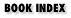8.7. Programming Assistance
vi was developed primarily as a programmer's editor. It has features that make things especially easy for the UNIX programmer—someone writing C programs and troff documentation. (Real Programmers write Real Documentation in troff.) Several of the clones are proud bearers of this tradition, adding a number of features that make them even more usable and capable for the "power user."[46]
[46]In contrast to the What You See Is What You Get (WYSIWYG) philosophy, UNIX is the You Asked For It, You Got It operating system. (With thanks to Scott Lee.)
Two features (among many) most deserve discussion:
- Edit-compile speedup
- elvis, vim, and vile allow you to easily invoke make(1), capture the errors from your compiler, and automatically move to the lines containing the errors. You can then fix the errors and re-run make, all from within the editor.
- Syntax highlighting
- elvis, vim, and vile have the ability to highlight and/or change the color of different syntactic elements in different kinds of files.
8.7.1. Edit-Compile Speedup
Programming often consists of a "compile-test-debug" cycle. You make changes, compile the new code, and then test and debug it. When learning a new language, syntax errors are especially common, and it is frustrating to be constantly stopping and restarting (or suspending and resuming) the editor in between compiles.
elvis, vim, and vile all provide facilities that allow you to stay within the editor while compiling your program. Furthermore, they capture the compiler's output and use it to automatically go to each line that contains an error.[47] Consistent use of this ability can save time and improve programmer productivity.
[47]Yet another feature that emacs users are accustomed to comes to vi.
Here is an example, using elvis. You are beginning to learn C++, so you start out with the obligatory first program:
| Keystrokes | Results |
|---|---|
| :w hello.C | 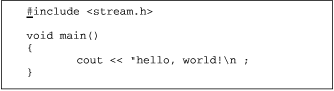 You enter the program, forgetting the closing quote, and then write the program to hello.C. |
| :make hello | 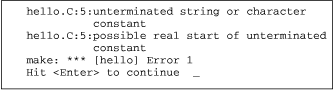 You type the :make command to run make, which in turn runs the C++ compiler. (In this case, g++.) |
| :errlist | 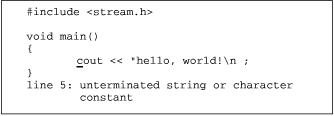 The :errlist command moves to the line with the error and displays the first compiler error message in the status line. |
You can fix the error, resave the file, re-run :make and eventually compile your program without errors.
All of the editors have similar facilities. They will all compensate for changes in the file, correctly moving you to subsequent lines with errors. More details are provided in each editor's chapter.
8.7.2. Syntax Highlighting
elvis, vim, and vile all provide some form of syntax highlighting. All three also provide syntax coloring, changing the color of different parts of the file on displays that can do so (such as under X11 or the Linux console). See each editor's chapter for more information.

Copyright © 2003 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.