
3.2. Strings
A string is a sequence of Unicode letters, digits, punctuation characters, and so on -- it is the JavaScript data type for representing text. As you'll see shortly, you can include string literals in your programs by enclosing them in matching pairs of single or double quotation marks. Note that JavaScript does not have a character data type such as char, like C, C++, and Java do. To represent a single character, you simply use a string that has a length of 1.
3.2.1. String Literals
A string is a sequence of zero or more Unicode characters enclosed within single or double quotes (' or "). Double-quote characters may be contained within strings delimited by single-quote characters, and single-quote characters may be contained within strings delimited by double quotes. String literals must be written on a single line; they may not be broken across two lines. If you need to include a newline character in a string literal, use the character sequence \n , which is documented in the next section. Examples of string literals are:
"" // The empty string: it has zero characters 'testing' "3.14" 'name="myform"' "Wouldn't you prefer O'Reilly's book?" "This string\nhas two lines" "Π is the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter"
As illustrated in the last example string shown, the ECMAScript v1 standard allows Unicode characters within string literals. Implementations prior to JavaScript 1.3, however, typically support only ASCII or Latin-1 characters in strings. As we'll see in the next section, you can also include Unicode characters in your string literals using special "escape sequences." This is useful if your text editor does not provide complete Unicode support.
Note that when you use single quotes to delimit your strings, you must be careful with English contractions and possessives like can't and O'Reilly's. Since the apostrophe is the same as the single-quote character, you must use the backslash character (\) to escape any apostrophes that appear in single-quoted strings (this is explained in the next section).
In client-side JavaScript programming, JavaScript code often contains strings of HTML code, and HTML code often contains strings of JavaScript code. Like JavaScript, HTML uses either single or double quotes to delimit its strings. Thus, when combining JavaScript and HTML, it is a good idea to use one style of quotes for JavaScript and the other style for HTML. In the following example, the string "Thank you" is single-quoted within a JavaScript expression, which is double-quoted within an HTML event handler attribute:
<a href="" onclick="alert('Thank you')">Click Me</a>3.2.2. Escape Sequences in String Literals
The backslash character (\) has a special purpose in JavaScript strings. Combined with the character that follows it, it represents a character that is not otherwise representable within the string. For example, \n is an escape sequence that represents a newline character.[6]
[6]C, C++, and Java programmers will already be familiar with this and other JavaScript escape sequences.
Another example, mentioned in the previous section, is the \' escape, which represents the single quote (or apostrophe) character. This escape sequence is useful when you need to include an apostrophe in a string literal that is contained within single quotes. You can see why we call these escape sequences -- here, the backslash allows us to escape from the usual interpretation of the single-quote character. Instead of using it to mark the end of the string, we use it as an apostrophe:
'You\'re right, it can\'t be a quote'
Table 3-2 lists the JavaScript escape sequences
and the characters they represent. Two of the escape sequences are
generic ones that can be used to represent any character by
specifying its
Latin-1 or Unicode character code as
a hexadecimal number. For example, the sequence
\xA9 represents the copyright symbol, which has
the Latin-1 encoding given by the hexadecimal number A9. Similarly,
the \u escape represents an arbitrary Unicode
character specified by four hexadecimal digits.
\u03c0 represents the character 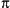 , for
example. Note that Unicode escapes are required by the
ECMAScript v1 standard but are not
typically supported in implementations prior to JavaScript 1.3. Some
implementations of JavaScript also allow a Latin-1 character to be
specified by three octal digits following a backslash,
but this escape sequence is not
supported in the ECMAScript v3
standard and should no longer be used.
, for
example. Note that Unicode escapes are required by the
ECMAScript v1 standard but are not
typically supported in implementations prior to JavaScript 1.3. Some
implementations of JavaScript also allow a Latin-1 character to be
specified by three octal digits following a backslash,
but this escape sequence is not
supported in the ECMAScript v3
standard and should no longer be used.
Table 3-2. JavaScript escape sequences
|
Sequence |
Character represented |
|---|---|
|
\0 |
The NUL character (\u0000). |
|
\b |
Backspace (\u0008). |
|
\t |
Horizontal tab (\u0009). |
|
\n |
Newline (\u000A). |
|
\v |
Vertical tab (\u000B). |
|
\f |
Form feed (\u000C). |
|
\r |
Carriage return (\u000D). |
|
\" |
Double quote (\u0022). |
|
\' |
Apostrophe or single quote (\u0027). |
|
\\ |
Backslash (\u005C). |
|
\xXX |
The Latin-1 character specified by the two hexadecimal digits XX. |
|
\uXXXX |
The Unicode character specified by the four hexadecimal digits XXXX. |
|
\XXX |
The Latin-1 character specified by the octal digits XXX, between 1 and 377. Not supported by ECMAScript v3; do not use this escape sequence. |
Finally, note that the backslash escape cannot be used before a line break to continue a string (or other JavaScript) token across two lines or to include a literal line break in a string. If the \ character precedes any character other than those shown in Table 3-2, the backslash is simply ignored (although future versions of the language may, of course, define new escape sequences). For example, \# is the same thing as #.
3.2.3. Working with Strings
One of the built-in features of JavaScript is the ability to concatenate strings. If you use the + operator with numbers, it adds them. But if you use this operator on strings, it joins them by appending the second to the first. For example:
msg = "Hello, " + "world"; // Produces the string "Hello, world" greeting = "Welcome to my home page," + " " + name;
To determine the length of a string -- the number of characters it contains -- use the length property of the string. If the variable s contains a string, you access its length like this:
s.length
You can use a number of methods to operate on strings. For example, to get the last character of a string s:
last_char = s.charAt(s.length - 1)
To extract the second, third, and fourth characters from a string s:
sub = s.substring(1,4);
To find the position of the first letter a in a string s:
i = s.indexOf('a'); There are quite a few other methods that you can use to manipulate strings. You'll find full documentation of these methods in the core reference section of this book, under the String object and subsequent listings.
As you can tell from the previous examples, JavaScript strings (and JavaScript arrays, as we'll see later) are indexed starting with zero. That is, the first character in a string is character 0. C, C++, and Java programmers should be perfectly comfortable with this convention, but programmers used to languages with 1-based strings and arrays may find that it takes some getting used to.
In some implementations of JavaScript, individual characters can be read from strings (but not written into strings) using array notation, so the earlier call to charAt( ) could also be written like this:
last_char = s[s.length - 1];
Note, however, that this syntax is not part of the ECMAScript v3 standard, is not portable, and should be avoided.
When we discuss the object data type, you'll see that object properties and methods are used in the same way that string properties and methods are used in the previous examples. This does not mean that strings are a type of object. In fact, strings are a distinct JavaScript data type. They use object syntax for accessing properties and methods, but they are not themselves objects. We'll see just why this is at the end of this chapter.

Copyright © 2003 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.



