Glossary
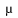 -LAW
-LAW-
(Pronounced "myew-lah") UNIX standard audio file format.
- accessibility
-
Refers to making web pages available and readable to all users, including those with disabilities such as sight or hearing impairments.
- AIFF
-
Audio Interchange File Format. Standard audio format originally developed for the Macintosh, which is now supported on PCs as well. It is one of the formats commonly used for distributing audio on the Web.
- alpha channel
-
In graphics, an extra channel for storing information about an image. The alpha channel works like a mask that applies properties (such as transparency) to the pixels in the image. Other channels typically include color value information -- as in the red, green, and blue channels of an RGB image.
- alpha-channel transparency
-
The method of transparency used by 24-bit PNGs, which use an additional (alpha) channel to store variable levels of transparency (up to 256) for each pixel in the image.
- animated gif
-
A GIF89a that contains multiple frames and a "control block" for controlling the animation timing and display.
- applet
-
A self-contained mini-executable program, such as one written in the Java programming language.
- ASCII files
-
Files that are comprised of alphanumeric characters. Some FTP programs refer to ASCII files as "text" files.
- ASP
-
Active Server Pages. The part of Microsoft's Internet Information Server software that allows server-side scripting for the creation of dynamically generated web pages and database functions. Web pages created with ASP commonly have the suffix .asp.
- audio bit depth
-
The number of bits used to define the resolution of the amplitude (or volume) of a digital audio waveform -- the more bits, the more accurate the rendering of the original audio source and the larger the resulting audio file. Some common bit depths are 8-bit (which sounds thin or tinny, like a telephone signal) and 16-bit, which is required to describe music of CD quality.
- AVI
-
Audio/Video Interleaved. A digital video format developed by Microsoft in which audio and video information are interleaved in every frame for smoother playback.
- binary files
-
Files made up of compiled data (ones and zeros), such as executable programs, graphic images, movies, etc. Some programs refer to the binary mode as "raw data" or "image data."
- CGI
-
Common Gateway Interface. The mechanism for communication between the web server and other programs (CGI scripts) running on the server.
- character entities
-
Strings of characters used to specify characters not found in the normal alphanumeric character set in HTML documents.
- character set
-
An organization of characters -- units of a written language system -- in which each character is assigned a specific number.
- client
-
A software application that extracts services from a server somewhere on the network. A web browser is a client that renders and displays documents on remote servers.
- CLUT
-
Color Look Up Table. A list of colors and associated index numbers used to render eight-bit images.
- CMYK
-
Cyan-Magenta-Yellow-Black. The four ink colors used in process printing. Not appropriate for generating web graphics. (RGB is the color mode for web graphics.)
- codec
-
Compression/decompression algorithms applied to media files.
- CSS
-
Cascading Style Sheets. An addition to HMTL for controlling presentation of a document, including color, typography, alignment of text and images, etc.
- CSS-P
-
CSS with positioning. Refers to a proposal for adding positioning capabilities with style sheets. The CSS-P proposal has since been rolled into the CSS2 Specification.
- data fork
-
The portion of a Macintosh file that contains the actual data of the document. See also resource fork.
- data rate
-
In video, the rate at which data must be transferred in order for the video to play smoothly without interruption. The data rate (also called "bit rate") for a movie is measured in kilobytes per second (K/s or KB/s). It can be calculated by dividing the size of the file (in K) by the length of the movie (in seconds).
- deprecated
-
In the HTML 4.0 Specification, a label identifying an HTML tag or attribute as "outdated" and discouraged from use in favor of newer constructs (often style sheet controls).
- DHTML
-
Dynamic HTML. An integration of JavaScript, Cascading Style Sheets, and the Document Object Model. With DHTML, content can move across the screen or respond to user inputs.
- dithering
-
The approximation of a color by mixing pixels of similar colors that are available in the image palette. The result of dithering is a random dot pattern or noise in the image.
- Document Object Model (DOM)
-
The browser's internal hierarchical organization of the elements in a document. The existence of a DOM makes page elements available for manipulation via scripting or style sheets. Netscape Navigator's and Microsoft Internet Explorer's DOMs differ significantly.
- dpi
-
Dots per inch. In graphics, this is the measurement of the resolution of a printed image. It is commonly (although incorrectly) used to refer to the screen resolution of web graphics, which is technically measured in ppi (pixels per inch). See also ppi.
- DTD
-
Document Type Definition. A file associated with an SGML or XML document that defines how the tags should be interpreted and displayed by the application reading the document.
- encoding
-
The process of converting an analog source (such as an analog audio signal) into digital format. An encoder is the software that does the converting.
- frame rate
-
In video, frames per second; used as a measure of video quality.
- FTP
-
File Transfer Protocol. A protocol for moving files over the Internet from one computer to another. FTP is a client/server system: one machine must be running an FTP server, the other an FTP client.
- gamma
-
Refers to the overall brightness of a computer monitor's display. In technical terms, it is a numerical adjustment for the nonlinear relationship of voltage to light intensity.
- GIF
-
Graphic Interchange Format. Common file format of web graphic images. GIF is a palette-based, 8-bit format that compresses images with the lossless LZW compression scheme. GIF is most appropriate for images with areas of flat color and sharp contrast. See also LZW compression.
- HDML
-
Handheld Device Markup Language. A specialized set of HTML tags for creating documents to be displayed on handheld devices such as mobile phones. It has been replaced by WML. See also WML.
- hexadecimal
-
A base-16 numbering system consisting of the characters 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, A, B, C, D, E, and F, where A through F represent the decimal values 10 through 15. It is used in HTML for specifying RGB color values.
- HTML
-
Hypertext Markup Language. The format of web documents.
- HTTP
-
Hypertext Transfer Protocol. The protocol that defines how web pages and media are requested and transferred between servers and browsers.
- i18n
-
The W3C abbreviation for "Internationalization" ("i", 18 letters, then "n"), relating to efforts to make the Web accessible in all languages.
- imagemap
-
A single image that contains multiple hypertext links.
- indexed color
-
In graphics, a system for rendering colors in 8-bit images. Indexed color files, such as GIFs, contain an index (also called a palette or color lookup table) of colors and associated index numbers, which is used to render color in the image.
- Java
-
A cross-platform, object-oriented programming language developed by Sun Microsystems. It can be used to create whole applications; however, its primary contribution to the Web has been in the form of Java applets, self-contained, mini-executable programs.
- JavaScript
-
A client-side scripting language developed by Netscape that adds interactivity and conditional behavior to web pages. It has little in common with Java.
- JPEG
-
A lossy compression algorithm developed by the Joint Photographic Experts Group. It is used by files in the JFIF format, which are commonly referred to as "JPEG files." JPEG is most efficient at compressing images with gradations in tone and no sharp edge contrasts. Photographic images are typically best saved in JPEG format.
- key frames
-
In video, master frames placed throughout a video against which the following frames are compared (for use with temporal, or interframe, compression).
- Linux
-
A version of Unix designed to run on PCs.
- lossy compression
-
A method for reducing file size in which some data (usually indiscernible to human perception) is deleted in order to achieve a higher compression rate.
- lossless compression
-
A method for reducing the size of a file without loss of data; in lossless compression, redundant information is removed.
- LZW compression
-
Short for Lempel-Zev-Welch, the names of the inventors. A lossless compression scheme that takes advantage of repetition in data streams (such as a row of pixels of identical color). It is the compression scheme used by graphic files in the GIF format.
- MathML
-
Math Markup Language. An XML application for describing mathematical notation and capturing its structure and content.
- MIDI
-
Musical Instrument Digital Interface. This audio format uses numerical commands to describe the pitch and endurance of notes that are "played" by available digital instrument sounds.
- MIME types
-
Multimedia Internet Mail Extensions. A protocol that defines a number of content types and subtypes and allows programs like web browsers, newsreaders, and email clients to recognize different kinds of files and deal with them appropriately. The MIME type specifies what media a file is, such as an image, audio, or video, and the subtype identifies the precise file format.
- MP3
-
Audio file format (MPEG I, Level-III) capable of high levels of compression with little discernible loss of quality. It has become the standard for sharing audio files over the Internet.
- MPEG
-
A family of multimedia standards created by the Motion Picture Experts Group, commonly used to refer to audio and video files saved using one of the MPEG compression schemes.
- namespace
-
A uniquely named group of element and attribute names. XML documents refer to namespaces in order to prevent confusion between competing DTD tag names.
- palette
-
A table in an 8-bit indexed color file (such as GIF) that provides color information for the pixels in the image. See also CLUT.
-
Portable Document Format. A file format developed by Adobe Systems used for capturing formatted page layouts for distribution. PDF documents, when viewed with the required Adobe Acrobat Reader, will appear exactly as they were intended.
- PHP
-
Hypertext Preprocessor. An open source, server-side tool for creating dynamically generated web pages (similar to Microsoft's ASP).
- PNG
-
Portable Network Format. A versatile graphics file format that features support for both 8-bit (PNG8) indexed images and 24-bit images (PNG24). PNGs also feature variable transparency levels, automatic color correction controls, and a lossless yet highly efficient compression scheme.
- ppi
-
Pixels per inch. The measurement of the resolution of a screen image.
- QuickTime
-
A system extension that makes it possible to view audio and video information on a computer. It was originally developed for the Macintosh but is now available for Windows machines as well, and has been adopted as the video standard by the ISO in their development of MPEG-4. The term also refers to the file format.
- RDF
-
Resource Description Framework. An XML application used to define the structure of metadata for documents, i.e., data that is useful for indexing, navigating, and searching a site.
- RMF
-
Rich Music Format. A proprietary audio format used by the Beatnik system.
- resource fork
-
Extra code added in the Macintosh file format, used for storing icons, previews, and file type information. This information should be stripped out when sending the file to a non-Macintosh server. See also data fork.
- RGB color
-
A color system that describes colors based on combinations of red, green, and blue light.
- rollover
-
The act of passing the mouse pointer over an element's space, or the events triggered by that action (such as a changing graphic or pop-up message, sometimes called rollover events).
- sampling rate
-
In a digital audio file, the number of samples taken per second.
- server
-
A networked computer that provides some kind of service or information.
- Server Side Includes (SSI)
-
Special placeholders in an HTML document that the server is to replace with actual data just before sending the final document to the browser. Extended SSI (XSSI) (part of Apache 1.2 and higher) provides more advanced command functions, including conditional behaviors.
- SGML
-
Standard Generalized Markup Language. A metalanguage that provides a comprehensive set of syntax rules for marking up the structure of documents and data. HTML is a subset of SGML.
- Shockwave
-
Proprietary technology from Macromedia, Inc., for the web delivery of multimedia content.
- SMIL
-
Synchronized Multimedia Integration Language, an XML-based language for creating multimedia, time-based presentation. SMIL combines audio, video, text, animation, and graphics in a precise, synchronized fashion.
- spatial compression
-
In video, spatial compression is applied to each individual frame of the video, using compression schemes commonly used on still images (also called "intraframe" compression).
- spatial frequency
-
Refers to the concentration of detail in an image. For example, an image of a blue sky would be considered to have low frequency. A detailed image, such as a close-up of blades of grass, has high frequency.
- SVG
-
Standardized Vector Graphics. A language for defining two-dimensional vector graphics in XML.
- telnet
-
An internet protocol for logging into and using a remote system on the Internet. Telnet is a client/server system that requires a telnet server running on one computer and a telnet client on the other.
- temporal compression
-
In video, temporal compression takes place over a series of frames, deleting information that is repeated between frames (also called "interframe" compression).
- Unix
-
A multiuser, multitasking operating system developed by Bell Laboratories. It also provides programs for editing text, sending email, preparing tables, performing calculations, and many other specialized functions that normally require separate applications programs.
- valid code
-
In an XML application, code that properly uses the elements and attributes as specified in a Document Type Definition (DTD).
- W3C
-
The World Wide Web Consortium. A consortium of many companies and organizations that "exists to develop common standards for the evolution of the World Wide Web." It is run by a joint effort between the Laboratory for Computer Science at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and CERN, the European Particle Physics Laboratory, where the WWW was first developed.
- WAI
-
Web Accessibility Initiative. The committee at the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) that ensures that web technologies are accessible to users with disabilities.
- WAP
-
Wireless Application Protocol. A collection of standards and specifications for delivering Internet-like information to wireless devices such as mobile phones, pagers, PDAs, etc.
- WAVE
-
Waveform Audio File Format. This format was developed for the PC but is now supported on Macintosh as well.
- Web Palette
-
The set of 216 colors that will not dither or shift when viewed with browsers on 8-bit monitors.
- well-formed code
-
Code that abides by the strict syntax rules of XML.
- WML
-
Wireless Markup Language. An XML-based language for creating applications for wireless devices. It is part of the Wireless Application Protocol (WAP).
- XHTML
-
A reworking of the HTML 4.0 Specification to abide by the rules and syntax of XML.
- XML
-
Extensible Markup Language. A new standard for marking up documents and data. XML is based on SGML, but with a reduced feature set that is more appropriate for distribution via the Web. XML allows authors to create customized tag sets to provide functionality not available with HTML.
- XSL
-
Extensible Style Language. A system for controlling the presentation of complex XML documents and structured data.
- XSSI
-
Extended SSI. See Server Side Includes.

Copyright © 2002 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.