Appendix A. Quick Reference
This appendix lists vi commands and ex commands according to their use.
Table A.1. Movement Commands
| Command | Function |
|---|---|
| Character | |
| h,j,k,l | Left, down, up, right (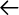 , , 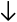 , , 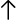 , , 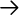 ). ). |
| Text | |
| w,W,b,B | Forward, backward by word. |
| e,E | End of word. |
| ),( | Beginning of next, previous sentence. |
| },{ | Beginning of next, previous paragraph. |
| ]],[[ | Beginning of next, previous section. |
| Lines | |
| RETURN | First non-blank character of next line. |
| 0, $ | First, last position of current line. |
| ^ | First non-blank character of current line. |
| +, - | First non-blank character of next, previous line. |
| n| | Column n of current line. |
| H | Top line of screen. |
| M | Middle line of screen. |
| L | Last line of screen. |
| nH | n (number) of lines after top line. |
| nL | n (number) of lines before last line. |
| Scrolling | |
| CTRL-F, CTRL-B | Scroll forward, backward one screen. |
| CTRL-D, CTRL-U | Scroll down, up one-half screen. |
| CTRL-E, CTRL-Y | Show one more line at bottom, top of window. |
| z RETURN | Reposition line with cursor: to top of screen. |
| z. | Reposition line with cursor: to middle of screen. |
| z- | Reposition line with cursor: to bottom of screen. |
| CTRL-L | Redraw screen (without scrolling). |
| Searches | |
| /pattern | Search forward for pattern. |
| ?pattern | Search backward for pattern. |
| n, N | Repeat last search in same, opposite direction. |
| /, ? | Repeat previous search forward, backward. |
| fx | Search forward for character x in current line. |
| Fx | Search backward for character x in current line. |
| tx | Search forward to character before x in current line. |
| Tx | Search backward to character after x in current line. |
| ; | Repeat previous current-line search. |
| , | Repeat previous current-line search in opposite direction. |
| Line number | |
| CTRL-G | Display current line number. |
| nG | Move to line number n. |
| G | Move to last line in file. |
| :n | Move to line n in file. |
| Marking position | |
| mx | Mark current position as x. |
| `x | Move cursor to mark x. |
| ` ` | Return to previous mark or context. |
| 'x | Move to beginning of line containing mark x. |
| '' | Return to beginning of line containing previous mark. |
Table A.2. Editing Commands
| Command | Function |
|---|---|
| Insert | |
| i, a | Insert text before, after cursor. |
| I, A | Insert text before beginning, after end of line. |
| o, O | Open new line for text below, above cursor. |
| Change | |
| r | Replace character. |
| cw | Change word. |
| cc | Change current line. |
| cmotion | Change text between the cursor and the target of motion. |
| C | Change to end of line. |
| R | Type over (overwrite) characters. |
| s | Substitute: delete character and insert new text. |
| S | Substitute: delete current line and insert new text. |
| Delete, move | |
| x | Delete character under cursor. |
| X | Delete character before cursor. |
| dw | Delete word. |
| dd | Delete current line. |
| dmotion | Delete text between the cursor and the target of motion. |
| D | Delete to end of line. |
| p, P | Put deleted text after, before cursor. |
| "np | Put text from delete buffer number n after cursor (for last nine deletions). |
| Yank | |
| yw | Yank (copy) word. |
| yy | Yank current line. |
| "ayy | Yank current line into named buffer a (a-z). Uppercase names append text. |
| ymotion | Yank text between the cursor and the target of motion. |
| p, P | Put yanked text after, before cursor. |
| "aP | Put text from buffer a before cursor (a-z). |
| Other commands | |
| . | Repeat last edit command. |
| u, U | Undo last edit; restore current line. |
| J | Join two lines. |
| ex edit commands | |
| :d | Delete lines. |
| :m | Move lines. |
| :co or :t | Copy lines. |
| :.,$d | Delete from current line to end of file. |
| :30,60m0 | Move lines 30 through 60 to top of file. |
| :.,/pattern/co$ | Copy from current line through line containing pattern to end of file. |
Table A.3. Exit Commands
| Command | Function |
|---|---|
| ZZ | Write (save) the file if modified, and quit file. |
| :x | Write (save) the file if modified, and quit file. |
| :wq | Write (save) the file unconditionally, and quit file. |
| :w | Write (save) file. |
| :w! | Write (save) file, overriding protection. |
| :30,60w newfile | Write from line 30 through line 60 as newfile. |
| :30,60w>> file | Write from line 30 through line 60 and append to file. |
| :w %.new | Write current buffer named file as file.new. |
| :q | Quit file. |
| :q! | Quit file, overriding protection. |
| Q | Quit vi and invoke ex. |
| :e file2 | Edit file2 without leaving vi. |
| :r newfile | Read contents of newfile into current file. |
| :n | Edit next file. |
| :e! | Return to version of current file at time of last write (save). |
| :e # | Edit alternate file. |
| :vi | Invoke vi editor from ex. |
| : | Invoke one ex command from vi editor. |
| % | Current filename (substitutes into ex command line). |
| # | Alternate filename (substitutes into ex command line). |
Table A.4. Solaris vi Command Mode Tag Commands
| Command | Function |
|---|---|
| ^] | Look up the location of the identifier under the cursor in the tags file, and move to that location. If tag stacking is enabled, the current location is automatically pushed onto the tag stack. |
| ^T | Return to the previous location in the tag stack, i.e., pop off one element. |
Table A.5. Command-Line Options
| Command | Function |
|---|---|
| vi file | Invoke vi editor on file. |
| vi file1 file2 | Invoke vi editor on files sequentially. |
| view file | Invoke vi editor on file in read-only mode. |
| vi -R file | Invoke vi editor on file in read-only mode. |
| vi -r file | Recover file and recent edits after a crash. |
| vi -t tag | Look up tag and start editing at its definition. |
| vi -w n | Set the window size to n; useful over a slow connection. |
| vi + file | Open file at last line. |
| vi +n file | Open file directly at line number n. |
| vi -c command file | Open file, execute command, which is usually a search command or line number (POSIX). |
| vi +/pattern file | Open file directly at pattern. |
| ex file | Invoke ex editor on file. |
| ex - file < script | Invoke ex editor on file, taking commands from script; suppress informative messages and prompts. |
| ex -s file < script | Invoke ex editor on file, taking commands from script; suppress informative messages and prompts (POSIX). |
Table A.6. Other ex Commands
| Command | Function |
|---|---|
| Abbreviations [63] | |
| :map x sequence | Define keystroke x as a command sequence. x can be multiple characters. |
| :map! x sequence | Define x as command sequence for insert mode. |
| :unmap x | Disable the map x. |
| :unmap! x | Disable the insert mode map x. |
| :ab abbr phrase | Abbreviate phrase as abbr; when abbr is typed in insert mode, it expands to full words or phrases. |
| :unab abbr | Disable abbreviation abbr. |
| Customizing environment: [63] | |
| :set option | Activate option. |
| :set option=value | Assign value to option. |
| :set nooption | Deactivate option. |
| :set | Display options set by user. |
| :set all | Display list of all current option settings, both default and those set by the user. |
| :set option? | Display value of option. |
| Accessing UNIX | |
| :sh | Invoke shell. |
| ^D | Return to editor from shell. |
| :! command | Give UNIX command. |
| :n,m! command | Filter lines n to m through UNIX command. |
| :r !command | Read output of UNIX command into current file. |
[63]In .exrc files, omit the colon at the start of ex commands.

Copyright © 2003 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.