1-21
Cisco AVVID Network Infrastructure Enterprise Quality of Service Design
956467
Chapter 1 Overview
What is the Quality of Service Toolset?
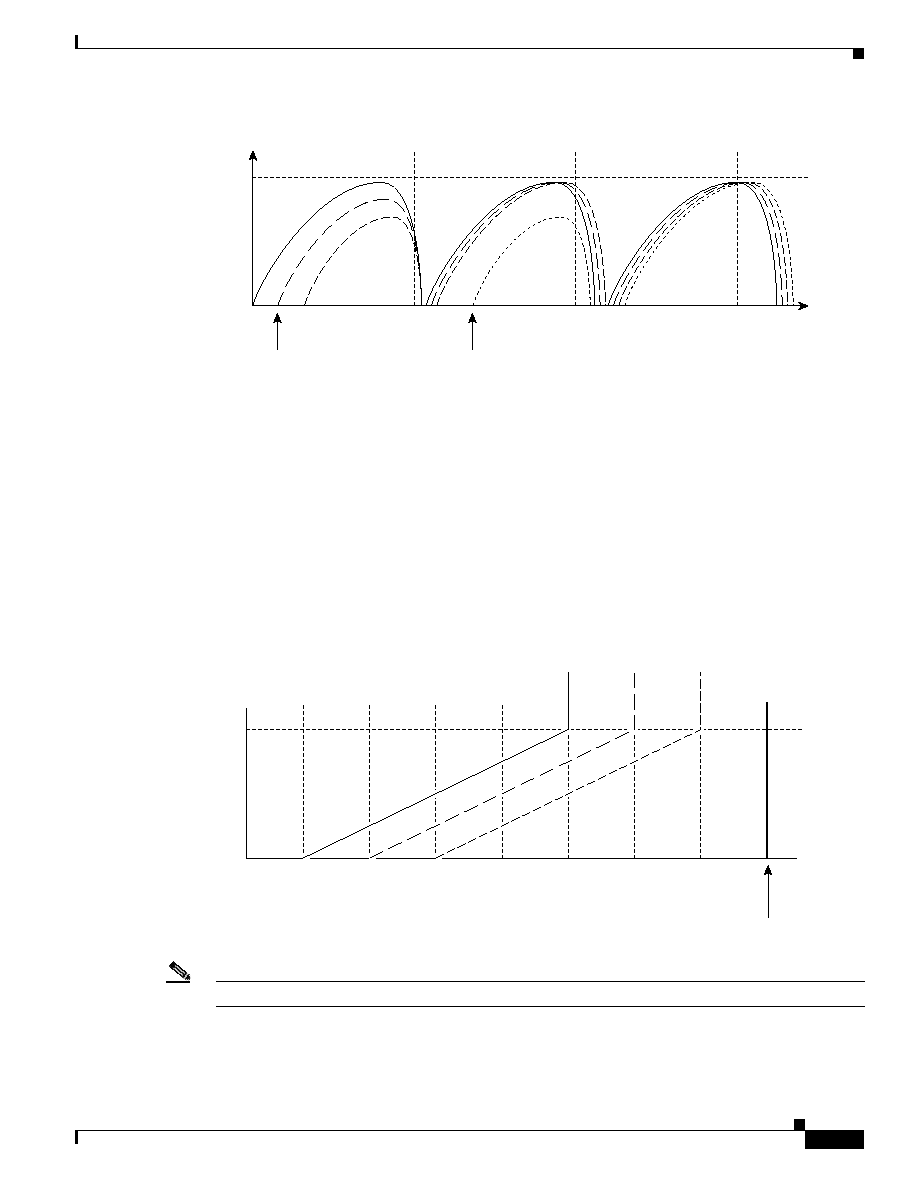
Figure 1-12 Congestion Waves Attributable to Tail-Drop
WRED obviates this situation proactively by providing congestion avoidance. That is, instead of waiting
for buffers to fill before dropping packets, the router monitors the buffer depth and performs early
discards on selected packets sent over selected connections.
WRED is primarily designed to work with TCP applications. When WRED is used and the TCP source
detects the dropped packet, the source slows its transmission. WRED can selectively discard lower
priority traffic when the interface begins to get congested.
WRED can also be configured to use the DSCP value when it calculates the drop probability of a packet.
The DiffServ Compliant WRED feature extends the functionality of WRED to enable support for PHBs.
Thus, packets marked with Assured Forwarding PHBs will be assigned preferential drop probabilities
based on these markings by the WRED algorithm.
illustrates a simplified (3 PHB) example
of DSCP-based WRED.
Figure 1-13 DSCP-Based WRED for AF11, AF12, and AF13
Note
Distributed WRED (dWRED) is the distributed counterpart of WRED.
81037
100
Three traffic flows
start at different times
Another traffic flow
starts at this point
Time
Queue
utilization
81038
1
0
Begin
dropping
AF13
Begin
dropping
AF12
Begin
dropping
AF11
Drop
all
AF13
Drop
all
AF12
Drop
all
AF11
Max queue length
(tail drop everything)
Drop
probability
