components. getParent() returns the Container that contains a Component. setBackground(), setForeground(), and setFont() set the specified display attributes of a component. hide(), show(), enable(), and disable() perform the specified actions for a component. createImage() creates either an Image object from a specified ImageProducer or an off-screen image that can be drawn into and used for double-buffering during animation. Component also has quite a few deprecated methods, as a result of the Java 1.1 event model and the introduction of the JavaBeans method-naming conventions. The class defines numerous methods for handling many types of events, using the 1.0 and 1.1 event models, in both their high-level and low-level forms.
In Personal Java environments, the setCursor() method can be ignored. Also, the Personal Java API supports the isDoubleBuffered() method, even though it is not part of the Java 1.1 API from which Personal Java is derived.
| public abstract class Component implements java.awt.image.ImageObserver, MenuContainer, Serializable { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected Component (); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| 1.1 | public static final float BOTTOM_ALIGNMENT ; | =1.0 |
| 1.1 | public static final float CENTER_ALIGNMENT ; | =0.5 |
| 1.1 | public static final float LEFT_ALIGNMENT ; | =0.0 |
| 1.1 | public static final float RIGHT_ALIGNMENT ; | =1.0 |
| 1.1 | public static final float TOP_ALIGNMENT ; | =0.0 |
| // | Event Registration Methods (by event name) | |
| 1.1 | public void addComponentListener (java.awt.event.ComponentListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void removeComponentListener (java.awt.event.ComponentListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void addFocusListener (java.awt.event.FocusListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void removeFocusListener (java.awt.event.FocusListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.2 | public void addInputMethodListener (java.awt.event.InputMethodListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.2 | public void removeInputMethodListener (java.awt.event.InputMethodListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void addKeyListener (java.awt.event.KeyListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void removeKeyListener (java.awt.event.KeyListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void addMouseListener (java.awt.event.MouseListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void removeMouseListener (java.awt.event.MouseListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void addMouseMotionListener (java.awt.event.MouseMotionListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void removeMouseMotionListener (java.awt.event.MouseMotionListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.2 | public void addPropertyChangeListener (java.beans.PropertyChangeListener listener); | synchronized |
| 1.2 | public void removePropertyChangeListener (java.beans.PropertyChangeListener listener); | synchronized |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.1 | public float getAlignmentX (); | |
| 1.1 | public float getAlignmentY (); | |
| public Color getBackground (); | ||
| public void setBackground (Color c); | ||
| 1.1 | public Rectangle getBounds (); | |
| 1.2 | public Rectangle getBounds (Rectangle rv); | |
| 1.1 | public void setBounds (Rectangle r); | |
| 1.1 | public void setBounds (int x, int y, int width, int height); | |
| public java.awt.image.ColorModel getColorModel (); | ||
| 1.2 | public ComponentOrientation getComponentOrientation (); | |
| 1.2 | public void setComponentOrientation (ComponentOrientation o); | |
| 1.1 | public Cursor getCursor (); | |
| 1.1 | public void setCursor (Cursor cursor); | synchronized |
| 1.2 | public boolean isDisplayable (); | |
| 1.2 | public boolean isDoubleBuffered (); | constant |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.dnd.DropTarget getDropTarget (); | synchronized |
| 1.2 | public void setDropTarget (java.awt.dnd.DropTarget dt); | synchronized |
| public boolean isEnabled (); | ||
| 1.1 | public void setEnabled (boolean b); | |
| 1.1 | public boolean isFocusTraversable (); | |
| public Font getFont (); | Implements:MenuContainer | |
| public void setFont (Font f); | ||
| public Color getForeground (); | ||
| public void setForeground (Color c); | ||
| public Graphics getGraphics (); | ||
| 1.2 | public int getHeight (); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.im.InputContext getInputContext (); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.im.InputMethodRequests getInputMethodRequests (); | constant |
| 1.2 | public boolean isLightweight (); | |
| 1.1 | public java.util.Locale getLocale (); | |
| 1.1 | public void setLocale (java.util.Locale l); | |
| 1.1 | public Point getLocation (); | |
| 1.2 | public Point getLocation (Point rv); | |
| 1.1 | public void setLocation (Point p); | |
| 1.1 | public void setLocation (int x, int y); | |
| 1.1 | public Point getLocationOnScreen (); | |
| 1.1 | public Dimension getMaximumSize (); | |
| 1.1 | public Dimension getMinimumSize (); | |
| 1.1 | public String getName (); | |
| 1.1 | public void setName (String name); | |
| 1.2 | public boolean isOpaque (); | |
| public Container getParent (); | ||
| 1.1 | public Dimension getPreferredSize (); | |
| public boolean isShowing (); | ||
| 1.1 | public Dimension getSize (); | |
| 1.2 | public Dimension getSize (Dimension rv); | |
| 1.1 | public void setSize (Dimension d); | |
| 1.1 | public void setSize (int width, int height); | |
| public Toolkit getToolkit (); | ||
| 1.1 | public final Object getTreeLock (); | |
| public boolean isValid (); | ||
| public boolean isVisible (); | ||
| 1.1 | public void setVisible (boolean b); | |
| 1.2 | public int getWidth (); | |
| 1.2 | public int getX (); | |
| 1.2 | public int getY (); | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| 1.1 | public void add (PopupMenu popup); | synchronized |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| 1.2 | public void addPropertyChangeListener (String propertyName, java.beans.PropertyChangeListener listener); | synchronized |
| public int checkImage (Image image, java.awt.image.ImageObserver observer); | ||
| public int checkImage (Image image, int width, int height, java.awt.image.ImageObserver observer); | ||
| 1.1 | public boolean contains (Point p); | |
| 1.1 | public boolean contains (int x, int y); | |
| public Image createImage (java.awt.image.ImageProducer producer); | ||
| public Image createImage (int width, int height); | ||
| 1.1 | public final void dispatchEvent (AWTEvent e); | |
| 1.1 | public void doLayout (); | |
| 1.2 | public void enableInputMethods (boolean enable); | |
| 1.1 | public Component getComponentAt (Point p); | |
| 1.1 | public Component getComponentAt (int x, int y); | |
| public FontMetrics getFontMetrics (Font font); | ||
| 1.2 | public boolean hasFocus (); | |
| public void invalidate (); | ||
| public void list (); | ||
| 1.1 | public void list (java.io.PrintWriter out); | |
| public void list (java.io.PrintStream out); | ||
| 1.1 | public void list (java.io.PrintWriter out, int indent); | |
| public void list (java.io.PrintStream out, int indent); | ||
| public void paint (Graphics g); | empty | |
| public void paintAll (Graphics g); | ||
| public boolean prepareImage (Image image, java.awt.image.ImageObserver observer); | ||
| public boolean prepareImage (Image image, int width, int height, java.awt.image.ImageObserver observer); | ||
| public void print (Graphics g); | ||
| public void printAll (Graphics g); | ||
| public void removeNotify (); | ||
| 1.2 | public void removePropertyChangeListener (String propertyName, java.beans.PropertyChangeListener listener); | synchronized |
| public void repaint (); | ||
| public void repaint (long tm); | ||
| public void repaint (int x, int y, int width, int height); | ||
| public void repaint (long tm, int x, int y, int width, int height); | ||
| public void requestFocus (); | ||
| 1.1 | public void transferFocus (); | |
| public void update (Graphics g); | ||
| public void validate (); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing ImageObserver | |
| public boolean imageUpdate (Image img, int flags, int x, int y, int w, int h); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing MenuContainer | |
| public Font getFont (); | ||
| 1.1 | public void remove (MenuComponent popup); | synchronized |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| 1.2 | protected AWTEvent coalesceEvents (AWTEvent existingEvent, AWTEvent newEvent); | |
| 1.1 | protected final void disableEvents (long eventsToDisable); | |
| 1.1 | protected final void enableEvents (long eventsToEnable); | |
| 1.2 | protected void firePropertyChange (String propertyName, Object oldValue, Object newValue); | |
| protected String paramString (); | ||
| 1.1 | protected void processComponentEvent (java.awt.event.ComponentEvent e); | |
| 1.1 | protected void processEvent (AWTEvent e); | |
| 1.1 | protected void processFocusEvent (java.awt.event.FocusEvent e); | |
| 1.2 | protected void processInputMethodEvent (java.awt.event.InputMethodEvent e); | |
| 1.1 | protected void processKeyEvent (java.awt.event.KeyEvent e); | |
| 1.1 | protected void processMouseEvent (java.awt.event.MouseEvent e); | |
| 1.1 | protected void processMouseMotionEvent (java.awt.event.MouseEvent e); | |
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public boolean action (Event evt, Object what); | constant |
| # | public Rectangle bounds (); | |
| # | public void deliverEvent (Event e); | |
| # | public void disable (); | |
| # | public void enable (); | |
| # | public void enable (boolean b); | |
| # | public java.awt.peer.ComponentPeer getPeer (); | |
| # | public boolean gotFocus (Event evt, Object what); | constant |
| # | public boolean handleEvent (Event evt); | |
| # | public void hide (); | |
| # | public boolean inside (int x, int y); | |
| # | public boolean keyDown (Event evt, int key); | constant |
| # | public boolean keyUp (Event evt, int key); | constant |
| # | public void layout (); | empty |
| # | public Component locate (int x, int y); | |
| # | public Point location (); | |
| # | public boolean lostFocus (Event evt, Object what); | constant |
| # | public Dimension minimumSize (); | |
| # | public boolean mouseDown (Event evt, int x, int y); | constant |
| # | public boolean mouseDrag (Event evt, int x, int y); | constant |
| # | public boolean mouseEnter (Event evt, int x, int y); | constant |
| # | public boolean mouseExit (Event evt, int x, int y); | constant |
| # | public boolean mouseMove (Event evt, int x, int y); | constant |
| # | public boolean mouseUp (Event evt, int x, int y); | constant |
| # | public void move (int x, int y); | |
| # | public void nextFocus (); | |
| # | public boolean postEvent (Event e); | Implements:MenuContainer |
| # | public Dimension preferredSize (); | |
| # | public void reshape (int x, int y, int width, int height); | |
| # | public void resize (Dimension d); | |
| # | public void resize (int width, int height); | |
| # | public void show (); | |
| # | public void show (boolean b); | |
| # | public Dimension size (); | |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Component(java.awt.image.ImageObserver,MenuContainer,Serializable)
Subclasses: Button, Canvas, Checkbox, Choice, Container, Label, java.awt.List, Scrollbar, TextComponent, javax.swing.Box.Filler
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Too many methods to list.
Type Of: Too many fields to list.
| ComponentOrientation | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable | |
This class encapsulates differences in the way characters in GUI components are arranged into lines and the way lines are grouped into blocks. In western languages like English, characters are arranged left to right and lines are arranged top to bottom, but this is not true throughout the world. In Hebrew, for example, characters are arranged from right to left, and in traditional Chinese, characters are arranged from top to bottom.
The isHorizontal() and isLeftToRight() methods specify the necessary orientation information. The class defines two constants for commonly used orientation types. Authors of AWT, Swing, and JavaBeans components may want to take orientation into account when developing their components (see the getComponentOrientation() method of Component). Applications that use these components should typically not have to worry about this class.
You can query the default orientation for a given java.util.Locale by calling the static getOrientation() method. Set the componentOrientation property of all components in a window by passing a ResourceBundle object to the applyResourceBundle() method of a Window. This looks up the "Orientation" resource in the bundle and, if it is not found, uses the default orientation for the locale of the bundle.
| public final class ComponentOrientation implements Serializable { | ||
| // | No Constructor | |
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final ComponentOrientation LEFT_TO_RIGHT ; | ||
| public static final ComponentOrientation RIGHT_TO_LEFT ; | ||
| public static final ComponentOrientation UNKNOWN ; | ||
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| public static ComponentOrientation getOrientation (java.util.ResourceBundle bdl); | ||
| public static ComponentOrientation getOrientation (java.util.Locale locale); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public boolean isHorizontal (); | ||
| public boolean isLeftToRight (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->ComponentOrientation(Serializable)
Passed To: Component.setComponentOrientation()
Returned By: Component.getComponentOrientation(), ComponentOrientation.getOrientation()
Type Of: ComponentOrientation.{LEFT_TO_RIGHT, RIGHT_TO_LEFT, UNKNOWN}
| Composite | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | ||
This interface defines how two colors are combined to yield a composite color. When Java 2D performs a drawing operation, it uses a Composite object to combine the colors it wants to draw with the colors that already exist on the screen or in the off-screen image.
The default compositing operation is to draw the new color on top of the color already on the screen. If the new color is fully opaque, the existing color is ignored. If the new color is partially transparent, however, it is combined with the color already on the screen to produce a composite color. To specify a different compositing operation, pass a Composite object to the setComposite() method of a Graphics2D object.
AlphaComposite is a commonly used implementation of Composite; it combines colors in a number of possible ways based on their alpha-transparency levels. AlphaComposite is suitable for most uses; very few applications should have to define a custom implementation of Composite.
Note that the only method of Composite, createContext(), does not perform compositing itself. Instead, it returns a CompositeContext object suitable for compositing colors encoded using the specified color models and rendering hints. It is the CompositeContext object that performs the actual work of combining colors.
| public abstract interface Composite { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract CompositeContext createContext (java.awt.image.ColorModel srcColorModel, java.awt.image.ColorModel dstColorModel, RenderingHints hints); | ||
| } | ||
Implementations: AlphaComposite
Passed To: Graphics2D.setComposite()
Returned By: Graphics2D.getComposite()
| CompositeContext | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | ||
This interface defines the methods that do the actual work of compositing colors. The CompositeContext interface is used internally by Java 2D; applications never need to call CompositeContext methods. And only applications that implement a custom Composite class need to implement this interface.
A CompositeContext object holds the state for a particular compositing operation (in multi-threaded programs, there may be several compositing operations in progress at once). A Graphics2D object creates CompositeContext objects as needed by calling the createContext() method of its Composite object.
Once a CompositeContext object has been created, its compose() method is responsible for combining the colors of the first two Raster objects passed to it and storing the resulting colors in the specified WriteableRaster. (This WriteableRaster is usually the same object as one of the first two arguments.) The dispose() method should free any resources held by the CompositeContext. It is called when the Graphics2D no longer requires the CompositeContext.
| public abstract interface CompositeContext { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract void compose (java.awt.image.Raster src, java.awt.image.Raster dstIn, java.awt.image.WritableRaster dstOut); | ||
| public abstract void dispose (); | ||
| } | ||
Returned By: AlphaComposite.createContext(), Composite.createContext()
| Container | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1 | |
This class implements a component that can contain other components. You cannot instantiate Container directly but must use one of its subclasses, such as Panel, Frame, or Dialog. Once a Container is created, you can set its LayoutManager with setLayout(), add components to it with add(), and remove them with remove(). getComponents() returns an array of the components contained in a Container. locate() determines within which contained component a specified point falls. list() produces helpful debugging output.
| public class Container extends Component { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Container (); | ||
| // | Event Registration Methods (by event name) | |
| 1.1 | public void addContainerListener (java.awt.event.ContainerListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void removeContainerListener (java.awt.event.ContainerListener l); | synchronized |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.1 | public float getAlignmentX (); | Overrides:Component default:0.5 |
| 1.1 | public float getAlignmentY (); | Overrides:Component default:0.5 |
| 1.1 | public int getComponentCount (); | default:0 |
| public Component[ ] getComponents (); | ||
| 1.2 | public void setCursor (Cursor cursor); | Overrides:Component synchronized |
| 1.2 | public void setFont (Font f); | Overrides:Component |
| 1.1 | public Insets getInsets (); | |
| public LayoutManager getLayout (); | default:null | |
| public void setLayout (LayoutManager mgr); | ||
| 1.1 | public Dimension getMaximumSize (); | Overrides:Component |
| 1.1 | public Dimension getMinimumSize (); | Overrides:Component |
| 1.1 | public Dimension getPreferredSize (); | Overrides:Component |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public Component add (Component comp); | ||
| 1.1 | public void add (Component comp, Object constraints); | |
| public Component add (String name, Component comp); | ||
| public Component add (Component comp, int index); | ||
| 1.1 | public void add (Component comp, Object constraints, int index); | |
| 1.2 | public Component findComponentAt (Point p); | |
| 1.2 | public Component findComponentAt (int x, int y); | |
| public Component getComponent (int n); | ||
| 1.1 | public boolean isAncestorOf (Component c); | |
| public void paintComponents (Graphics g); | ||
| public void printComponents (Graphics g); | ||
| public void remove (Component comp); | ||
| 1.1 | public void remove (int index); | |
| public void removeAll (); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Component | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| 1.1 | public void doLayout (); | |
| 1.1 | public Component getComponentAt (Point p); | |
| 1.1 | public Component getComponentAt (int x, int y); | |
| 1.1 | public void invalidate (); | |
| 1.1 | public void list (java.io.PrintWriter out, int indent); | |
| public void list (java.io.PrintStream out, int indent); | ||
| 1.1 | public void paint (Graphics g); | |
| 1.1 | public void print (Graphics g); | |
| public void removeNotify (); | ||
| 1.1 | public void update (Graphics g); | |
| public void validate (); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Component | |
| protected String paramString (); | ||
| 1.1 | protected void processEvent (AWTEvent e); | |
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| 1.1 | protected void addImpl (Component comp, Object constraints, int index); | |
| 1.1 | protected void processContainerEvent (java.awt.event.ContainerEvent e); | |
| 1.1 | protected void validateTree (); | |
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public int countComponents (); | |
| # | public void deliverEvent (Event e); | Overrides:Component |
| # | public Insets insets (); | |
| # | public void layout (); | Overrides:Component |
| # | public Component locate (int x, int y); | Overrides:Component |
| # | public Dimension minimumSize (); | Overrides:Component |
| # | public Dimension preferredSize (); | Overrides:Component |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Component(java.awt.image.ImageObserver,MenuContainer,Serializable)-->Container
Subclasses: Panel, ScrollPane, Window, javax.swing.Box, javax.swing.CellRendererPane, javax.swing.JComponent, javax.swing.tree.DefaultTreeCellEditor.EditorContainer
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Too many methods to list.
Type Of: javax.swing.JRootPane.contentPane, javax.swing.tree.DefaultTreeCellEditor.editingContainer
| Cursor | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable PJ1.1 | |
This class represents a mouse cursor. It defines a number of constants, which represent the 14 predefined cursors provided by Java 1.0 and Java 1.1. You can pass one of these constants to the constructor to create a cursor of the specified type. Call getType() to determine the type of an existing Cursor object. Since there are only a fixed number of available cursors, the static method getPredefinedCursor() is more efficient than the Cursor() constructor--it maintains a cache of Cursor objects that can be reused. The static getDefaultCursor() method returns the default cursor for the underlying system.
In Java 1.2, the Cursor class has a new getSystemCustomCursor() method that returns a named cursor defined by a system administrator in a systemwide cursors.properties file. Since there is no way to query the list of system-specific custom cursors, however, this method is rarely used. Instead, you can create your own custom cursor by calling the createCustomCursor() method of the Toolkit object. You should first check whether custom cursors are supported by calling the getBestCursorSize() method of Toolkit. If this method indicates a width or height of 0, custom cursors are not supported (by either the Java implementation or the underlying windowing system).
| public class Cursor implements Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Cursor (int type); | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| 1.2 | protected Cursor (String name); | |
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int CROSSHAIR_CURSOR ; | =1 | |
| 1.2 | public static final int CUSTOM_CURSOR ; | =-1 |
| public static final int DEFAULT_CURSOR ; | =0 | |
| public static final int E_RESIZE_CURSOR ; | =11 | |
| public static final int HAND_CURSOR ; | =12 | |
| public static final int MOVE_CURSOR ; | =13 | |
| public static final int N_RESIZE_CURSOR ; | =8 | |
| public static final int NE_RESIZE_CURSOR ; | =7 | |
| public static final int NW_RESIZE_CURSOR ; | =6 | |
| public static final int S_RESIZE_CURSOR ; | =9 | |
| public static final int SE_RESIZE_CURSOR ; | =5 | |
| public static final int SW_RESIZE_CURSOR ; | =4 | |
| public static final int TEXT_CURSOR ; | =2 | |
| public static final int W_RESIZE_CURSOR ; | =10 | |
| public static final int WAIT_CURSOR ; | =3 | |
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| public static Cursor getDefaultCursor (); | ||
| public static Cursor getPredefinedCursor (int type); | ||
| 1.2 | public static Cursor getSystemCustomCursor (String name) throws AWTException; | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| 1.2 | public String getName (); | |
| public int getType (); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| 1.2 | public String toString (); | |
| // | Protected Class Fields | |
| protected static Cursor[ ] predefined ; | ||
| // | Protected Instance Fields | |
| 1.2 | protected String name ; | |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Cursor(Serializable)
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Too many methods to list.
Type Of: Cursor.predefined, java.awt.dnd.DragSource.{DefaultCopyDrop, DefaultCopyNoDrop, DefaultLinkDrop, DefaultLinkNoDrop, DefaultMoveDrop, DefaultMoveNoDrop}
| Dialog | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1(mod) | |
This class represents a dialog box window. A Dialog can be modal, so that it blocks user input to all other windows until dismissed. It is optional whether a dialog has a title and whether it is resizable. A Dialog object is a Container, so you can add Component objects to it in the normal way with the add() method. The default LayoutManager for Dialog is BorderLayout. You can specify a different LayoutManager object with setLayout(). Call the pack() method of Window to initiate layout management of the dialog and set its initial size appropriately. Call show() to pop a dialog up and setVisible(false) to pop it down. For modal dialogs, show() blocks until the dialog is dismissed. Event handling continues while show() is blocked, using a new event dispatcher thread. In Java 1.0, show() is inherited from Window. Call the Window.dispose() method when the Dialog is no longer needed so that its window system resources may be reused.
In Personal Java environments, support for modeless dialogs is optional, and the Dialog() constructors can throw an exception if you attempt to create a modeless dialog. Also, the setResizable() method is optional, and calls to it can be ignored.
| public class Dialog extends Window { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| 1.1 | public Dialog (Frame owner); | |
| 1.2 | public Dialog (Dialog owner); | |
| 1.2 | public Dialog (Dialog owner, String title); | |
| 1.1 | public Dialog (Frame owner, String title); | |
| public Dialog (Frame owner, boolean modal); | ||
| public Dialog (Frame owner, String title, boolean modal); | ||
| 1.2 | public Dialog (Dialog owner, String title, boolean modal); | |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public boolean isModal (); | ||
| 1.1 | public void setModal (boolean b); | |
| public boolean isResizable (); | ||
| public void setResizable (boolean resizable); | ||
| public String getTitle (); | ||
| public void setTitle (String title); | synchronized | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Window | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| 1.2 | public void dispose (); | |
| 1.2 | public void hide (); | |
| 1.1 | public void show (); | |
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Container | |
| protected String paramString (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Component(java.awt.image.ImageObserver,MenuContainer,Serializable)-->Container-->Window-->Dialog
Subclasses: FileDialog, javax.swing.JDialog
Passed To: Dialog.Dialog(), Toolkit.createDialog(), javax.swing.JDialog.JDialog()
| Dimension | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | cloneable serializable PJ1.1 | |
This class contains two integer fields that describe a width and a height of something. The fields are public and can be manipulated directly.
In Java 1.0 and Java 1.1, Dimension is a subclass of Object. In Java 1.2, with the introduction of Java 2D, it has become a concrete subclass of java.awt.geom.Dimension2D. Contrast Dimension with Dimension2D,which represents the width and height with double values.
| public class Dimension extends java.awt.geom.Dimension2D implements Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Dimension (); | ||
| public Dimension (Dimension d); | ||
| public Dimension (int width, int height); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| 1.1 | public Dimension getSize (); | |
| 1.1 | public void setSize (Dimension d); | |
| 1.1 | public void setSize (int width, int height); | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Dimension2D | |
| 1.2 | public double getHeight (); | default:0.0 |
| 1.2 | public double getWidth (); | default:0.0 |
| 1.2 | public void setSize (double width, double height); | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| 1.1 | public boolean equals (Object obj); | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public int height ; | ||
| public int width ; | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->java.awt.geom.Dimension2D(Cloneable)-->Dimension(Serializable)
Subclasses: javax.swing.plaf.DimensionUIResource
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Too many methods to list.
Type Of: javax.swing.JTable.preferredViewportSize
| Event | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable PJ1.1 | |
This class contains public instance variables that describe some kind of GUI event. In Java 1.1, this class has been superseded by AWTEvent and the java.awt.event package.
The class contains a large number of constants. Some of the constants specify the event type and are values for the id variable. Other constants are values for keys, such as the function keys, that do not have ASCII (Latin-1) values and are set on the key field. Other constants are mask values that are ORed into the modifiers field to describe the state of the modifier keys on the keyboard. The target field is very important--it is the object for which the event occurred. The when field specifies when the event occurred. The x and y fields specify the mouse coordinates at which it occurred. Finally, the arg field is a value specific to the type of the event. Not all fields have valid values for all types of events.
| public class Event implements Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Event (Object target, int id, Object arg); | ||
| public Event (Object target, long when, int id, int x, int y, int key, int modifiers); | ||
| public Event (Object target, long when, int id, int x, int y, int key, int modifiers, Object arg); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int ACTION_EVENT ; | =1001 | |
| public static final int ALT_MASK ; | =8 | |
| 1.1 | public static final int BACK_SPACE ; | =8 |
| 1.1 | public static final int CAPS_LOCK ; | =1022 |
| public static final int CTRL_MASK ; | =2 | |
| 1.1 | public static final int DELETE ; | =127 |
| public static final int DOWN ; | =1005 | |
| public static final int END ; | =1001 | |
| 1.1 | public static final int ENTER ; | =10 |
| 1.1 | public static final int ESCAPE ; | =27 |
| public static final int F1 ; | =1008 | |
| public static final int F10 ; | =1017 | |
| public static final int F11 ; | =1018 | |
| public static final int F12 ; | =1019 | |
| public static final int F2 ; | =1009 | |
| public static final int F3 ; | =1010 | |
| public static final int F4 ; | =1011 | |
| public static final int F5 ; | =1012 | |
| public static final int F6 ; | =1013 | |
| public static final int F7 ; | =1014 | |
| public static final int F8 ; | =1015 | |
| public static final int F9 ; | =1016 | |
| public static final int GOT_FOCUS ; | =1004 | |
| public static final int HOME ; | =1000 | |
| 1.1 | public static final int INSERT ; | =1025 |
| public static final int KEY_ACTION ; | =403 | |
| public static final int KEY_ACTION_RELEASE ; | =404 | |
| public static final int KEY_PRESS ; | =401 | |
| public static final int KEY_RELEASE ; | =402 | |
| public static final int LEFT ; | =1006 | |
| public static final int LIST_DESELECT ; | =702 | |
| public static final int LIST_SELECT ; | =701 | |
| public static final int LOAD_FILE ; | =1002 | |
| public static final int LOST_FOCUS ; | =1005 | |
| public static final int META_MASK ; | =4 | |
| public static final int MOUSE_DOWN ; | =501 | |
| public static final int MOUSE_DRAG ; | =506 | |
| public static final int MOUSE_ENTER ; | =504 | |
| public static final int MOUSE_EXIT ; | =505 | |
| public static final int MOUSE_MOVE ; | =503 | |
| public static final int MOUSE_UP ; | =502 | |
| 1.1 | public static final int NUM_LOCK ; | =1023 |
| 1.1 | public static final int PAUSE ; | =1024 |
| public static final int PGDN ; | =1003 | |
| public static final int PGUP ; | =1002 | |
| 1.1 | public static final int PRINT_SCREEN ; | =1020 |
| public static final int RIGHT ; | =1007 | |
| public static final int SAVE_FILE ; | =1003 | |
| public static final int SCROLL_ABSOLUTE ; | =605 | |
| 1.1 | public static final int SCROLL_BEGIN ; | =606 |
| 1.1 | public static final int SCROLL_END ; | =607 |
| public static final int SCROLL_LINE_DOWN ; | =602 | |
| public static final int SCROLL_LINE_UP ; | =601 | |
| 1.1 | public static final int SCROLL_LOCK ; | =1021 |
| public static final int SCROLL_PAGE_DOWN ; | =604 | |
| public static final int SCROLL_PAGE_UP ; | =603 | |
| public static final int SHIFT_MASK ; | =1 | |
| 1.1 | public static final int TAB ; | =9 |
| public static final int UP ; | =1004 | |
| public static final int WINDOW_DEICONIFY ; | =204 | |
| public static final int WINDOW_DESTROY ; | =201 | |
| public static final int WINDOW_EXPOSE ; | =202 | |
| public static final int WINDOW_ICONIFY ; | =203 | |
| public static final int WINDOW_MOVED ; | =205 | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public boolean controlDown (); | ||
| public boolean metaDown (); | ||
| public boolean shiftDown (); | ||
| public void translate (int x, int y); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| protected String paramString (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public Object arg ; | ||
| public int clickCount ; | ||
| public Event evt ; | ||
| public int id ; | ||
| public int key ; | ||
| public int modifiers ; | ||
| public Object target ; | ||
| public long when ; | ||
| public int x ; | ||
| public int y ; | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Event(Serializable)
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Type Of: Event.evt
| EventQueue | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | PJ1.1 | |
This class implements an event queue for AWT events in Java 1.1. When an EventQueue is created, a new thread is automatically created and started to remove events from the front of the queue and dispatch them to the appropriate component. It is this thread, created by the EventQueue, that notifies event listeners and executes most of the code in a typical GUI-driven application.
An application can create and use its own private EventQueue, but all AWT events are placed on and dispatched from a single system EventQueue. Use the getSystemEventQueue() method of the Toolkit class to get the system EventQueue object.
getNextEvent() removes and returns the event at the front of the queue. It blocks if there are no events in the queue. peekEvent() returns the event at the front of the queue without removing it from the queue. Passed an optional AWTEventid field, it returns the first event of the specified type. Finally, postEvent() places a new event on the end of the event queue.
In Java 1.2, EventQueue defines three useful static methods. isDispatchThread() returns true if the calling thread is the AWT event dispatch thread. To avoid thread-safety issues, all modifications to AWT and Swing components should be done from this dispatch thread. If another thread needs to operate on a component, it should wrap the desired operation in a Runnable object and pass that object to invokeLater() or invokeAndWait(). These methods bundle the Runnable object into an ActiveEvent that is placed on the queue. When the ActiveEvent reaches the head of the queue, the Runnable code is invoked by the event dispatch thread and can safely modify any AWT and Swing components. invokeLater() returns immediately, while invokeAndWait() blocks until the Runnable code has been run. It is an error to call invokeAndWait() from the event dispatch thread itself. See also ActiveEvent and javax.swing.SwingUtilities. Except for these useful static methods, most applications do not need to use the EventQueue class at all; they can simply rely on the system to dispatch events automatically.
| public class EventQueue { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public EventQueue (); | ||
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| 1.2 | public static void invokeAndWait (Runnable runnable) throws InterruptedException, java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException; | |
| 1.2 | public static void invokeLater (Runnable runnable); | |
| 1.2 | public static boolean isDispatchThread (); | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public AWTEvent getNextEvent () throws InterruptedException; | synchronized | |
| public AWTEvent peekEvent (); | synchronized | |
| public AWTEvent peekEvent (int id); | synchronized | |
| public void postEvent (AWTEvent theEvent); | ||
| 1.2 | public void push (EventQueue newEventQueue); | synchronized |
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| 1.2 | protected void dispatchEvent (AWTEvent event); | |
| 1.2 | protected void pop () throws java.util.EmptyStackException; | |
| } | ||
Passed To: EventQueue.push()
Returned By: Toolkit.{getSystemEventQueue(), getSystemEventQueueImpl()}
| FileDialog | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1(opt) | |
This class represents a file selection dialog box. The constants LOAD and SAVE are values of an optional constructor argument that specifies whether the dialog should be an Open File dialog or a Save As dialog. You may specify a FilenameFilter object to control the files that are displayed in the dialog.
The inherited show() method pops the dialog up. For dialogs of this type, show() blocks, not returning until the user has selected a file and dismissed the dialog (which pops down automatically--you don't have to call hide()). Once show() has returned, use getFile() to get the name of the file the user selected.
| public class FileDialog extends Dialog { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| 1.1 | public FileDialog (Frame parent); | |
| public FileDialog (Frame parent, String title); | ||
| public FileDialog (Frame parent, String title, int mode); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int LOAD ; | =0 | |
| public static final int SAVE ; | =1 | |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public String getDirectory (); | ||
| public void setDirectory (String dir); | ||
| public String getFile (); | ||
| public void setFile (String file); | ||
| public java.io.FilenameFilter getFilenameFilter (); | ||
| public void setFilenameFilter (java.io.FilenameFilter filter); | synchronized | |
| public int getMode (); | ||
| 1.1 | public void setMode (int mode); | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Dialog | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Dialog | |
| protected String paramString (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Component(java.awt.image.ImageObserver,MenuContainer,Serializable)-->Container-->Window-->Dialog-->FileDialog
Passed To: Toolkit.createFileDialog()
| FlowLayout | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable layout manager PJ1.1 | |
A LayoutManager that arranges components in a container likes words on a page: from left to right and top to bottom. It fits as many components as it can in a row before moving on to the next row. The constructor allows you to specify one of five constants as an alignment value for the rows. LEFT, CENTER, and RIGHT specify left, center, and right alignment, obviously. LEADING and TRAILING alignment are the same as LEFT and RIGHT alignment in locales where writing is done left to right, but they have the opposite meaning in locales where writing is done primarily right to left. You can also specify the horizontal spacing between components and the vertical spacing between rows.
Applications should never call the LayoutManager methods of this class directly; the Container for which the FlowLayout is registered does this.
| public class FlowLayout implements LayoutManager, Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public FlowLayout (); | ||
| public FlowLayout (int align); | ||
| public FlowLayout (int align, int hgap, int vgap); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int CENTER ; | =1 | |
| 1.2 | public static final int LEADING ; | =3 |
| public static final int LEFT ; | =0 | |
| public static final int RIGHT ; | =2 | |
| 1.2 | public static final int TRAILING ; | =4 |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.1 | public int getAlignment (); | default:1 |
| 1.1 | public void setAlignment (int align); | |
| 1.1 | public int getHgap (); | default:5 |
| 1.1 | public void setHgap (int hgap); | |
| 1.1 | public int getVgap (); | default:5 |
| 1.1 | public void setVgap (int vgap); | |
| // | Methods Implementing LayoutManager | |
| public void addLayoutComponent (String name, Component comp); | empty | |
| public void layoutContainer (Container target); | ||
| public Dimension minimumLayoutSize (Container target); | ||
| public Dimension preferredLayoutSize (Container target); | ||
| public void removeLayoutComponent (Component comp); | empty | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->FlowLayout(LayoutManager,Serializable)
| Font | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable PJ1.1 | |
This class represents a font. The Font() constructor is passed a name, a style, and a point size. The style should be one of the constants PLAIN, BOLD, or ITALIC or the sum BOLD+ITALIC.
The allowed font names have changed with each release of Java. In Java 1.0, the supported font names are "TimesRoman", "Helvetica", "Courier", "Dialog", "DialogInput", and "Symbol". In Java 1.1, "serif", "sansserif", and "monospaced" should be used in preference to the first three names.
With the introduction of Java 2D, you may continue to use these logical names, but you are not limited to them. In Java 1.2, you may specify the name of any font family available on the system. These are names such as "Times New Roman," "Arial," "New Century Schoolbook," "Bookman," and so on. You can obtain a list of available font families by calling the getAvailableFontFamilyNames() method of GraphicsEnvironment. You may also pass the name of a specific font face to the Font() constructor. These are names such as "Copperplate DemiBold Oblique." When you specify the name of a specific font face, you typically specify a font style of PLAIN, since the style you want is implicit in the name.
With Java 1.2, you can also create a font by passing a Map object that contains attribute names and values to either the Font() constructor or the static getFont() method. The attribute names and values are defined by java.awt.font.TextAttribute. The TextAttribute constants FAMILY, WEIGHT, POSTURE, and SIZE identify the attributes of interest.
In Java 1.2, new fonts can be derived from old fonts in a variety of ways, using the deriveFont() methods. Most generally, the glyphs of a font may all be transformed with the specified AffineTransform.
If you need to know the height or width (or other metrics) of characters or strings drawn using a Font, call the getFontMetrics() method of a Graphics object to obtain a FontMetrics object. The methods of this object return font measurement information as integer values. In Java 1.2, you can obtain higher-precision floating-point font measurements with the getLineMetrics(), getMaxCharBounds(), and getStringBounds() methods of a Font. These methods require a FontRenderContext, which is obtained by calling the getFontRenderContext() method of Graphics2D.
The canDisplay() method tests whether a Font can display a given character (i.e., whether the font contains a glyph for that character). canDisplayUpTo() tests whether the Font can display all the characters in a string and returns the index of the first character it cannot display.
| public class Font implements Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| 1.2 | public Font (java.util.Map attributes); | |
| public Font (String name, int style, int size); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int BOLD ; | =1 | |
| 1.2 | public static final int CENTER_BASELINE ; | =1 |
| 1.2 | public static final int HANGING_BASELINE ; | =2 |
| public static final int ITALIC ; | =2 | |
| public static final int PLAIN ; | =0 | |
| 1.2 | public static final int ROMAN_BASELINE ; | =0 |
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| 1.1 | public static Font decode (String str); | |
| 1.2 | public static Font getFont (java.util.Map attributes); | |
| public static Font getFont (String nm); | ||
| public static Font getFont (String nm, Font font); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.2 | public java.util.Map getAttributes (); | |
| 1.2 | public java.text.AttributedCharacterIterator.Attribute[ ] getAvailableAttributes (); | |
| public boolean isBold (); | ||
| public String getFamily (); | ||
| 1.2 | public String getFamily (java.util.Locale l); | |
| 1.2 | public String getFontName (); | |
| 1.2 | public String getFontName (java.util.Locale l); | |
| public boolean isItalic (); | ||
| 1.2 | public float getItalicAngle (); | |
| 1.2 | public int getMissingGlyphCode (); | |
| public String getName (); | ||
| 1.2 | public int getNumGlyphs (); | |
| public boolean isPlain (); | ||
| 1.2 | public String getPSName (); | |
| public int getSize (); | ||
| 1.2 | public float getSize2D (); | |
| public int getStyle (); | ||
| 1.2 | public java.awt.geom.AffineTransform getTransform (); | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| 1.2 | public boolean canDisplay (char c); | |
| 1.2 | public int canDisplayUpTo (String str); | |
| 1.2 | public int canDisplayUpTo (char[ ] text, int start, int limit); | |
| 1.2 | public int canDisplayUpTo (java.text.CharacterIterator iter, int start, int limit); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.font.GlyphVector createGlyphVector (java.awt.font.FontRenderContext frc, java.text.CharacterIterator ci); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.font.GlyphVector createGlyphVector (java.awt.font.FontRenderContext frc, char[ ] chars); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.font.GlyphVector createGlyphVector (java.awt.font.FontRenderContext frc, int[ ] glyphCodes); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.font.GlyphVector createGlyphVector (java.awt.font.FontRenderContext frc, String str); | |
| 1.2 | public Font deriveFont (float size); | |
| 1.2 | public Font deriveFont (int style); | |
| 1.2 | public Font deriveFont (java.awt.geom.AffineTransform trans); | |
| 1.2 | public Font deriveFont (java.util.Map attributes); | |
| 1.2 | public Font deriveFont (int style, java.awt.geom.AffineTransform trans); | |
| 1.2 | public Font deriveFont (int style, float size); | |
| 1.2 | public byte getBaselineFor (char c); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.font.LineMetrics getLineMetrics (String str, java.awt.font.FontRenderContext frc); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.font.LineMetrics getLineMetrics (char[ ] chars, int beginIndex, int limit, java.awt.font.FontRenderContext frc); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.font.LineMetrics getLineMetrics (java.text.CharacterIterator ci, int beginIndex, int limit, java.awt.font.FontRenderContext frc); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.font.LineMetrics getLineMetrics (String str, int beginIndex, int limit, java.awt.font.FontRenderContext frc); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getMaxCharBounds (java.awt.font.FontRenderContext frc); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getStringBounds (String str, java.awt.font.FontRenderContext frc); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getStringBounds (char[ ] chars, int beginIndex, int limit, java.awt.font.FontRenderContext frc); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getStringBounds (java.text.CharacterIterator ci, int beginIndex, int limit, java.awt.font.FontRenderContext frc); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getStringBounds (String str, int beginIndex, int limit, java.awt.font.FontRenderContext frc); | |
| 1.2 | public boolean hasUniformLineMetrics (); | constant |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public boolean equals (Object obj); | ||
| public int hashCode (); | ||
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Object | |
| 1.2 | protected void finalize () throws Throwable; | |
| // | Protected Instance Fields | |
| protected String name ; | ||
| 1.2 | protected float pointSize ; | |
| protected int size ; | ||
| protected int style ; | ||
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| 1.1# | public java.awt.peer.FontPeer getPeer (); | |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Font(Serializable)
Subclasses: javax.swing.plaf.FontUIResource
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Too many methods to list.
Type Of: FontMetrics.font, javax.swing.border.TitledBorder.titleFont, javax.swing.tree.DefaultTreeCellEditor.font
| FontMetrics | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable PJ1.1 | |
This class represents font metrics for a specified Font. The methods allow you to determine the overall metrics for the font (ascent, descent, and so on) and compute the width of strings that are to be displayed in a particular font. The FontMetrics() constructor is protected; you can obtain a FontMetrics object for a font with the getFontMetrics() method of Component, Graphics, or Toolkit.
In Java 1.2, with the introduction of Java 2D, you can obtain more precise (floating-point) metrics using the getLineMetrics(), getMaxCharBounds(), and getStringBounds() methods of FontMetrics or a Font object itself. See also java.awt.font.LineMetrics.
| public abstract class FontMetrics implements Serializable { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected FontMetrics (Font font); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public int getAscent (); | ||
| public int getDescent (); | constant | |
| public Font getFont (); | ||
| public int getHeight (); | ||
| public int getLeading (); | constant | |
| public int getMaxAdvance (); | constant | |
| public int getMaxAscent (); | ||
| public int getMaxDescent (); | ||
| public int[ ] getWidths (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public int bytesWidth (byte[ ] data, int off, int len); | ||
| public int charsWidth (char[ ] data, int off, int len); | ||
| public int charWidth (int ch); | ||
| public int charWidth (char ch); | ||
| 1.2 | public java.awt.font.LineMetrics getLineMetrics (String str, Graphics context); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.font.LineMetrics getLineMetrics (char[ ] chars, int beginIndex, int limit, Graphics context); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.font.LineMetrics getLineMetrics (java.text.CharacterIterator ci, int beginIndex, int limit, Graphics context); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.font.LineMetrics getLineMetrics (String str, int beginIndex, int limit, Graphics context); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getMaxCharBounds (Graphics context); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getStringBounds (String str, Graphics context); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getStringBounds (char[ ] chars, int beginIndex, int limit, Graphics context); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getStringBounds (java.text.CharacterIterator ci, int beginIndex, int limit, Graphics context); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getStringBounds (String str, int beginIndex, int limit, Graphics context); | |
| 1.2 | public boolean hasUniformLineMetrics (); | |
| public int stringWidth (String str); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Protected Instance Fields | |
| protected Font font ; | ||
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public int getMaxDecent (); | |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->FontMetrics(Serializable)
Passed To: javax.swing.SwingUtilities.{computeStringWidth(), layoutCompoundLabel()}, javax.swing.text.Utilities.{getBreakLocation(), getTabbedTextOffset(), getTabbedTextWidth()}
Returned By: Too many methods to list.
Type Of: javax.swing.text.PlainView.metrics
| Frame | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1(mod) | |
This class represents an optionally resizable top-level application window with a titlebar and other platform-dependent window decorations. setTitle() specifies a title, setMenuBar() specifies a menu bar, setCursor() specifies a cursor, and setIconImage() specifies an icon for the window. Call the pack() method of Window to initiate layout management of the window and set its initial size appropriately. Call the show() method of Window to make the window appear and be brought to the top of the window stack. Call setVisible(false) to make the window disappear. Call setState(Frame.ICONIFIED) to iconify the window, and call setState(Frame.NORMAL) to deiconify it. Use getState() to determine whether the window is iconified or not. Call the static getFrames() method to obtain an array of all Frame objects that have been created by the application or applet. Call the dispose() method when the Frame is no longer needed, so that it can release its window system resources for reuse.
The constants defined by this class specify various cursor types. As of Java 1.1, these constants and the cursor methods of Frame are deprecated in favor of the Cursor class and cursor methods of Component.
Personal Java environments can support only a single Frame object, and any calls to the Frame() constructor after the first can throw an exception.
| public class Frame extends Window implements MenuContainer { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Frame (); | ||
| public Frame (String title); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| 1.2 | public static final int ICONIFIED ; | =1 |
| 1.2 | public static final int NORMAL ; | =0 |
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| 1.2 | public static Frame[ ] getFrames (); | |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public Image getIconImage (); | default:null | |
| public void setIconImage (Image image); | synchronized | |
| public MenuBar getMenuBar (); | default:null | |
| public void setMenuBar (MenuBar mb); | ||
| public boolean isResizable (); | default:true | |
| public void setResizable (boolean resizable); | ||
| 1.2 | public int getState (); | synchronized default:0 |
| 1.2 | public void setState (int state); | synchronized |
| public String getTitle (); | default:"" | |
| public void setTitle (String title); | synchronized | |
| // | Methods Implementing MenuContainer | |
| public void remove (MenuComponent m); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Window | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Window | |
| 1.2 | protected void finalize () throws Throwable; | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Container | |
| 1.2 | public void removeNotify (); | |
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Container | |
| protected String paramString (); | ||
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public int getCursorType (); | default:0 |
| # | public void setCursor (int cursorType); | synchronized |
| // | Deprecated Public Fields | |
| # | public static final int CROSSHAIR_CURSOR ; | =1 |
| # | public static final int DEFAULT_CURSOR ; | =0 |
| # | public static final int E_RESIZE_CURSOR ; | =11 |
| # | public static final int HAND_CURSOR ; | =12 |
| # | public static final int MOVE_CURSOR ; | =13 |
| # | public static final int N_RESIZE_CURSOR ; | =8 |
| # | public static final int NE_RESIZE_CURSOR ; | =7 |
| # | public static final int NW_RESIZE_CURSOR ; | =6 |
| # | public static final int S_RESIZE_CURSOR ; | =9 |
| # | public static final int SE_RESIZE_CURSOR ; | =5 |
| # | public static final int SW_RESIZE_CURSOR ; | =4 |
| # | public static final int TEXT_CURSOR ; | =2 |
| # | public static final int W_RESIZE_CURSOR ; | =10 |
| # | public static final int WAIT_CURSOR ; | =3 |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Component(java.awt.image.ImageObserver,MenuContainer,Serializable)-->Container-->Window-->Frame(MenuContainer)
Subclasses: javax.swing.JFrame
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Frame.getFrames(), javax.swing.JOptionPane.{getFrameForComponent(), getRootFrame()}
| GradientPaint | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | ||
This implementation of Paint fills shapes with a color gradient. To use a GradientPaint object for filling shapes, pass it to the setPaint() method of a Graphics2D object.
The color of the fill varies linearly between a color C1 and another color C2. The orientation of the color gradient is defined by a line between points P1 and P2. For example, if these points define a horizontal line, the color of the fill varies from left to right. If P1 is at the upper left of a rectangle and P2 is at the lower right, the fill color varies from upper left to lower right.
Color C1 is always used at point P1 and color C2 is used at P2. If the area to be filled includes points outside of the fill region defined by P1 and P2, these points can be filled in one of two ways. If the GradientPaint object is created with the cyclic constructor argument set to true, colors repeatedly cycle from C1 to C2 and back to C1 again. If cyclic is specified as false or if this argument is omitted, the gradient does not repeat. When an acyclic GradientPaint object is used, all points beyond P1 are given the color C1, and all points beyond C2 are given the color P2.
| public class GradientPaint implements Paint { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public GradientPaint (java.awt.geom.Point2D pt1, Color color1, java.awt.geom.Point2D pt2, Color color2); | ||
| public GradientPaint (java.awt.geom.Point2D pt1, Color color1, java.awt.geom.Point2D pt2, Color color2, boolean cyclic); | ||
| public GradientPaint (float x1, float y1, Color color1, float x2, float y2, Color color2); | ||
| public GradientPaint (float x1, float y1, Color color1, float x2, float y2, Color color2, boolean cyclic); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public Color getColor1 (); | ||
| public Color getColor2 (); | ||
| public boolean isCyclic (); | ||
| public java.awt.geom.Point2D getPoint1 (); | ||
| public java.awt.geom.Point2D getPoint2 (); | ||
| public int getTransparency (); | Implements:Transparency | |
| // | Methods Implementing Paint | |
| public PaintContext createContext (java.awt.image.ColorModel cm, Rectangle deviceBounds, java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D userBounds, java.awt.geom.AffineTransform xform, RenderingHints hints); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing Transparency | |
| public int getTransparency (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->GradientPaint(Paint(Transparency))
| Graphics | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | PJ1.1(mod) | |
This abstract class defines a device-independent interface to graphics. It specifies methods for drawing lines, filling areas, painting images, copying areas, and clipping graphics output. Specific subclasses of Graphics are implemented for different platforms and different graphics output devices. A Graphics object cannot be created directly through a constructor--it must either be obtained with the getGraphics() method of a Component or an Image or copied from an existing Graphics object with create(). When a Graphics object is no longer needed, you should call dispose() to free up the window system resources it uses.
In Personal Java environments, the setXORMode() method may be unsupported.
| public abstract class Graphics { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected Graphics (); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.1 | public abstract Shape getClip (); | |
| 1.1 | public abstract void setClip (Shape clip); | |
| 1.1 | public abstract void setClip (int x, int y, int width, int height); | |
| 1.1 | public abstract Rectangle getClipBounds (); | |
| 1.2 | public Rectangle getClipBounds (Rectangle r); | |
| public abstract Color getColor (); | ||
| public abstract void setColor (Color c); | ||
| public abstract Font getFont (); | ||
| public abstract void setFont (Font font); | ||
| public FontMetrics getFontMetrics (); | ||
| public abstract FontMetrics getFontMetrics (Font f); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract void clearRect (int x, int y, int width, int height); | ||
| public abstract void clipRect (int x, int y, int width, int height); | ||
| public abstract void copyArea (int x, int y, int width, int height, int dx, int dy); | ||
| public abstract Graphics create (); | ||
| public Graphics create (int x, int y, int width, int height); | ||
| public abstract void dispose (); | ||
| public void draw3DRect (int x, int y, int width, int height, boolean raised); | ||
| public abstract void drawArc (int x, int y, int width, int height, int startAngle, int arcAngle); | ||
| public void drawBytes (byte[ ] data, int offset, int length, int x, int y); | ||
| public void drawChars (char[ ] data, int offset, int length, int x, int y); | ||
| public abstract boolean drawImage (Image img, int x, int y, java.awt.image.ImageObserver observer); | ||
| public abstract boolean drawImage (Image img, int x, int y, Color bgcolor, java.awt.image.ImageObserver observer); | ||
| public abstract boolean drawImage (Image img, int x, int y, int width, int height, java.awt.image.ImageObserver observer); | ||
| public abstract boolean drawImage (Image img, int x, int y, int width, int height, Color bgcolor, java.awt.image.ImageObserver observer); | ||
| 1.1 | public abstract boolean drawImage (Image img, int dx1, int dy1, int dx2, int dy2, int sx1, int sy1, int sx2, int sy2, java.awt.image.ImageObserver observer); | |
| 1.1 | public abstract boolean drawImage (Image img, int dx1, int dy1, int dx2, int dy2, int sx1, int sy1, int sx2, int sy2, Color bgcolor, java.awt.image.ImageObserver observer); | |
| public abstract void drawLine (int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2); | ||
| public abstract void drawOval (int x, int y, int width, int height); | ||
| public void drawPolygon (Polygon p); | ||
| public abstract void drawPolygon (int[ ] xPoints, int[ ] yPoints, int nPoints); | ||
| 1.1 | public abstract void drawPolyline (int[ ] xPoints, int[ ] yPoints, int nPoints); | |
| public void drawRect (int x, int y, int width, int height); | ||
| public abstract void drawRoundRect (int x, int y, int width, int height, int arcWidth, int arcHeight); | ||
| 1.2 | public abstract void drawString (java.text.AttributedCharacterIterator iterator, int x, int y); | |
| public abstract void drawString (String str, int x, int y); | ||
| public void fill3DRect (int x, int y, int width, int height, boolean raised); | ||
| public abstract void fillArc (int x, int y, int width, int height, int startAngle, int arcAngle); | ||
| public abstract void fillOval (int x, int y, int width, int height); | ||
| public void fillPolygon (Polygon p); | ||
| public abstract void fillPolygon (int[ ] xPoints, int[ ] yPoints, int nPoints); | ||
| public abstract void fillRect (int x, int y, int width, int height); | ||
| public abstract void fillRoundRect (int x, int y, int width, int height, int arcWidth, int arcHeight); | ||
| 1.2 | public boolean hitClip (int x, int y, int width, int height); | |
| public abstract void setPaintMode (); | ||
| public abstract void setXORMode (Color c1); | ||
| public abstract void translate (int x, int y); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public void finalize (); | ||
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public Rectangle getClipRect (); | |
| } | ||
Subclasses: Graphics2D, javax.swing.DebugGraphics
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Component.getGraphics(), Graphics.create(), Image.getGraphics(), PrintJob.getGraphics(), java.awt.image.BufferedImage.getGraphics(), java.awt.peer.ComponentPeer.getGraphics(), javax.swing.DebugGraphics.create(), javax.swing.JComponent.{getComponentGraphics(), getGraphics()}
| Graphics2D | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | ||
This class is the Java 2D graphics context that encapsulates all drawing and filling operations. It generalizes and extends the Graphics class. A number of attributes control how the Graphics2D object performs drawing and filling operations. You can set these attributes with the following methods:
- setBackground()
-
Specifies the background color used by the clearRect() method of the Graphics object. Prior to Java 2D, the background color could not be set.
- setClip()
-
Sets the clipping region, outside of which no drawing is done. This method is inherited from the Graphics object. Use setClip() to establish an initial clipping region and then use clip() to narrow that region by intersecting it with other regions.
- setComposite()
-
Specifies a Composite object (typically an instance of AlphaComposite) that should be used to combine drawing colors with the colors that are already present on the drawing surface.
- setFont()
-
Sets the default Font object used to draw text. This is a Graphics method, inherited by Graphics2D.
- setPaint()
-
Specifies the Paint object that controls the color or pattern used for drawing. See Color, GradientPaint, and TexturePaint.
- setRenderingHints()
-
Sets hints about how drawing should be done. This method allows you to turn antialiasing and color dithering on and off, for example. You can also set hints with addRenderingHints() and setRenderingHint().
- setStroke()
-
Specifies the Stroke object (typically an instance of BasicStroke) used to trace the outline of shapes that are drawn. The Stroke object effectively defines the pen that is used for drawing operations.
- setTransform()
-
Sets the AffineTransform object used to convert from user coordinates to device coordinates. Note that you do not usually call setTransform() directly, but instead modify the current transform with transform() or the more specific rotate(), scale(), shear(), and translate() methods.
Once you have used these methods to configure a Graphics2D object as desired, you can proceed to draw with it. The following methods are commonly used:
- draw()
-
Draw the outline of a Shape, using the line style specified by the current Stroke object and the color or pattern specified by the current Paint object. The java.awt.geom package contains a number of commonly used implementations of the Shape interface.
- fill()
-
Fill the interior of a Shape, using the color or pattern specified by the current Paint object.
- drawString()
-
Draw the specified text using the specified Font object and Paint object. drawGlyphVector() is similar. See also the drawString() methods inherited from Graphics.
- drawImage()
-
Draw an Image with an optional filtering operation and/or an optional transformation. Also drawRenderableImage() and drawRenderedImage(). See also the drawImage() methods inherited from Graphics.
| public abstract class Graphics2D extends Graphics { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected Graphics2D (); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract Color getBackground (); | ||
| public abstract void setBackground (Color color); | ||
| public abstract Composite getComposite (); | ||
| public abstract void setComposite (Composite comp); | ||
| public abstract GraphicsConfiguration getDeviceConfiguration (); | ||
| public abstract java.awt.font.FontRenderContext getFontRenderContext (); | ||
| public abstract Paint getPaint (); | ||
| public abstract void setPaint (Paint paint); | ||
| public abstract RenderingHints getRenderingHints (); | ||
| public abstract void setRenderingHints (java.util.Map hints); | ||
| public abstract Stroke getStroke (); | ||
| public abstract void setStroke (Stroke s); | ||
| public abstract java.awt.geom.AffineTransform getTransform (); | ||
| public abstract void setTransform (java.awt.geom.AffineTransform Tx); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract void addRenderingHints (java.util.Map hints); | ||
| public abstract void clip (Shape s); | ||
| public abstract void draw (Shape s); | ||
| public abstract void drawGlyphVector (java.awt.font.GlyphVector g, float x, float y); | ||
| public abstract boolean drawImage (Image img, java.awt.geom.AffineTransform xform, java.awt.image.ImageObserver obs); | ||
| public abstract void drawImage (java.awt.image.BufferedImage img, java.awt.image.BufferedImageOp op, int x, int y); | ||
| public abstract void drawRenderableImage (java.awt.image.renderable.RenderableImage img, java.awt.geom.AffineTransform xform); | ||
| public abstract void drawRenderedImage (java.awt.image.RenderedImage img, java.awt.geom.AffineTransform xform); | ||
| public abstract void drawString (java.text.AttributedCharacterIterator iterator, float x, float y); | ||
| public abstract void drawString (String s, float x, float y); | ||
| public abstract void fill (Shape s); | ||
| public abstract Object getRenderingHint (RenderingHints.Key hintKey); | ||
| public abstract boolean hit (Rectangle rect, Shape s, boolean onStroke); | ||
| public abstract void rotate (double theta); | ||
| public abstract void rotate (double theta, double x, double y); | ||
| public abstract void scale (double sx, double sy); | ||
| public abstract void setRenderingHint (RenderingHints.Key hintKey, Object hintValue); | ||
| public abstract void shear (double shx, double shy); | ||
| public abstract void transform (java.awt.geom.AffineTransform Tx); | ||
| public abstract void translate (double tx, double ty); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Graphics | |
| public void draw3DRect (int x, int y, int width, int height, boolean raised); | ||
| public abstract void drawString (java.text.AttributedCharacterIterator iterator, int x, int y); | ||
| public abstract void drawString (String str, int x, int y); | ||
| public void fill3DRect (int x, int y, int width, int height, boolean raised); | ||
| public abstract void translate (int x, int y); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Graphics-->Graphics2D
Passed To: java.awt.font.GraphicAttribute.draw(), java.awt.font.ImageGraphicAttribute.draw(), java.awt.font.ShapeGraphicAttribute.draw(), java.awt.font.TextLayout.draw()
Returned By: GraphicsEnvironment.createGraphics(), java.awt.image.BufferedImage.createGraphics()
| GraphicsConfigTemplate | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable | |
This abstract class is designed to support a matching operation that selects the best configuration from an array of GraphicsConfiguration objects. The best configuration is defined as the one that most closely matches the desired criteria. GraphicsConfigTemplate does not define what those criteria might be, however: the criteria and the matching algorithm are left entirely to the concrete subclass that provides definitions of the abstract methods.
This class in not commonly used. There are not any implementations of GraphicsConfigTemplate built into Java 1.2. On many platforms, such as Windows, a screen has only one available GraphicsConfiguration, so there is never a need to try to find the best one.
| public abstract class GraphicsConfigTemplate implements Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public GraphicsConfigTemplate (); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int PREFERRED ; | =2 | |
| public static final int REQUIRED ; | =1 | |
| public static final int UNNECESSARY ; | =3 | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract GraphicsConfiguration getBestConfiguration (GraphicsConfiguration[ ] gc); | ||
| public abstract boolean isGraphicsConfigSupported (GraphicsConfiguration gc); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->GraphicsConfigTemplate(Serializable)
Passed To: GraphicsDevice.getBestConfiguration()
| GraphicsConfiguration | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | ||
This class describes a configuration of a graphics device. It stores information about the available resolution and colors of the device.
Resolution information is stored in the form of AffineTransform objects. getDefaultTransform() returns the default transform used to map user coordinates to device coordinates. For screen devices, this is usually an identity transform: by default, user coordinates are measured in screen pixels. For printers, the default transform is such that 72 units in user space maps to one inch on the printed page. getNormalizingTransform() returns an AffineTransform that, when concatenated to the default transform, yields a coordinate system in which 72 units of user space equal one inch on the screen or on a printed piece of paper. (For printers, this normalizing transform is obviously the identity transform, since the default transform is already 72 units to the inch.)
Color information about the device is returned by getColorModel(), in the form of a java.awt.image.ColorModel object. A ColorModel maps pixel values to their individual color components. The zero-argument form of getColorModel() returns the default color model for the configuration. If you pass one of the constants defined by the Transparency interface, the method returns a ColorModel object suitable for the configuration and the specified level of transparency.
createCompatibleImage() creates an off-screen BufferedImage object with the specified size and transparency that is compatible with the device color model. However, that most applications create off-screen images using a higher-level method, such as the createImage() method of Component.
See also GraphicsDevice and GraphicsEnvironment.
| public abstract class GraphicsConfiguration { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected GraphicsConfiguration (); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract java.awt.image.ColorModel getColorModel (); | ||
| public abstract java.awt.image.ColorModel getColorModel (int transparency); | ||
| public abstract java.awt.geom.AffineTransform getDefaultTransform (); | ||
| public abstract GraphicsDevice getDevice (); | ||
| public abstract java.awt.geom.AffineTransform getNormalizingTransform (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract java.awt.image.BufferedImage createCompatibleImage (int width, int height); | ||
| public abstract java.awt.image.BufferedImage createCompatibleImage (int width, int height, int transparency); | ||
| } | ||
Passed To: Canvas.Canvas(), GraphicsConfigTemplate.{getBestConfiguration(), isGraphicsConfigSupported()}
Returned By: Graphics2D.getDeviceConfiguration(), GraphicsConfigTemplate.getBestConfiguration(), GraphicsDevice.{getBestConfiguration(), getConfigurations(), getDefaultConfiguration()}
| GraphicsDevice | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | ||
The GraphicsDevice class represents a device capable of displaying graphics, such as a computer monitor, a printer, or an off-screen image.
A GraphicsDevice object stores the type of the device (getType()) and an identifying string (getIDString()). More importantly, it contains a list of possible configurations of the device. For example, a screen may be configured at different resolutions and color depths. This configuration information is stored by the GraphicsDevice as GraphicsConfiguration objects.
GraphicsDevice does not have a public constructor. Instances that represent screen devices can be obtained by calling the getDefaultScreenDevice() method of GraphicsEnvironment. More generally, the GraphicsDevice used by any Graphics2D object can be obtained by calling getDeviceConfiguration() on that object to obtain a GraphicsConfiguration, and then calling getDevice() on that object to get its GraphicsDevice.
| public abstract class GraphicsDevice { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected GraphicsDevice (); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int TYPE_IMAGE_BUFFER ; | =2 | |
| public static final int TYPE_PRINTER ; | =1 | |
| public static final int TYPE_RASTER_SCREEN ; | =0 | |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract GraphicsConfiguration[ ] getConfigurations (); | ||
| public abstract GraphicsConfiguration getDefaultConfiguration (); | ||
| public abstract String getIDstring (); | ||
| public abstract int getType (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public GraphicsConfiguration getBestConfiguration (GraphicsConfigTemplate gct); | ||
| } | ||
Returned By: GraphicsConfiguration.getDevice(), GraphicsEnvironment.{getDefaultScreenDevice(), getScreenDevices()}
| GraphicsEnvironment | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | ||
This class describes a Java 2D graphics environment. This class does not have a public constructor; use getLocalGraphicsEnvironment() to obtain the GraphicsEnvironment object that represents the environment available to the Java VM.
A graphics environment consists of a list of available screens and a list of available fonts. The screens are represented by GraphicsDevice objects. Use getDefaultScreenDevice() to obtain information about the default screen. Although the GraphicsDevice class can also describe printers and off-screen images, the methods of GraphicsEnvironment return only screen devices. Therefore, it is not possible to use the GraphicsEnvironment class to query the available printers.
getAllFonts() returns a list of all fonts available on the system. Use caution when calling this method, however, because on some systems it can take a long time to enumerate all installed fonts. Note that the fonts returned by this method all have a size of 1 unit; a font must be scaled to the desired size by calling deriveFont() on the Font. When possible, it is usually better to call getAvailableFontFamilyNames() to list available font families, then create only the individual Font objects desired.
See also GraphicsDevice and GraphicsConfiguration.
| public abstract class GraphicsEnvironment { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected GraphicsEnvironment (); | ||
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| public static GraphicsEnvironment getLocalGraphicsEnvironment (); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract Font[ ] getAllFonts (); | ||
| public abstract String[ ] getAvailableFontFamilyNames (); | ||
| public abstract String[ ] getAvailableFontFamilyNames (java.util.Locale l); | ||
| public abstract GraphicsDevice getDefaultScreenDevice (); | ||
| public abstract GraphicsDevice[ ] getScreenDevices (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract Graphics2D createGraphics (java.awt.image.BufferedImage img); | ||
| } | ||
Returned By: GraphicsEnvironment.getLocalGraphicsEnvironment()
| GridBagConstraints | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | cloneable serializable PJ1.1 | |
This class encapsulates the instance variables that tell a GridBagLayout how to position a given Component within its Container:
- gridx, gridy
-
The grid position of the component. The RELATIVE constant specifies a position to the right of or below the previous component.
- gridwidth, gridheight
-
The height and width of the component in grid cells. The constant REMAINDER specifies that the component is the last one and should get all remaining cells.
- fill
-
The dimensions of a component that should grow when the space available for it is larger than its default size. Legal values are the constants NONE, BOTH, HORIZONTAL, and VERTICAL.
- ipadx, ipady
-
Internal padding to add on each side of the component in each dimension. This padding increases the size of the component beyond its default minimum size.
- insets
-
An Insets object that specifies margins to appear on all sides of the component.
- anchor
-
How the component should be displayed within its grid cells when it is smaller than those cells. The CENTER constant and the compass-point constants are legal values.
- weightx, weighty
-
How extra space in the container should be distributed among its components in the X and Y dimensions. Larger weights specify that a component should receive a proportionally larger amount of extra space. A 0 weight indicates that the component should not receive any extra space. These weights specify the resizing behavior of the component and its container.
See also GridBagLayout.
| public class GridBagConstraints implements Cloneable, Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public GridBagConstraints (); | ||
| 1.2 | public GridBagConstraints (int gridx, int gridy, int gridwidth, int gridheight, double weightx, double weighty, int anchor, int fill, Insets insets, int ipadx, int ipady); | |
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int BOTH ; | =1 | |
| public static final int CENTER ; | =10 | |
| public static final int EAST ; | =13 | |
| public static final int HORIZONTAL ; | =2 | |
| public static final int NONE ; | =0 | |
| public static final int NORTH ; | =11 | |
| public static final int NORTHEAST ; | =12 | |
| public static final int NORTHWEST ; | =18 | |
| public static final int RELATIVE ; | =-1 | |
| public static final int REMAINDER ; | =0 | |
| public static final int SOUTH ; | =15 | |
| public static final int SOUTHEAST ; | =14 | |
| public static final int SOUTHWEST ; | =16 | |
| public static final int VERTICAL ; | =3 | |
| public static final int WEST ; | =17 | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public Object clone (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public int anchor ; | ||
| public int fill ; | ||
| public int gridheight ; | ||
| public int gridwidth ; | ||
| public int gridx ; | ||
| public int gridy ; | ||
| public Insets insets ; | ||
| public int ipadx ; | ||
| public int ipady ; | ||
| public double weightx ; | ||
| public double weighty ; | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->GridBagConstraints(Cloneable,Serializable)
Passed To: GridBagLayout.{AdjustForGravity(), setConstraints()}
Returned By: GridBagLayout.{getConstraints(), lookupConstraints()}
Type Of: GridBagLayout.defaultConstraints
| GridBagLayout | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable layout manager PJ1.1 | |
The most complicated and most powerful LayoutManager in the java.awt package. GridBagLayout divides a container into a grid of rows and columns (that need not have the same width and height) and places the components into this grid, adjusting the size of the grid cells as necessary to ensure that components do not overlap. Each component controls how it is positioned within this grid by specifying a number of variables (or constraints) in a GridBagConstraints object. Do not confuse this class with the much simpler GridLayout, which arranges components in a grid of equally sized cells.
Use setConstraints() to specify a GridBagConstraints object for each of the components in the container. Or, as of Java 1.1, specify the GridBagConstraints object when adding the component to the container with add(). The variables in this object specify the position of the component in the grid and the number of horizontal and vertical grid cells that the component occupies and also control other important aspects of component layout. See GridBagConstraints for more information on these constraint variables. setConstraints() makes a copy of the constraints object, so you may reuse a single object in your code.
Applications should never call the LayoutManager methods of this class directly; the Container for which the GridBagLayout is registered does this.
| public class GridBagLayout implements LayoutManager2, Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public GridBagLayout (); | ||
| // | Protected Constants | |
| protected static final int MAXGRIDSIZE ; | =512 | |
| protected static final int MINSIZE ; | =1 | |
| protected static final int PREFERREDSIZE ; | =2 | |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public int[ ][ ] getLayoutDimensions (); | ||
| public Point getLayoutOrigin (); | ||
| public double[ ][ ] getLayoutWeights (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public GridBagConstraints getConstraints (Component comp); | ||
| public Point location (int x, int y); | ||
| public void setConstraints (Component comp, GridBagConstraints constraints); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing LayoutManager | |
| public void addLayoutComponent (String name, Component comp); | empty | |
| public void layoutContainer (Container parent); | ||
| public Dimension minimumLayoutSize (Container parent); | ||
| public Dimension preferredLayoutSize (Container parent); | ||
| public void removeLayoutComponent (Component comp); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing LayoutManager2 | |
| 1.1 | public void addLayoutComponent (Component comp, Object constraints); | |
| 1.1 | public float getLayoutAlignmentX (Container parent); | |
| 1.1 | public float getLayoutAlignmentY (Container parent); | |
| 1.1 | public void invalidateLayout (Container target); | empty |
| 1.1 | public Dimension maximumLayoutSize (Container target); | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| protected void AdjustForGravity (GridBagConstraints constraints, Rectangle r); | ||
| protected void ArrangeGrid (Container parent); | ||
| protected GridBagLayoutInfo GetLayoutInfo (Container parent, int sizeflag); | ||
| protected Dimension GetMinSize (Container parent, GridBagLayoutInfo info); | ||
| protected GridBagConstraints lookupConstraints (Component comp); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public double[ ] columnWeights ; | ||
| public int[ ] columnWidths ; | ||
| public int[ ] rowHeights ; | ||
| public double[ ] rowWeights ; | ||
| // | Protected Instance Fields | |
| protected java.util.Hashtable comptable ; | ||
| protected GridBagConstraints defaultConstraints ; | ||
| protected GridBagLayoutInfo layoutInfo ; | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->GridBagLayout(LayoutManager2(LayoutManager),Serializable)
| GridLayout | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable layout manager PJ1.1 | |
A LayoutManager that divides a Container into a specified number of equally sized rows and columns and arranges the components in those rows and columns, left to right and top to bottom. If either the number of rows or the number of columns is set to 0, its value is computed from the other dimension and the total number of components. Do not confuse this class with the more flexible and complicated GridBagLayout.
Applications should never call the LayoutManager methods of this class directly; the Container for which the GridLayout is registered does this.
| public class GridLayout implements LayoutManager, Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| 1.1 | public GridLayout (); | |
| public GridLayout (int rows, int cols); | ||
| public GridLayout (int rows, int cols, int hgap, int vgap); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.1 | public int getColumns (); | default:0 |
| 1.1 | public void setColumns (int cols); | |
| 1.1 | public int getHgap (); | default:0 |
| 1.1 | public void setHgap (int hgap); | |
| 1.1 | public int getRows (); | default:1 |
| 1.1 | public void setRows (int rows); | |
| 1.1 | public int getVgap (); | default:0 |
| 1.1 | public void setVgap (int vgap); | |
| // | Methods Implementing LayoutManager | |
| public void addLayoutComponent (String name, Component comp); | empty | |
| public void layoutContainer (Container parent); | ||
| public Dimension minimumLayoutSize (Container parent); | ||
| public Dimension preferredLayoutSize (Container parent); | ||
| public void removeLayoutComponent (Component comp); | empty | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->GridLayout(LayoutManager,Serializable)
| IllegalComponentStateException | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable unchecked PJ1.1 | |
Signals that an AWT component is not in the appropriate state for some requested operation (e.g., it hasn't been added to a container yet or is currently hidden).
| public class IllegalComponentStateException extends java.lang.IllegalStateException { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public IllegalComponentStateException (); | ||
| public IllegalComponentStateException (String s); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Throwable(Serializable)-->Exception-->RuntimeException-->java.lang.IllegalStateException-->IllegalComponentStateException
Thrown By: AccessibleContext.getLocale()
| Image | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | PJ1.1 | |
This abstract class represents a displayable image in a platform-independent way. An Image object cannot be instantiated directly through a constructor; it must be obtained through a method like the getImage() method of Applet or the createImage() method of Component. getSource() method returns the ImageProducer object that produces the image data. getGraphics() returns a Graphics object that can be used for drawing into off-screen images (but not images that are downloaded or generated by an ImageProducer).
| public abstract class Image { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Image (); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| 1.1 | public static final int SCALE_AREA_AVERAGING ; | =16 |
| 1.1 | public static final int SCALE_DEFAULT ; | =1 |
| 1.1 | public static final int SCALE_FAST ; | =2 |
| 1.1 | public static final int SCALE_REPLICATE ; | =8 |
| 1.1 | public static final int SCALE_SMOOTH ; | =4 |
| public static final Object UndefinedProperty ; | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract Graphics getGraphics (); | ||
| public abstract java.awt.image.ImageProducer getSource (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract void flush (); | ||
| public abstract int getHeight (java.awt.image.ImageObserver observer); | ||
| public abstract Object getProperty (String name, java.awt.image.ImageObserver observer); | ||
| 1.1 | public Image getScaledInstance (int width, int height, int hints); | |
| public abstract int getWidth (java.awt.image.ImageObserver observer); | ||
| } | ||
Subclasses: java.awt.image.BufferedImage
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Too many methods to list.
Type Of: javax.swing.JViewport.backingStoreImage
| Insets | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | cloneable serializable PJ1.1 | |
This class holds four values that represent the top, left, bottom, and right margins, in pixels, of a Container or other Component. An object of this type can be specified in a GridBagConstraints layout object and is returned by Container.insets(), which queries the margins of a container.
| public class Insets implements Cloneable, Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Insets (int top, int left, int bottom, int right); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public Object clone (); | ||
| 1.1 | public boolean equals (Object obj); | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public int bottom ; | ||
| public int left ; | ||
| public int right ; | ||
| public int top ; | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Insets(Cloneable,Serializable)
Subclasses: javax.swing.plaf.InsetsUIResource
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Too many methods to list.
Type Of: GridBagConstraints.insets
| ItemSelectable | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | PJ1.1 | |
This interface abstracts the functionality of an AWT component that presents one or more items to the user and allows the user to select none, one, or several of them. It is implemented by several components in the AWT and Swing.
getSelectedObjects() returns an array of selected objects or null, if none are selected. addItemListener() and removeItemListener() are standard methods for adding and removing ItemListener objects to be notified when an item is selected.
| public abstract interface ItemSelectable { | ||
| // | Event Registration Methods (by event name) | |
| public abstract void addItemListener (java.awt.event.ItemListener l); | ||
| public abstract void removeItemListener (java.awt.event.ItemListener l); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract Object[ ] getSelectedObjects (); | ||
| } | ||
Implementations: Checkbox, CheckboxMenuItem, Choice, java.awt.List, javax.swing.AbstractButton, javax.swing.ButtonModel, javax.swing.JComboBox
Passed To: java.awt.event.ItemEvent.ItemEvent()
Returned By: java.awt.event.ItemEvent.getItemSelectable()
| Label | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1 | |
This class is a Component that displays a single specified line of read-only text. The constant values specify the text alignment within the component and can be specified in a call to the constructor or used with setAlignment().
| public class Label extends Component { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Label (); | ||
| public Label (String text); | ||
| public Label (String text, int alignment); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int CENTER ; | =1 | |
| public static final int LEFT ; | =0 | |
| public static final int RIGHT ; | =2 | |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public int getAlignment (); | default:0 | |
| public void setAlignment (int alignment); | synchronized | |
| public String getText (); | default:"" | |
| public void setText (String text); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Component | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Component | |
| protected String paramString (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Component(java.awt.image.ImageObserver,MenuContainer,Serializable)-->Label
Passed To: Toolkit.createLabel()
| LayoutManager | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | layout manager PJ1.1 | |
This interface defines the methods necessary for a class to be able to arrange Component objects within a Container object. Most programs use one of the existing classes that implement this interface: BorderLayout, CardLayout, FlowLayout, GridBagConstraints, GridBagLayout, or GridLayout.
To define a new class that lays out components, you must implement each of the methods defined by this interface. addLayoutComponent() is called when a component is added to the container. removeLayoutComponent() is called when a component is removed. layoutContainer() should perform the actual positioning of components by setting the size and position of each component in the specified container. minimumLayoutSize() should return the minimum container width and height that the LayoutManager needs in order to lay out its components. preferredLayoutSize() should return the optimal container width and height for the LayoutManager to lay out its components.
As of Java 1.1, layout managers should implement the LayoutManager2 interface, which is an extension of this one. A Java applet or application never directly calls any of these LayoutManager methods--the Container object for which the LayoutManager is registered does that.
| public abstract interface LayoutManager { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract void addLayoutComponent (String name, Component comp); | ||
| public abstract void layoutContainer (Container parent); | ||
| public abstract Dimension minimumLayoutSize (Container parent); | ||
| public abstract Dimension preferredLayoutSize (Container parent); | ||
| public abstract void removeLayoutComponent (Component comp); | ||
| } | ||
Implementations: FlowLayout, GridLayout, LayoutManager2, javax.swing.ScrollPaneLayout, javax.swing.ViewportLayout
Passed To: Container.setLayout(), Panel.Panel(), ScrollPane.setLayout(), javax.swing.Box.setLayout(), javax.swing.JApplet.setLayout(), javax.swing.JDialog.setLayout(), javax.swing.JFrame.setLayout(), javax.swing.JInternalFrame.setLayout(), javax.swing.JPanel.JPanel(), javax.swing.JScrollPane.setLayout(), javax.swing.JWindow.setLayout()
Returned By: Container.getLayout(), javax.swing.JRootPane.createRootLayout(), javax.swing.JViewport.createLayoutManager()
| LayoutManager2 | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | layout manager PJ1.1 | |
This interface is an extension of the LayoutManager interface. It defines additional layout management methods for layout managers that perform constraint-based layout. GridBagLayout is an example of a constraint-based layout manager--each component added to the layout is associated with a GridBagConstraints object that specifies the constraints on how the component is to be laid out.
Java programs do not directly invoke the methods of this interface--they are used by the Container object for which the layout manager is registered.
| public abstract interface LayoutManager2 extends LayoutManager { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract void addLayoutComponent (Component comp, Object constraints); | ||
| public abstract float getLayoutAlignmentX (Container target); | ||
| public abstract float getLayoutAlignmentY (Container target); | ||
| public abstract void invalidateLayout (Container target); | ||
| public abstract Dimension maximumLayoutSize (Container target); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: (LayoutManager2(LayoutManager))
Implementations: BorderLayout, CardLayout, GridBagLayout, javax.swing.BoxLayout, javax.swing.JRootPane.RootLayout, javax.swing.OverlayLayout
| List | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1 | |
This class is a Component that graphically displays a list of strings. The list is scrollable if necessary. The constructor takes optional arguments that specify the number of visible rows in the list and whether selection of more than one item is allowed. The various instance methods allow strings to be added and removed from the List and allow the selected item or items to be queried.
| public class List extends Component implements ItemSelectable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public List (); | ||
| 1.1 | public List (int rows); | |
| public List (int rows, boolean multipleMode); | ||
| // | Event Registration Methods (by event name) | |
| 1.1 | public void addActionListener (java.awt.event.ActionListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void removeActionListener (java.awt.event.ActionListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void addItemListener (java.awt.event.ItemListener l); | Implements:ItemSelectable synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void removeItemListener (java.awt.event.ItemListener l); | Implements:ItemSelectable synchronized |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.1 | public int getItemCount (); | default:0 |
| 1.1 | public String[ ] getItems (); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public Dimension getMinimumSize (); | Overrides:Component |
| 1.1 | public Dimension getMinimumSize (int rows); | |
| 1.1 | public boolean isMultipleMode (); | default:false |
| 1.1 | public void setMultipleMode (boolean b); | |
| 1.1 | public Dimension getPreferredSize (); | Overrides:Component |
| 1.1 | public Dimension getPreferredSize (int rows); | |
| public int getRows (); | default:4 | |
| public int getSelectedIndex (); | synchronized default:-1 | |
| public int[ ] getSelectedIndexes (); | synchronized | |
| public String getSelectedItem (); | synchronized default:null | |
| public String[ ] getSelectedItems (); | synchronized | |
| 1.1 | public Object[ ] getSelectedObjects (); | Implements:ItemSelectable |
| public int getVisibleIndex (); | default:-1 | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| 1.1 | public void add (String item); | |
| 1.1 | public void add (String item, int index); | |
| public void deselect (int index); | synchronized | |
| public String getItem (int index); | ||
| 1.1 | public boolean isIndexSelected (int index); | |
| public void makeVisible (int index); | synchronized | |
| 1.1 | public void remove (String item); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void remove (int position); | |
| 1.1 | public void removeAll (); | |
| public void replaceItem (String newValue, int index); | synchronized | |
| public void select (int index); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing ItemSelectable | |
| 1.1 | public void addItemListener (java.awt.event.ItemListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public Object[ ] getSelectedObjects (); | |
| 1.1 | public void removeItemListener (java.awt.event.ItemListener l); | synchronized |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Component | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| public void removeNotify (); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Component | |
| protected String paramString (); | ||
| 1.1 | protected void processEvent (AWTEvent e); | |
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| 1.1 | protected void processActionEvent (java.awt.event.ActionEvent e); | |
| 1.1 | protected void processItemEvent (java.awt.event.ItemEvent e); | |
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public void addItem (String item); | |
| # | public void addItem (String item, int index); | synchronized |
| # | public boolean allowsMultipleSelections (); | |
| # | public void clear (); | synchronized |
| # | public int countItems (); | |
| # | public void delItem (int position); | |
| # | public void delItems (int start, int end); | synchronized |
| # | public boolean isSelected (int index); | |
| # | public Dimension minimumSize (); | Overrides:Component |
| # | public Dimension minimumSize (int rows); | |
| # | public Dimension preferredSize (); | Overrides:Component |
| # | public Dimension preferredSize (int rows); | |
| # | public void setMultipleSelections (boolean b); | synchronized |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Component(java.awt.image.ImageObserver,MenuContainer,Serializable)-->java.awt.List(ItemSelectable)
Passed To: Toolkit.createList()
| MediaTracker | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable PJ1.1 | |
This class provides a convenient way to asynchronously load and keep track of the status of any number of Image objects. You can use it to load one or more images and then wait until those images have been completely loaded and are ready to be used.
The addImage() method registers an image to be loaded and tracked, assigning it a specified identifier value. waitForID() loads all the images that have been assigned the specified identifier and returns when they have all finished loading or it receives an error. isErrorAny() and isErrorID() check whether any errors have occurred while loading images. statusAll() and statusID() return the status of all images and of all images with the specified identifier, respectively. The return value of each of these methods is one of the defined constants.
| public class MediaTracker implements Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public MediaTracker (Component comp); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int ABORTED ; | =2 | |
| public static final int COMPLETE ; | =8 | |
| public static final int ERRORED ; | =4 | |
| public static final int LOADING ; | =1 | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void addImage (Image image, int id); | ||
| public void addImage (Image image, int id, int w, int h); | synchronized | |
| public boolean checkAll (); | ||
| public boolean checkAll (boolean load); | ||
| public boolean checkID (int id); | ||
| public boolean checkID (int id, boolean load); | ||
| public Object[ ] getErrorsAny (); | synchronized | |
| public Object[ ] getErrorsID (int id); | synchronized | |
| public boolean isErrorAny (); | synchronized | |
| public boolean isErrorID (int id); | synchronized | |
| 1.1 | public void removeImage (Image image); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void removeImage (Image image, int id); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void removeImage (Image image, int id, int width, int height); | synchronized |
| public int statusAll (boolean load); | ||
| public int statusID (int id, boolean load); | ||
| public void waitForAll () throws InterruptedException; | ||
| public boolean waitForAll (long ms) throws InterruptedException; | synchronized | |
| public void waitForID (int id) throws InterruptedException; | ||
| public boolean waitForID (int id, long ms) throws InterruptedException; | synchronized | |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->MediaTracker(Serializable)
Type Of: javax.swing.ImageIcon.tracker
| Menu | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1(opt) | |
This class represents a pulldown menu pane that appears within a MenuBar. Each Menu has a label that appears in the MenuBar and can optionally be a tear-off menu. The add() and addSeparator() methods add individual items to a Menu.
| public class Menu extends MenuItem implements MenuContainer { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| 1.1 | public Menu (); | |
| public Menu (String label); | ||
| public Menu (String label, boolean tearOff); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.1 | public int getItemCount (); | default:0 |
| public boolean isTearOff (); | default:false | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void add (String label); | ||
| public MenuItem add (MenuItem mi); | ||
| public void addSeparator (); | ||
| public MenuItem getItem (int index); | ||
| 1.1 | public void insert (String label, int index); | |
| 1.1 | public void insert (MenuItem menuitem, int index); | |
| 1.1 | public void insertSeparator (int index); | |
| public void remove (int index); | ||
| 1.1 | public void removeAll (); | |
| // | Methods Implementing MenuContainer | |
| public void remove (MenuComponent item); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding MenuItem | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| 1.1 | public String paramString (); | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding MenuComponent | |
| public void removeNotify (); | ||
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public int countItems (); | |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->MenuComponent(Serializable)-->MenuItem-->Menu(MenuContainer)
Subclasses: PopupMenu
Passed To: MenuBar.{add(), setHelpMenu()}, Toolkit.createMenu(), java.awt.peer.MenuBarPeer.{addHelpMenu(), addMenu()}
Returned By: MenuBar.{add(), getHelpMenu(), getMenu()}
| MenuBar | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1(opt) | |
This class represents a menu bar. add() adds Menu objects to the menu bar, and setHelpMenu() adds a Help menu in a reserved location of the menu bar. A MenuBar object may be displayed within a Frame by passing it to the setMenuBar() of the Frame.
| public class MenuBar extends MenuComponent implements MenuContainer { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public MenuBar (); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public Menu getHelpMenu (); | default:null | |
| public void setHelpMenu (Menu m); | ||
| 1.1 | public int getMenuCount (); | default:0 |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public Menu add (Menu m); | ||
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| 1.1 | public void deleteShortcut (MenuShortcut s); | |
| public Menu getMenu (int i); | ||
| 1.1 | public MenuItem getShortcutMenuItem (MenuShortcut s); | |
| public void remove (int index); | ||
| 1.1 | public java.util.Enumeration shortcuts (); | synchronized |
| // | Methods Implementing MenuContainer | |
| public void remove (MenuComponent m); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding MenuComponent | |
| public void removeNotify (); | ||
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public int countMenus (); | |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->MenuComponent(Serializable)-->MenuBar(MenuContainer)
Passed To: Frame.setMenuBar(), Toolkit.createMenuBar(), java.awt.peer.FramePeer.setMenuBar()
Returned By: Frame.getMenuBar()
| MenuComponent | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1 | |
This class is the superclass of all menu-related classes: You never need to instantiate a MenuComponent directly. setFont() specifies the font to be used for all text within the menu component.
| public abstract class MenuComponent implements Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public MenuComponent (); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public Font getFont (); | ||
| public void setFont (Font f); | ||
| 1.1 | public String getName (); | |
| 1.1 | public void setName (String name); | |
| public MenuContainer getParent (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| 1.1 | public final void dispatchEvent (AWTEvent e); | |
| public void removeNotify (); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| 1.1 | protected final Object getTreeLock (); | |
| protected String paramString (); | ||
| 1.1 | protected void processEvent (AWTEvent e); | empty |
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public java.awt.peer.MenuComponentPeer getPeer (); | |
| # | public boolean postEvent (Event evt); | |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->MenuComponent(Serializable)
Subclasses: MenuBar, MenuItem
Passed To: Component.remove(), Frame.remove(), Menu.remove(), MenuBar.remove(), MenuContainer.remove()
| MenuContainer | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | PJ1.1 | |
This interface defines the methods necessary for MenuContainer types, such as Menu, Frame, and MenuBar objects. Unless you implement new menulike components, you never need to use it.
| public abstract interface MenuContainer { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract Font getFont (); | ||
| public abstract void remove (MenuComponent comp); | ||
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public abstract boolean postEvent (Event evt); | |
| } | ||
Implementations: Component, Frame, Menu, MenuBar
Returned By: MenuComponent.getParent()
| MenuItem | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1 | |
This class encapsulates a menu item with a specified textual label. A MenuItem can be added to a menu pane with the add() method of Menu. The disable() method makes an item nonselectable; you might use it to gray out a menu item when the command it represents is not valid in the current context. The enable() method makes an item selectable again. In Java 1.1, use setActionCommand() to specify an identifying string that is included in ActionEvent events generated by the menu item.
| public class MenuItem extends MenuComponent { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| 1.1 | public MenuItem (); | |
| public MenuItem (String label); | ||
| 1.1 | public MenuItem (String label, MenuShortcut s); | |
| // | Event Registration Methods (by event name) | |
| 1.1 | public void addActionListener (java.awt.event.ActionListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void removeActionListener (java.awt.event.ActionListener l); | synchronized |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.1 | public String getActionCommand (); | default:"" |
| 1.1 | public void setActionCommand (String command); | |
| public boolean isEnabled (); | default:true | |
| 1.1 | public void setEnabled (boolean b); | synchronized |
| public String getLabel (); | default:"" | |
| public void setLabel (String label); | synchronized | |
| 1.1 | public MenuShortcut getShortcut (); | default:null |
| 1.1 | public void setShortcut (MenuShortcut s); | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| 1.1 | public void deleteShortcut (); | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding MenuComponent | |
| public String paramString (); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding MenuComponent | |
| 1.1 | protected void processEvent (AWTEvent e); | |
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| 1.1 | protected final void disableEvents (long eventsToDisable); | |
| 1.1 | protected final void enableEvents (long eventsToEnable); | |
| 1.1 | protected void processActionEvent (java.awt.event.ActionEvent e); | |
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public void disable (); | synchronized |
| # | public void enable (); | synchronized |
| # | public void enable (boolean b); | |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->MenuComponent(Serializable)-->MenuItem
Subclasses: CheckboxMenuItem, Menu
Passed To: Menu.{add(), insert()}, Toolkit.createMenuItem(), java.awt.peer.MenuPeer.addItem()
Returned By: Menu.{add(), getItem()}, MenuBar.getShortcutMenuItem()
| MenuShortcut | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable PJ1.1(opt) | |
This class represents a keystroke used to select a MenuItem without actually pulling down the menu. A MenuShortcut object can be specified for a MenuItem when the MenuItem is created or by calling the item's setShortcut() method. The keystroke sequence for the menu shortcut automatically appears in the label for the menu item, so you do not need to add this information yourself.
When you create a MenuShortcut, you specify the keycode of the shortcut--this is one of the VK_ constants defined by java.awt.event.KeyEvent and is not always the same as a corresponding character code. You may optionally specify a boolean value that, if true, indicates that the MenuShortcut requires the Shift key to be held down.
Note that menu shortcuts are triggered in a platform-dependent way. When you create a shortcut, you specify only the keycode and an optional Shift modifier. The shortcut is not triggered, however, unless an additional modifier key is held down. On Windows platforms, for example, the Ctrl key is used for menu shortcuts. You can query the platform-specific menu shortcut key with the getMenuShortcutKeyMask() method of Toolkit.
| public class MenuShortcut implements Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public MenuShortcut (int key); | ||
| public MenuShortcut (int key, boolean useShiftModifier); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public boolean equals (MenuShortcut s); | ||
| public int getKey (); | ||
| public boolean usesShiftModifier (); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| 1.2 | public boolean equals (Object obj); | |
| 1.2 | public int hashCode (); | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| protected String paramString (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->MenuShortcut(Serializable)
Passed To: MenuBar.{deleteShortcut(), getShortcutMenuItem()}, MenuItem.{MenuItem(), setShortcut()}, MenuShortcut.equals()
Returned By: MenuItem.getShortcut()
| Paint | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | ||
This interface defines a color or pattern used by Java 2D in drawing and filling operations. Color is the simplest implementation: it performs drawing and filling using a solid color. GradientPaint and TexturePaint are two other commonly used implementations. Most applications can simply use these predefined Paint implementations and do not need to implement this interface themselves.
Because a single Paint object may be used by different threads with different Graphics2D objects, the Paint object does not perform painting operations itself. Instead, it defines a createContext() method that returns a PaintContext object that is capable of performing painting in a particular context. See PaintContext for details.
| public abstract interface Paint extends Transparency { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract PaintContext createContext (java.awt.image.ColorModel cm, Rectangle deviceBounds, java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D userBounds, java.awt.geom.AffineTransform xform, RenderingHints hints); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: (Paint(Transparency))
Implementations: Color, GradientPaint, TexturePaint
Passed To: Graphics2D.setPaint()
Returned By: Graphics2D.getPaint()
| PaintContext | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | ||
This interface defines the methods that do the actual work of computing the colors to be used in Java 2D drawing and filling operations. PaintContext is used internally by Java 2D; applications never need to call any of its methods. Only applications that implement custom Paint objects need to implement this interface.
A Graphics2D object creates a PaintContext object by calling the createContext() method of its Paint object. The getRaster() method of the PaintContext is called to perform the actual painting; this method must return a java.awt.image.Raster object that contains the appropriate colors for the specified rectangle. The Graphics2D object calls dispose() when the PaintContext is no longer needed. The dispose() method should release any system resources held by the PaintContext.
| public abstract interface PaintContext { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract void dispose (); | ||
| public abstract java.awt.image.ColorModel getColorModel (); | ||
| public abstract java.awt.image.Raster getRaster (int x, int y, int w, int h); | ||
| } | ||
Returned By: Color.createContext(), GradientPaint.createContext(), Paint.createContext(), SystemColor.createContext(), TexturePaint.createContext()
| Panel | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1 | |
This class is a Container that is itself contained within a container. Unlike Frame and Dialog, Panel is a container that does not create a separate window of its own. Panel is suitable for holding portions of a larger interface within a parent Frame or Dialog or within another Panel. (Because Applet is a subclass of Panel, applets are displayed in a Panel that is contained within a web browser or applet viewer.) The default LayoutManager for a Panel is FlowLayout.
| public class Panel extends Container { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Panel (); | ||
| 1.1 | public Panel (LayoutManager layout); | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Container | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Component(java.awt.image.ImageObserver,MenuContainer,Serializable)-->Container-->Panel
Subclasses: java.applet.Applet
Passed To: Toolkit.createPanel()
| Point | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | cloneable serializable PJ1.1 | |
This class holds the integer X and Y coordinates of a two-dimensional point. The move() and setLocation() methods set the coordinates, and the translate() method adds specified values to the coordinates. Also, the x and y fields are public and may be manipulated directly.
In Java 1.0 and Java 1.1, Point is a subclass of Object. In Java 1.2, with the introduction of Java 2D, Point has become a concrete subclass of java.awt.geom.Point2D. Contrast Point with Point2D.Float and Point2D.Double, which use float and double fields to represent the coordinates of the point.
| public class Point extends java.awt.geom.Point2D implements Serializable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| 1.1 | public Point (); | |
| 1.1 | public Point (Point p); | |
| public Point (int x, int y); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| 1.1 | public Point getLocation (); | |
| public void move (int x, int y); | ||
| 1.1 | public void setLocation (Point p); | |
| 1.1 | public void setLocation (int x, int y); | |
| public void translate (int x, int y); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Point2D | |
| public boolean equals (Object obj); | ||
| 1.2 | public double getX (); | default:0.0 |
| 1.2 | public double getY (); | default:0.0 |
| 1.2 | public void setLocation (double x, double y); | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public int x ; | ||
| public int y ; | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->java.awt.geom.Point2D(Cloneable)-->Point(Serializable)
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Too many methods to list.
Type Of: javax.swing.JViewport.lastPaintPosition
| Polygon | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable shape PJ1.1 | |
This class defines a polygon as an array of points. The points of the polygon can be passed to the constructor or specified with addPoint(). getBoundingBox() returns the smallest Rectangle that contains the polygon, and inside() tests whether a specified point is within the Polygon. Note that the arrays of X and Y points and the number of points in the polygon (not necessarily the same as the array size) are defined as public variables. Polygon objects are used when drawing polygons with the drawPolygon() and fillPolygon() methods of Graphics. In Java 2, Polygon has become part of the Java 2D API. It implements the Shape interface and can be passed to the draw() and fill() method of a Graphics2D object.
| public class Polygon implements Serializable, Shape { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Polygon (); | ||
| public Polygon (int[ ] xpoints, int[ ] ypoints, int npoints); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void addPoint (int x, int y); | ||
| 1.1 | public boolean contains (Point p); | |
| 1.1 | public boolean contains (int x, int y); | |
| 1.1 | public void translate (int deltaX, int deltaY); | |
| // | Methods Implementing Shape | |
| 1.2 | public boolean contains (java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D r); | |
| 1.2 | public boolean contains (java.awt.geom.Point2D p); | |
| 1.2 | public boolean contains (double x, double y); | |
| 1.2 | public boolean contains (double x, double y, double w, double h); | |
| 1.1 | public Rectangle getBounds (); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | default:Rectangle2D.Float |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.geom.PathIterator getPathIterator (java.awt.geom.AffineTransform at); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.geom.PathIterator getPathIterator (java.awt.geom.AffineTransform at, double flatness); | |
| 1.2 | public boolean intersects (java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D r); | |
| 1.2 | public boolean intersects (double x, double y, double w, double h); | |
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public int npoints ; | ||
| public int[ ] xpoints ; | ||
| public int[ ] ypoints ; | ||
| // | Protected Instance Fields | |
| protected Rectangle bounds ; | ||
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public Rectangle getBoundingBox (); | |
| # | public boolean inside (int x, int y); | |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Polygon(Serializable,Shape)
Passed To: Graphics.{drawPolygon(), fillPolygon()}
| PopupMenu | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1(mod) | |
PopupMenu is a simple subclass of Menu that represents a popup menu rather than a pulldown menu. You create a PopupMenu just as you would create a Menu object. The main difference is that a popup menu must be popped up in response to a user event by calling its show() method. Another difference is that, unlike a Menu, which can only appear within a MenuBar or another Menu, a PopupMenu can be associated with any component in a graphical user interface. A PopupMenu is associated with a component by calling the add() method of the component.
Popup menus are popped up by the user in different ways on different platforms. In order to hide this platform dependency, the MouseEvent class defines the isPopupTrigger() method. If this method returns true, the specified MouseEvent represents the platform-specific popup menu trigger event, and you should use the show() method to display your PopupMenu. Note that the X and Y coordinates passed to show() should be in the coordinate system of the specified Component.
Support for nested popup menus is optional in Personal Java environments, and the inherited add() method may throw an exception if you attempt to add a Menu child to a PopupMenu.
| public class PopupMenu extends Menu { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public PopupMenu (); | ||
| public PopupMenu (String label); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void show (Component origin, int x, int y); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Menu | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->MenuComponent(Serializable)-->MenuItem-->Menu(MenuContainer)-->PopupMenu
Passed To: Component.add(), Toolkit.createPopupMenu()
| PrintGraphics | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | PJ1.1 | |
The Graphics object returned by the getGraphics() method of PrintJob always implements this PrintGraphics interface. You can use this fact to distinguish a Graphics object that draws to the screen from one that generates hardcopy. This is a useful thing to do in a paint() method, when you want to generate hardcopy that differs somewhat from what is being displayed on-screen.
The getPrintJob() method defined by this interface can be used to return the PrintJob with which the PrintGraphics object is associated.
| public abstract interface PrintGraphics { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract PrintJob getPrintJob (); | ||
| } | ||
| PrintJob | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | PJ1.1 | |
A PrintJob object represents a single printing session, or job. The job may consist of one or more individual pages.
PrintJob is abstract, so it cannot be instantiated directly. Instead, you must call the getPrintJob() method of the Toolkit object. Calling this method posts an appropriate print dialog box to request information from the user, such as which printer should be used. An application has no control over this process, but may pass a Properties object in which the dialog stores the user's printing preferences. This Properties object can then be reused when initiating subsequent print jobs.
Once a PrintJob object has been obtained from the Toolkit object, you call the getGraphics() method of PrintJob to obtain a Graphics object. Any drawing done with this Graphics object is printed, instead of displayed on-screen. The object returned by getGraphics() implements the PrintGraphics interface. Do not make any assumptions about the initial state of the Graphics object; in particular, note that you must specify a font before you can draw any text.
When you are done drawing all the desired output on a page, call the dispose() method of the Graphics object to force the current page to be printed. You can call getGraphics() and dispose() repeatedly to print any number of pages required by your application. However, if the lastPageFirst() method returns true, the user has requested that pages be printed in reverse order. It is up to your application to implement this feature.
The getPageDimension() method returns the size of the page in pixels. getPageResolution() returns the resolution of the page in pixels per inch. This resolution is closer to a screen resolution (70 to 100 pixels per inch) than a typical printer resolution (300 to 600 pixels per inch). This means that on-screen drawings can be drawn directly to the printer without scaling. It also means, however, that you cannot take full advantage of the extra resolution provided by printers.
When you are done with a PrintJob and have called dispose() on the Graphics object returned by getGraphics(), you should call end() to terminate the job.
As of Java 1.2, the PrintJob class has been superseded by a more complete printing API provided in the java.awt.print package.
| public abstract class PrintJob { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public PrintJob (); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract Graphics getGraphics (); | ||
| public abstract Dimension getPageDimension (); | ||
| public abstract int getPageResolution (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract void end (); | ||
| public abstract boolean lastPageFirst (); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public void finalize (); | ||
| } | ||
Returned By: PrintGraphics.getPrintJob(), Toolkit.getPrintJob()
| Rectangle | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | cloneable serializable shape PJ1.1 | |
This class defines a rectangle using four integer values: the X and Y coordinates of its upper-left corner and its width and height. The instance methods perform various tests and transformations on the rectangle. The x, y, width, and height methods are public and may thus be manipulated directly. Rectangle is used for a variety of purposes throughout java.awt and related packages.
In Java 1.0 and Java 1.1, Rectangle is a subclass of Object. In Java 2, with the introduction of Java 2D, Rectangle has become a concrete subclass of java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D. Contrast Rectangle with Rectangle2D.Float and Rectangle2D.Double, which use float and double fields to represent the coordinates of the rectangle.
| public class Rectangle extends java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D implements Serializable, Shape { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Rectangle (); | ||
| 1.1 | public Rectangle (Rectangle r); | |
| public Rectangle (Dimension d); | ||
| public Rectangle (Point p); | ||
| public Rectangle (int width, int height); | ||
| public Rectangle (Point p, Dimension d); | ||
| public Rectangle (int x, int y, int width, int height); | ||
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.1 | public Rectangle getBounds (); | Implements:Shape |
| 1.1 | public void setBounds (Rectangle r); | |
| 1.1 | public void setBounds (int x, int y, int width, int height); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | Implements:Shape default:Rectangle |
| public boolean isEmpty (); | Overrides:RectangularShape default:true | |
| 1.2 | public double getHeight (); | Overrides:RectangularShape default:0.0 |
| 1.1 | public Point getLocation (); | |
| 1.1 | public void setLocation (Point p); | |
| 1.1 | public void setLocation (int x, int y); | |
| 1.1 | public Dimension getSize (); | |
| 1.1 | public void setSize (Dimension d); | |
| 1.1 | public void setSize (int width, int height); | |
| 1.2 | public double getWidth (); | Overrides:RectangularShape default:0.0 |
| 1.2 | public double getX (); | Overrides:RectangularShape default:0.0 |
| 1.2 | public double getY (); | Overrides:RectangularShape default:0.0 |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void add (Rectangle r); | ||
| public void add (Point pt); | ||
| public void add (int newx, int newy); | ||
| 1.2 | public boolean contains (Rectangle r); | |
| 1.1 | public boolean contains (Point p); | |
| 1.1 | public boolean contains (int x, int y); | |
| 1.2 | public boolean contains (int X, int Y, int W, int H); | |
| public void grow (int h, int v); | ||
| public Rectangle intersection (Rectangle r); | ||
| public boolean intersects (Rectangle r); | ||
| public void translate (int x, int y); | ||
| public Rectangle union (Rectangle r); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing Shape | |
| 1.1 | public Rectangle getBounds (); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | default:Rectangle |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Rectangle2D | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D createIntersection (java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D r); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D createUnion (java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D r); | |
| public boolean equals (Object obj); | ||
| 1.2 | public int outcode (double x, double y); | |
| 1.2 | public void setRect (double x, double y, double width, double height); | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public String toString (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Fields | |
| public int height ; | ||
| public int width ; | ||
| public int x ; | ||
| public int y ; | ||
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public boolean inside (int x, int y); | |
| # | public void move (int x, int y); | |
| # | public void reshape (int x, int y, int width, int height); | |
| # | public void resize (int width, int height); | |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->java.awt.geom.RectangularShape(Cloneable,Shape)-->java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D-->Rectangle(Serializable,Shape)
Subclasses: javax.swing.text.DefaultCaret
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Too many methods to list.
Type Of: Polygon.bounds
| RenderingHints | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | cloneable collection | |
This class contains a set of key-to-value mappings that provide hints to Java 2D about the speed-versus-quality trade-offs it should make. The constants that begin with KEY_ are the hints, while the constants that begin with VALUE_ are the values that may be specified for those hints. Use put() to add a hint to the RenderingHints object. Once you have specified all desired hints, pass the RenderingHints object to the setRenderingHints() or addRenderingHints() method of a Graphics2D object. If you want to set only a single rendering hint, you don't need to create a RenderingHints object at all; you can simply pass a key and value to the setRenderingHint() method of Graphics2D.
| public class RenderingHints implements Cloneable, java.util.Map { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public RenderingHints (java.util.Map init); | ||
| public RenderingHints (RenderingHints.Key key, Object value); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final RenderingHints.Key KEY_ALPHA_INTERPOLATION ; | ||
| public static final RenderingHints.Key KEY_ANTIALIASING ; | ||
| public static final RenderingHints.Key KEY_COLOR_RENDERING ; | ||
| public static final RenderingHints.Key KEY_DITHERING ; | ||
| public static final RenderingHints.Key KEY_FRACTIONALMETRICS ; | ||
| public static final RenderingHints.Key KEY_INTERPOLATION ; | ||
| public static final RenderingHints.Key KEY_RENDERING ; | ||
| public static final RenderingHints.Key KEY_TEXT_ANTIALIASING ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_ALPHA_INTERPOLATION_DEFAULT ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_ALPHA_INTERPOLATION_QUALITY ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_ALPHA_INTERPOLATION_SPEED ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_ANTIALIAS_DEFAULT ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_ANTIALIAS_OFF ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_COLOR_RENDER_DEFAULT ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_COLOR_RENDER_QUALITY ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_COLOR_RENDER_SPEED ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_DITHER_DEFAULT ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_DITHER_DISABLE ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_DITHER_ENABLE ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_FRACTIONALMETRICS_DEFAULT ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_FRACTIONALMETRICS_OFF ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_FRACTIONALMETRICS_ON ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_INTERPOLATION_BICUBIC ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_INTERPOLATION_BILINEAR ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_INTERPOLATION_NEAREST_NEIGHBOR ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_RENDER_DEFAULT ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_RENDER_QUALITY ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_RENDER_SPEED ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_TEXT_ANTIALIAS_DEFAULT ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_TEXT_ANTIALIAS_OFF ; | ||
| public static final Object VALUE_TEXT_ANTIALIAS_ON ; | ||
| // | Inner Classes | |
| ; | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void add (RenderingHints hints); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing Map | |
| public void clear (); | ||
| public boolean containsKey (Object key); | ||
| public boolean containsValue (Object value); | ||
| public java.util.Set entrySet (); | ||
| public boolean equals (Object o); | ||
| public Object get (Object key); | ||
| public int hashCode (); | ||
| public boolean isEmpty (); | ||
| public java.util.Set keySet (); | ||
| public Object put (Object key, Object value); | ||
| public void putAll (java.util.Map m); | ||
| public Object remove (Object key); | ||
| public int size (); | ||
| public java.util.Collection values (); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public Object clone (); | ||
| public String toString (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->RenderingHints(Cloneable,java.util.Map)
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Graphics2D.getRenderingHints(), java.awt.image.AffineTransformOp.getRenderingHints(), java.awt.image.BandCombineOp.getRenderingHints(), java.awt.image.BufferedImageOp.getRenderingHints(), java.awt.image.ColorConvertOp.getRenderingHints(), java.awt.image.ConvolveOp.getRenderingHints(), java.awt.image.LookupOp.getRenderingHints(), java.awt.image.RasterOp.getRenderingHints(), java.awt.image.RescaleOp.getRenderingHints(), java.awt.image.renderable.RenderContext.getRenderingHints()
| RenderingHints.Key | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | ||
This class is the type of the KEY_ constants defined by RenderingHints.
| public abstract static class RenderingHints.Key { | ||
| // | Protected Constructors | |
| protected Key (int privatekey); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract boolean isCompatibleValue (Object val); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Object | |
| public final boolean equals (Object o); | ||
| public final int hashCode (); | ||
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| protected final int intKey (); | ||
| } | ||
Passed To: Graphics2D.{getRenderingHint(), setRenderingHint()}, RenderingHints.RenderingHints()
Type Of: RenderingHints.{KEY_ALPHA_INTERPOLATION, KEY_ANTIALIASING, KEY_COLOR_RENDERING, KEY_DITHERING, KEY_FRACTIONALMETRICS, KEY_INTERPOLATION, KEY_RENDERING, KEY_TEXT_ANTIALIASING}
| Scrollbar | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1(opt) | |
This Component represents a graphical scrollbar. setValue() sets the displayed value of the scrollbar. setValues() sets the displayed value, the page size, and the minimum and maximum values. The constants HORIZONTAL and VERTICAL are legal values for the scrollbar orientation.
| public class Scrollbar extends Component implements Adjustable { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Scrollbar (); | ||
| public Scrollbar (int orientation); | ||
| public Scrollbar (int orientation, int value, int visible, int minimum, int maximum); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int HORIZONTAL ; | =0 | |
| public static final int VERTICAL ; | =1 | |
| // | Event Registration Methods (by event name) | |
| 1.1 | public void addAdjustmentListener (java.awt.event.AdjustmentListener l); | Implements:Adjustable synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void removeAdjustmentListener (java.awt.event.AdjustmentListener l); | Implements:Adjustable synchronized |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.1 | public int getBlockIncrement (); | Implements:Adjustable default:10 |
| 1.1 | public void setBlockIncrement (int v); | Implements:Adjustable |
| public int getMaximum (); | Implements:Adjustable default:100 | |
| 1.1 | public void setMaximum (int newMaximum); | Implements:Adjustable |
| public int getMinimum (); | Implements:Adjustable default:0 | |
| 1.1 | public void setMinimum (int newMinimum); | Implements:Adjustable |
| public int getOrientation (); | Implements:Adjustable default:1 | |
| 1.1 | public void setOrientation (int orientation); | |
| 1.1 | public int getUnitIncrement (); | Implements:Adjustable default:1 |
| 1.1 | public void setUnitIncrement (int v); | Implements:Adjustable |
| public int getValue (); | Implements:Adjustable default:0 | |
| public void setValue (int newValue); | Implements:Adjustable | |
| 1.1 | public int getVisibleAmount (); | Implements:Adjustable default:10 |
| 1.1 | public void setVisibleAmount (int newAmount); | Implements:Adjustable |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void setValues (int value, int visible, int minimum, int maximum); | synchronized | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Component | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Component | |
| protected String paramString (); | ||
| 1.1 | protected void processEvent (AWTEvent e); | |
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| 1.1 | protected void processAdjustmentEvent (java.awt.event.AdjustmentEvent e); | |
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public int getLineIncrement (); | default:1 |
| # | public int getPageIncrement (); | default:10 |
| # | public int getVisible (); | default:10 |
| # | public void setLineIncrement (int v); | synchronized |
| # | public void setPageIncrement (int v); | synchronized |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Component(java.awt.image.ImageObserver,MenuContainer,Serializable)-->Scrollbar(Adjustable)
Passed To: Toolkit.createScrollbar()
| ScrollPane | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1(mod) | |
This Container class creates horizontal and vertical scrollbars surrounding a viewport and allows a single child component to be displayed and scrolled within this viewport. Typically, the child of the ScrollPane is larger than the ScrollPane itself, so scrollbars allow the user to select the currently visible portion.
When you call the ScrollPane() constructor, you may optionally specify a scrollbar display policy, which should be one of the three constants defined by this class. If you do not specify a policy, ScrollPane uses the SCROLLBARS_AS_NEEDED policy. Personal Java environments may provide a scrolling mechanism other than scrollbars. In this case, the scrollbar display policy may be ignored.
A program can programmatically scroll the child within the viewport by calling setScrollPosition(). getHAdjustable() and getVAdjustable() return the horizontal and vertical Adjustable objects that control scrolling (typically these are not actually instances of Scrollbar). You can use these Adjustable objects to specify the unit and block increment values for the scrollbars. You can also directly set the Adjustable value as an alternative to calling setScrollPosition(), but you should not set other values of an Adjustable object.
Use setSize() to set the size of the ScrollPane container. You may want to take the size of the scrollbars into account when computing the overall container size--use getHScrollbarHeight() and getVScrollbarWidth() to obtain these values.
ScrollPane overrides the printComponents() method of Container, so that when a ScrollPane is printed, the entire child component, rather than only the currently visible portion, is printed.
| public class ScrollPane extends Container { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public ScrollPane (); | ||
| public ScrollPane (int scrollbarDisplayPolicy); | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int SCROLLBARS_ALWAYS ; | =1 | |
| public static final int SCROLLBARS_AS_NEEDED ; | =0 | |
| public static final int SCROLLBARS_NEVER ; | =2 | |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public Adjustable getHAdjustable (); | ||
| public int getHScrollbarHeight (); | default:0 | |
| public final void setLayout (LayoutManager mgr); | Overrides:Container | |
| public int getScrollbarDisplayPolicy (); | default:0 | |
| public Point getScrollPosition (); | ||
| public void setScrollPosition (Point p); | ||
| public void setScrollPosition (int x, int y); | ||
| public Adjustable getVAdjustable (); | ||
| public Dimension getViewportSize (); | ||
| public int getVScrollbarWidth (); | default:0 | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Container | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| public void doLayout (); | ||
| public String paramString (); | ||
| public void printComponents (Graphics g); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Container | |
| protected final void addImpl (Component comp, Object constraints, int index); | ||
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public void layout (); | Overrides:Container |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Component(java.awt.image.ImageObserver,MenuContainer,Serializable)-->Container-->ScrollPane
Passed To: Toolkit.createScrollPane()
| Shape | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | shape PJ1.1 | |
This interface is one of the most important in all of Java 2D. It defines methods necessary for generalized operations on shapes, such as drawing, filling, and insideness testing. The package java.awt.geom contains a number of useful implementations of this interface, including GeneralPath, which can be used to describe arbitrary shapes composed of line and curve segments. java.awt.Polygon and java.awt.Rectangle are also important implementations of Shape. Most applications can rely on these predefined implementations and do not need to implement this interface themselves.
getBounds() and getBounds2D() return rectangular bounding boxes that completely enclose a Shape. contains() and intersects() test whether the shape contains or intersects a specified point or rectangle. The most important method of the Shape interface, however, is getPathIterator(). This method returns a java.awt.geom.PathIterator object that traces the outline of the shape using line and curve segments. The two-argument version of this method returns a PathIterator that is guaranteed to trace the outline using only straight line segments and no curves. The flatness argument is a measure of how closely the line segments must approximate the actual outline. Smaller values of flatness require increasingly accurate approximations.
The Shape interface was first defined in Java 1.1. In that version of the language it contained only the getBounds() method. The interface is so central to Java 2D and has grown so much since the Java 1.1 version, however, that it should generally be considered to be new in Java 1.2.
| public abstract interface Shape { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| 1.2 | public abstract boolean contains (java.awt.geom.Point2D p); | |
| 1.2 | public abstract boolean contains (java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D r); | |
| 1.2 | public abstract boolean contains (double x, double y); | |
| 1.2 | public abstract boolean contains (double x, double y, double w, double h); | |
| public abstract Rectangle getBounds (); | ||
| 1.2 | public abstract java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getBounds2D (); | |
| 1.2 | public abstract java.awt.geom.PathIterator getPathIterator (java.awt.geom.AffineTransform at); | |
| 1.2 | public abstract java.awt.geom.PathIterator getPathIterator (java.awt.geom.AffineTransform at, double flatness); | |
| 1.2 | public abstract boolean intersects (java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D r); | |
| 1.2 | public abstract boolean intersects (double x, double y, double w, double h); | |
| } | ||
Implementations: Polygon, Rectangle, java.awt.geom.Area, java.awt.geom.CubicCurve2D, java.awt.geom.GeneralPath, java.awt.geom.Line2D, java.awt.geom.QuadCurve2D, java.awt.geom.RectangularShape
Passed To: Too many methods to list.
Returned By: Too many methods to list.
| Stroke | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | ||
This interface defines how Java 2D draws the outline of a shape. It is responsible for graphical attributes such as line width and dash pattern. However, the Stroke is not responsible for the color or texture of the outline--those are the responsibility of the Paint interface. By default, lines are solid and are one pixel wide. To specify a different line style, pass a Stroke object to the setStroke() method of a Graphics2D object.
Mathematically, the outline of a shape is an infinitely thin line. Because it has no thickness, it cannot be drawn. The Stroke interface is responsible for defining how such infinitely thin outlines are drawn. The createStrokedShape() method is passed the Shape that is to be drawn. It returns a new Shape that places a finite width around the infinitely thin boundaries of the specified shape. The outline of the original shape can then be drawn by filling the interior of the returned shape.
BasicStroke implements Stroke and is the only implementation needed by most programs. Some programs may define their own implementations to achieve special effects not possible with BasicStroke, however.
| public abstract interface Stroke { | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract Shape createStrokedShape (Shape p); | ||
| } | ||
Implementations: BasicStroke
Passed To: Graphics2D.setStroke()
Returned By: Graphics2D.getStroke()
| SystemColor | Java 1.1 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable PJ1.1 | |
Instances of the SystemColor class represent colors used in the system desktop. You can use these colors to produce applications and custom components that fit well in the desktop color scheme. On platforms that allow the desktop colors to be modified dynamically, the actual colors represented by these symbolic system colors may be dynamically updated.
The SystemColor class does not have a constructor, but it defines constant SystemColor objects that represent each of the symbolic colors used by the system desktop. If you need to compare a SystemColor object to a regular Color object, use the getRGB() method of both objects and compare the resulting values.
| public final class SystemColor extends Color implements Serializable { | ||
| // | No Constructor | |
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int ACTIVE_CAPTION ; | =1 | |
| public static final int ACTIVE_CAPTION_BORDER ; | =3 | |
| public static final int ACTIVE_CAPTION_TEXT ; | =2 | |
| public static final SystemColor activeCaption ; | ||
| public static final SystemColor activeCaptionBorder ; | ||
| public static final SystemColor activeCaptionText ; | ||
| public static final SystemColor control ; | ||
| public static final int CONTROL ; | =17 | |
| public static final int CONTROL_DK_SHADOW ; | =22 | |
| public static final int CONTROL_HIGHLIGHT ; | =19 | |
| public static final int CONTROL_LT_HIGHLIGHT ; | =20 | |
| public static final int CONTROL_SHADOW ; | =21 | |
| public static final int CONTROL_TEXT ; | =18 | |
| public static final SystemColor controlDkShadow ; | ||
| public static final SystemColor controlHighlight ; | ||
| public static final SystemColor controlLtHighlight ; | ||
| public static final SystemColor controlShadow ; | ||
| public static final SystemColor controlText ; | ||
| public static final SystemColor desktop ; | ||
| public static final int DESKTOP ; | =0 | |
| public static final int INACTIVE_CAPTION ; | =4 | |
| public static final int INACTIVE_CAPTION_BORDER ; | =6 | |
| public static final int INACTIVE_CAPTION_TEXT ; | =5 | |
| public static final SystemColor inactiveCaption ; | ||
| public static final SystemColor inactiveCaptionBorder ; | ||
| public static final SystemColor inactiveCaptionText ; | ||
| public static final SystemColor info ; | ||
| public static final int INFO ; | =24 | |
| public static final int INFO_TEXT ; | =25 | |
| public static final SystemColor infoText ; | ||
| public static final SystemColor menu ; | ||
| public static final int MENU ; | =10 | |
| public static final int MENU_TEXT ; | =11 | |
| public static final SystemColor menuText ; | ||
| public static final int NUM_COLORS ; | =26 | |
| public static final SystemColor scrollbar ; | ||
| public static final int SCROLLBAR ; | =23 | |
| public static final int TEXT ; | =12 | |
| public static final SystemColor text ; | ||
| public static final int TEXT_HIGHLIGHT ; | =14 | |
| public static final int TEXT_HIGHLIGHT_TEXT ; | =15 | |
| public static final int TEXT_INACTIVE_TEXT ; | =16 | |
| public static final int TEXT_TEXT ; | =13 | |
| public static final SystemColor textHighlight ; | ||
| public static final SystemColor textHighlightText ; | ||
| public static final SystemColor textInactiveText ; | ||
| public static final SystemColor textText ; | ||
| public static final int WINDOW ; | =7 | |
| public static final SystemColor window ; | ||
| public static final int WINDOW_BORDER ; | =8 | |
| public static final int WINDOW_TEXT ; | =9 | |
| public static final SystemColor windowBorder ; | ||
| public static final SystemColor windowText ; | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Color | |
| 1.2 | public PaintContext createContext (java.awt.image.ColorModel cm, Rectangle r, java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D r2d, java.awt.geom.AffineTransform xform, RenderingHints hints); | |
| public int getRGB (); | ||
| public String toString (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Color(Paint(Transparency),Serializable)-->SystemColor(Serializable)
Type Of: Too many fields to list.
| TextArea | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1(mod) | |
This class is a GUI component that displays and optionally edits multiline text. The appendText(), insertText(), and replaceText() methods provide various techniques for specifying text to appear in the TextArea. Many important TextArea methods are defined by its TextComponent superclass. See also TextComponent and TextField.
The four-argument version of the TextArea() constructor allows you to specify a scrollbar display policy for the TextArea object. Personal Java environments can define a scrolling mechanism other than scrollbars. In this case, the scrollbar display policy can be ignored.
| public class TextArea extends TextComponent { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public TextArea (); | ||
| public TextArea (String text); | ||
| public TextArea (int rows, int columns); | ||
| public TextArea (String text, int rows, int columns); | ||
| 1.1 | public TextArea (String text, int rows, int columns, int scrollbars); | |
| // | Public Constants | |
| 1.1 | public static final int SCROLLBARS_BOTH ; | =0 |
| 1.1 | public static final int SCROLLBARS_HORIZONTAL_ONLY ; | =2 |
| 1.1 | public static final int SCROLLBARS_NONE ; | =3 |
| 1.1 | public static final int SCROLLBARS_VERTICAL_ONLY ; | =1 |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public int getColumns (); | default:0 | |
| 1.1 | public void setColumns (int columns); | |
| 1.1 | public Dimension getMinimumSize (); | Overrides:Component |
| 1.1 | public Dimension getMinimumSize (int rows, int columns); | |
| 1.1 | public Dimension getPreferredSize (); | Overrides:Component |
| 1.1 | public Dimension getPreferredSize (int rows, int columns); | |
| public int getRows (); | default:0 | |
| 1.1 | public void setRows (int rows); | |
| 1.1 | public int getScrollbarVisibility (); | default:0 |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| 1.1 | public void append (String str); | |
| 1.1 | public void insert (String str, int pos); | |
| 1.1 | public void replaceRange (String str, int start, int end); | |
| // | Protected Methods Overriding TextComponent | |
| protected String paramString (); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Component | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public void appendText (String str); | synchronized |
| # | public void insertText (String str, int pos); | synchronized |
| # | public Dimension minimumSize (); | Overrides:Component |
| # | public Dimension minimumSize (int rows, int columns); | |
| # | public Dimension preferredSize (); | Overrides:Component |
| # | public Dimension preferredSize (int rows, int columns); | |
| # | public void replaceText (String str, int start, int end); | synchronized |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Component(java.awt.image.ImageObserver,MenuContainer,Serializable)-->TextComponent-->TextArea
Passed To: Toolkit.createTextArea()
| TextComponent | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1 | |
This class is the superclass of the TextArea and TextField components. It cannot be instantiated itself but provides methods that are common to these two component types. setEditable() specifies whether the text in the component is editable. getText() returns the text in the component, and setText() specifies text to be displayed. getSelectedText() returns the currently selected text in the component, and getSelectionStart() and getSelectionEnd() return the extents of the selected region of text. select() and selectAll() select some and all of the text displayed in the text component, respectively.
See also TextField and TextArea.
| public class TextComponent extends Component { | ||
| // | No Constructor | |
| // | Event Registration Methods (by event name) | |
| 1.1 | public void addTextListener (java.awt.event.TextListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void removeTextListener (java.awt.event.TextListener l); | synchronized |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.1 | public int getCaretPosition (); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void setCaretPosition (int position); | synchronized |
| public boolean isEditable (); | ||
| public void setEditable (boolean b); | synchronized | |
| public String getSelectedText (); | synchronized | |
| public int getSelectionEnd (); | synchronized | |
| 1.1 | public void setSelectionEnd (int selectionEnd); | synchronized |
| public int getSelectionStart (); | synchronized | |
| 1.1 | public void setSelectionStart (int selectionStart); | synchronized |
| public String getText (); | synchronized | |
| public void setText (String t); | synchronized | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public void select (int selectionStart, int selectionEnd); | synchronized | |
| public void selectAll (); | synchronized | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Component | |
| public void removeNotify (); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Component | |
| protected String paramString (); | ||
| 1.1 | protected void processEvent (AWTEvent e); | |
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| 1.1 | protected void processTextEvent (java.awt.event.TextEvent e); | |
| // | Protected Instance Fields | |
| 1.1 | protected transient java.awt.event.TextListener textListener ; | |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Component(java.awt.image.ImageObserver,MenuContainer,Serializable)-->TextComponent
Subclasses: TextArea, TextField
| TextField | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1 | |
This Component displays a single line of optionally editable text. Most of its interesting methods are defined by its TextComponent superclass. Use setEchoChar() to specify a character to be echoed when requesting sensitive input, such as a password.
See also TextComponent and TextArea.
| public class TextField extends TextComponent { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public TextField (); | ||
| public TextField (int columns); | ||
| public TextField (String text); | ||
| public TextField (String text, int columns); | ||
| // | Event Registration Methods (by event name) | |
| 1.1 | public void addActionListener (java.awt.event.ActionListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void removeActionListener (java.awt.event.ActionListener l); | synchronized |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public int getColumns (); | default:0 | |
| 1.1 | public void setColumns (int columns); | synchronized |
| public char getEchoChar (); | default:\0 | |
| 1.1 | public void setEchoChar (char c); | |
| 1.1 | public Dimension getMinimumSize (); | Overrides:Component |
| 1.1 | public Dimension getMinimumSize (int columns); | |
| 1.1 | public Dimension getPreferredSize (); | Overrides:Component |
| 1.1 | public Dimension getPreferredSize (int columns); | |
| 1.2 | public void setText (String t); | Overrides:TextComponent |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public boolean echoCharIsSet (); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding TextComponent | |
| protected String paramString (); | ||
| 1.1 | protected void processEvent (AWTEvent e); | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Component | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| 1.1 | protected void processActionEvent (java.awt.event.ActionEvent e); | |
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public Dimension minimumSize (); | Overrides:Component |
| # | public Dimension minimumSize (int columns); | |
| # | public Dimension preferredSize (); | Overrides:Component |
| # | public Dimension preferredSize (int columns); | |
| # | public void setEchoCharacter (char c); | synchronized |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Component(java.awt.image.ImageObserver,MenuContainer,Serializable)-->TextComponent-->TextField
Passed To: Toolkit.createTextField()
| TexturePaint | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | ||
This implementation of Paint is used to perform Java 2D drawing and filling operations with a texture or pattern of colors defined in a BufferedImage object.
When you create a TexturePaint object, you must specify the BufferedImage that defines the texture. You must also specify a rectangle that defines both the initial position of the image and the tile size with which the image is replicated. Typically, you specify a rectangle with its upper-left corner at (0,0) and a width and height equal to the width and height of the image
| public class TexturePaint implements Paint { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public TexturePaint (java.awt.image.BufferedImage txtr, java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D anchor); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D getAnchorRect (); | ||
| public java.awt.image.BufferedImage getImage (); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing Paint | |
| public PaintContext createContext (java.awt.image.ColorModel cm, Rectangle deviceBounds, java.awt.geom.Rectangle2D userBounds, java.awt.geom.AffineTransform xform, RenderingHints hints); | ||
| // | Methods Implementing Transparency | |
| public int getTransparency (); | ||
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->TexturePaint(Paint(Transparency))
| Toolkit | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | PJ1.1(mod) | |
This abstract class defines methods that, when implemented, create platform-dependent peers for each of the Component types in java.awt. Java supports its platform-independent GUI interface by implementing a subclass of Toolkit for each platform. Portable programs should never use these methods to create peers directly--they should use the Component classes themselves. A Toolkit object cannot be instantiated directly. The getToolkit() method of Component returns the Toolkit being used for a particular component.
The Toolkit class also defines methods that you can use directly. The static method getDefaultToolkit() returns the default Toolkit that is in use. getScreenSize() returns the screen size in pixels, and getScreenResolution() returns the resolution in dots per inch. sync() flushes all pending graphics output, which can be useful for animation. Other methods of interest include beep(), getSystemClipboard(), createCustomCursor(), and addAWTEventListener(). getPrintJob() is part of the Java 1.1 printing API. In Personal Java environments, printing support is optional, and this method can throw an exception.
| public abstract class Toolkit { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| public Toolkit (); | ||
| // | Public Class Methods | |
| public static Toolkit getDefaultToolkit (); | synchronized | |
| 1.1 | public static String getProperty (String key, String defaultValue); | |
| // | Protected Class Methods | |
| 1.1 | protected static Container getNativeContainer (Component c); | |
| // | Event Registration Methods (by event name) | |
| 1.2 | public void removeAWTEventListener (java.awt.event.AWTEventListener listener); | |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| public abstract java.awt.image.ColorModel getColorModel (); | ||
| 1.2 | public int getMaximumCursorColors (); | constant |
| 1.1 | public int getMenuShortcutKeyMask (); | constant |
| public abstract int getScreenResolution (); | ||
| public abstract Dimension getScreenSize (); | ||
| 1.1 | public abstract java.awt.datatransfer.Clipboard getSystemClipboard (); | |
| 1.1 | public final EventQueue getSystemEventQueue (); | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| 1.2 | public void addAWTEventListener (java.awt.event.AWTEventListener listener, long eventMask); | |
| 1.2 | public void addPropertyChangeListener (String name, java.beans.PropertyChangeListener pcl); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public abstract void beep (); | |
| public abstract int checkImage (Image image, int width, int height, java.awt.image.ImageObserver observer); | ||
| 1.2 | public Cursor createCustomCursor (Image cursor, Point hotSpot, String name) throws IndexOutOfBoundsException; | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.dnd.DragGestureRecognizer createDragGestureRecognizer (Class abstractRecognizerClass, java.awt.dnd.DragSource ds, Component c, int srcActions, java.awt.dnd.DragGestureListener dgl); | constant |
| 1.2 | public abstract java.awt.dnd.peer.DragSourceContextPeer createDragSourceContextPeer (java.awt.dnd.DragGestureEvent dge) throws java.awt.dnd.InvalidDnDOperationException; | |
| 1.2 | public abstract Image createImage (java.net.URL url); | |
| 1.1 | public Image createImage (byte[ ] imagedata); | |
| 1.2 | public abstract Image createImage (String filename); | |
| public abstract Image createImage (java.awt.image.ImageProducer producer); | ||
| 1.1 | public abstract Image createImage (byte[ ] imagedata, int imageoffset, int imagelength); | |
| 1.2 | public Dimension getBestCursorSize (int preferredWidth, int preferredHeight); | |
| 1.2 | public final Object getDesktopProperty (String propertyName); | synchronized |
| public abstract Image getImage (java.net.URL url); | ||
| public abstract Image getImage (String filename); | ||
| 1.1 | public abstract PrintJob getPrintJob (Frame frame, String jobtitle, java.util.Properties props); | |
| public abstract boolean prepareImage (Image image, int width, int height, java.awt.image.ImageObserver observer); | ||
| 1.2 | public void removePropertyChangeListener (String name, java.beans.PropertyChangeListener pcl); | synchronized |
| public abstract void sync (); | ||
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| protected abstract java.awt.peer.ButtonPeer createButton (Button target); | ||
| protected abstract java.awt.peer.CanvasPeer createCanvas (Canvas target); | ||
| protected abstract java.awt.peer.CheckboxPeer createCheckbox (Checkbox target); | ||
| protected abstract java.awt.peer.CheckboxMenuItemPeer createCheckboxMenuItem (CheckboxMenuItem target); | ||
| protected abstract java.awt.peer.ChoicePeer createChoice (Choice target); | ||
| 1.1 | protected java.awt.peer.LightweightPeer createComponent (Component target); | |
| protected abstract java.awt.peer.DialogPeer createDialog (Dialog target); | ||
| protected abstract java.awt.peer.FileDialogPeer createFileDialog (FileDialog target); | ||
| protected abstract java.awt.peer.FramePeer createFrame (Frame target); | ||
| protected abstract java.awt.peer.LabelPeer createLabel (Label target); | ||
| protected abstract java.awt.peer.ListPeer createList (java.awt.List target); | ||
| protected abstract java.awt.peer.MenuPeer createMenu (Menu target); | ||
| protected abstract java.awt.peer.MenuBarPeer createMenuBar (MenuBar target); | ||
| protected abstract java.awt.peer.MenuItemPeer createMenuItem (MenuItem target); | ||
| protected abstract java.awt.peer.PanelPeer createPanel (Panel target); | ||
| 1.1 | protected abstract java.awt.peer.PopupMenuPeer createPopupMenu (PopupMenu target); | |
| protected abstract java.awt.peer.ScrollbarPeer createScrollbar (Scrollbar target); | ||
| 1.1 | protected abstract java.awt.peer.ScrollPanePeer createScrollPane (ScrollPane target); | |
| protected abstract java.awt.peer.TextAreaPeer createTextArea (TextArea target); | ||
| protected abstract java.awt.peer.TextFieldPeer createTextField (TextField target); | ||
| protected abstract java.awt.peer.WindowPeer createWindow (Window target); | ||
| 1.1 | protected abstract EventQueue getSystemEventQueueImpl (); | |
| 1.2 | protected void initializeDesktopProperties (); | empty |
| 1.2 | protected Object lazilyLoadDesktopProperty (String name); | constant |
| 1.1 | protected void loadSystemColors (int[ ] systemColors); | empty |
| 1.2 | protected final void setDesktopProperty (String name, Object newValue); | synchronized |
| // | Protected Instance Fields | |
| 1.2 | protected final java.util.Map desktopProperties ; | |
| 1.2 | protected final java.beans.PropertyChangeSupport desktopPropsSupport ; | |
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| # | public abstract String[ ] getFontList (); | |
| # | public abstract FontMetrics getFontMetrics (Font font); | |
| // | Deprecated Protected Methods | |
| 1.1# | protected abstract java.awt.peer.FontPeer getFontPeer (String name, int style); | |
| } | ||
Returned By: Component.getToolkit(), Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit(), Window.getToolkit(), java.awt.peer.ComponentPeer.getToolkit()
| Transparency | Java 1.2 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | ||
The integer constants defined by this interface identify the three types of transparency supported by Java 2D. Although the Transparency interface is implemented only by a couple of Java 2D classes, the constants it defines are more widely used. These constants are:
- OPAQUE
-
All colors are fully opaque, with no transparency. The alpha value of every pixel is 1.0.
- BITMASK
-
Colors are either fully opaque or fully transparent, as specified by the bits in a bit mask. That is, each pixel has 1 bit associated with it that specifies whether the pixel is opaque (alpha is 1.0) or transparent (alpha is 0.0).
- TRANSLUCENT
-
Colors may be totally opaque, totally transparent, or translucent. This model of transparency uses an alpha channel that is wider than 1 bit and supports a number of alpha transparency levels between 1.0 and 0.0.
| public abstract interface Transparency { | ||
| // | Public Constants | |
| public static final int BITMASK ; | =2 | |
| public static final int OPAQUE ; | =1 | |
| public static final int TRANSLUCENT ; | =3 | |
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| public abstract int getTransparency (); | ||
| } | ||
Implementations: Paint, java.awt.image.ColorModel
| Window | Java 1.0 | |
|
|
||
| java.awt | serializable AWT component PJ1.1(mod) | |
This class represents a top-level window with no borders or menu bar. Window is a Container with BorderLayout as its default layout manager. Window is rarely used directly; its subclasses Frame and Dialog are more commonly useful.
show() (which overrides the show() method of Component) makes a Window visible and brings it to the front of other windows. toFront() brings a window to the front, and toBack() buries a window beneath others. pack() is an important method that initiates layout management for the window, setting the window size to match the preferred size of the components contained within the window. getToolkit() returns the Toolkit() in use for this window. Call dispose() when a Window is no longer needed, to free its window system resources.
Although the Window class is part of the Personal Java API, Personal Java implementations can prohibit the creation of Window objects. In this case, the Window() constructor throws an exception.
| public class Window extends Container { | ||
| // | Public Constructors | |
| 1.2 | public Window (Window owner); | |
| public Window (Frame owner); | ||
| // | Event Registration Methods (by event name) | |
| 1.1 | public void addWindowListener (java.awt.event.WindowListener l); | synchronized |
| 1.1 | public void removeWindowListener (java.awt.event.WindowListener l); | synchronized |
| // | Property Accessor Methods (by property name) | |
| 1.1 | public Component getFocusOwner (); | |
| 1.2 | public java.awt.im.InputContext getInputContext (); | Overrides:Component |
| 1.1 | public java.util.Locale getLocale (); | Overrides:Component |
| 1.2 | public Window[ ] getOwnedWindows (); | |
| 1.2 | public Window getOwner (); | |
| 1.1 | public boolean isShowing (); | Overrides:Component |
| public Toolkit getToolkit (); | Overrides:Component | |
| public final String getWarningString (); | ||
| // | Public Instance Methods | |
| 1.2 | public void applyResourceBundle (java.util.ResourceBundle rb); | |
| 1.2 | public void applyResourceBundle (String rbName); | |
| public void dispose (); | ||
| public void pack (); | ||
| public void toBack (); | ||
| public void toFront (); | ||
| // | Public Methods Overriding Container | |
| public void addNotify (); | ||
| 1.2 | public void setCursor (Cursor cursor); | synchronized |
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Container | |
| 1.1 | protected void processEvent (AWTEvent e); | |
| // | Public Methods Overriding Component | |
| 1.2 | public void hide (); | |
| public void show (); | ||
| // | Protected Methods Overriding Object | |
| 1.2 | protected void finalize () throws Throwable; | |
| // | Protected Instance Methods | |
| 1.1 | protected void processWindowEvent (java.awt.event.WindowEvent e); | |
| // | Deprecated Public Methods | |
| 1.1# | public boolean postEvent (Event e); | Overrides:Component |
| } | ||
Hierarchy: Object-->Component(java.awt.image.ImageObserver,MenuContainer,Serializable)-->Container-->Window
Subclasses: Dialog, Frame, javax.swing.JWindow
Passed To: Toolkit.createWindow(), Window.Window(), java.awt.event.WindowEvent.WindowEvent(), javax.swing.JWindow.JWindow()
Returned By: Window.{getOwnedWindows(), getOwner()}, java.awt.event.WindowEvent.getWindow(), javax.swing.SwingUtilities.windowForComponent()

Copyright © 2001 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.