|
|

Cisco Transaction Connection (CTRC) is a Cisco IOS Software feature that enables access to host resident operational data in Customer Information Control System (CICS) and IBM relational database management system (DB2). It became available in then Cisco IOS Release 12.05(XN).
CTRC is available on the following platforms:
The CTRC, previously called Cisco Database Connection (CDBC), enables access to IBM's DB2 database resources from TCP/IP desktops and servers. It supports the Distributed Relational Database Architecture (DRDA).
CTRC provides a gateway between client workstations using DRDA requestors on TCP/IP networks and IBM DB2 databases on Systems Network Architecture (SNA) networks. Many of the available workstation-based DRDA requestors are Open Database Connectivity (ODBC) clients. ODBC is a call-level interface developed by Microsoft. It allows an application to use a single interface to access database management systems from different vendors.
CTRC accepts DRDA client requests over TCP/IP, and either converts the messages to SNA before sending them to DB2, or passes TCP messages on to DB2 across TCP/IP. On the reply, CTRC converts the SNA messages to TCP/IP and sends them across the network, back to the client.
CTRC supports TCP/IP pass through to DB2 systems that support direct TCP/IP access. In this case, TCP/IP can be used instead of SNA for connection between the router and the host database.
CTRC also supports Password Expiration Management (PEM) in SNA networks where PEM is supported to match functionality provided in DRDA over TCP/IP.
CTRC enables access to CICS from TCP/IP clients and servers. It allows Cisco routers to use the Intersystem Communication Protocol, and provides a gateway between CICS common clients running under Windows or UNIX on TCP/IP networks and CICS online transaction monitoring systems on IBM Multiple Virtual Storage (MVS) hosts running SNA.
 |
Note The IBM CICS Universal Client is also known as IBM CICS Common Client or the CICS Client. The terms are used interchangeably. In this document, CICS by itself refers to the CICS Server unless otherwise indicated. |
CTRC supports the IBM CICS Universal Client using the Extended Call Interface (ECI) and the Extended Presentation Interface (EPI). The ECI lets non-CICS client applications invoke CICS transaction programs. The EPI lets distributed applications call CICS transactions that were originally accessed via 3270 terminals.
CTRC also supports clients that use the Microsoft Common Object Module Transaction Interface (COMTI), IBM TXSeries running as clients, and other standard ISC-TCP based requestors.
CTRC supports route configuration for a CICS transaction. Each transaction can be routed to a specific CICS region.
Figures 1 through 3 show a few of the network topologies in which the CTRC router can be deployed. The Sample Router Configurations appendix provides a sample router and host configurations.
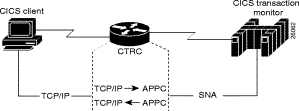
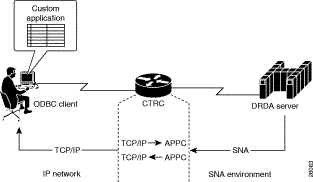
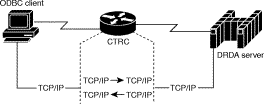
The following sections describe the hosts and clients that CTRC currently supports for access to CICS and DB2.
CTRC accepts database requests from end user workstations and servers running an ODBC driver using the DRDA protocol to communicate with IBM databases.
CTRC supports the following DB2 versions:
CTRC supports the following CICS servers:
 |
Note Versions marked with an asterisk (*) have limited server support. These versions support ECI but they do not support EPI or the Terminal Emulation function. |
CTRC supports the following CICS Servers connected as clients:
CTRC supports connectivity to DB2 from clients that use the following standard interfaces:
CTRC supports connectivity to CICS from the following clients:
The following are known issues when migrating from CDBC (CTRC Version 1.0) to CTRC Version 2.0:
The remaining chapters and appendix in this document describe the following steps required to configure CTRC:
Refer to the "Cisco Transaction Connection" sections of the Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Configuration Guide and the Cisco IOS Bridging and IBM Networking Command Reference for more information about configuring CTRC and using the CTRC commands.
The following documents, published by IBM, provide additional information that you may find helpful when setting up CTRC. The document titles and part numbers, which are provided in parentheses, were current when these lists were prepared but are subject to change by IBM.
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Posted: Tue Nov 5 11:18:26 PST 2002
All contents are Copyright © 1992--2002 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Important Notices and Privacy Statement.