2.3 Simple Edits
When you enter text in your file, it is rarely perfect. You find typos or want to improve on a phrase; sometimes your program has a bug. Once you enter text, you have to be able to change it, delete it, move it, or copy it. Figure 2.3 shows the kinds of edits you might want to make to a file. The edits are indicated by proofreading marks.
Figure 2.3: Proofreading edits

In vi
you can perform any of these edits with a few basic
keystrokes: i
for insert (which you've
already seen); a
for append; c
for change; and
d
for delete. To move or copy text, you use a pair of commands.
You move text with a
d
for delete, then a p
for put; you copy text
with a y
for "yank," then a p
for put.
Each type of edit is described in this section.
Figure 2.4
shows the vi
commands you use to make the
edits marked in
Figure 2.3
.
Figure 2.4: Edits with vi commands

2.3.1 Inserting New Text
You have already seen the insert command used to enter text into a new file. You also use the insert command while editing existing text to add missing characters, words, and sentences. In the file practice , suppose you have the sentence:

with the cursor positioned as shown. To insert With a screen editor at the beginning of the sentence, enter the following:
| Keystrokes | Results |
|---|---|
2k
|
 Move the cursor up two lines with the |
iWith a
|
 Press |
screen editor
[ESC]
|
 Finish inserting text, and press [ESC] to end the insert and return to command mode. |
On the screen shown in the example above, vi pushes existing text to the right as the new text is inserted. That is because we are assuming that you are using vi on an "intelligent" terminal that can rewrite the screen with each character you type. An insert on a "dumb" terminal (such as an adm3a ) will look different. The terminal itself cannot handle the overhead of updating the screen for each character typed (without a tremendous sacrifice of speed), so vi doesn't rewrite the screen until after you press [ESC] . On a dumb terminal, the same insert would appear:
| Keystrokes | Result |
|---|---|
iWith a
|
 Press |
screen editor
|
 The insertion appears to have overwritten existing text. |
| [ESC] |  After you have finished inserting text, press [ESC] to end the insert and return to command mode. vi now rewrites the line, so that you see all existing text. |
2.3.2 Appending Text
[a]
You can append text at any place in your file with the append
command a
.
a
works in almost the same way as i
, except that text
is inserted after
the cursor rather than before
the cursor.
You may
have noticed that when you press i
to enter insert mode,
the cursor doesn't move until after you enter some text.
On the other hand, when you press a
to enter insert mode, the
cursor moves one space to the right.
When you enter text, it appears after
the original cursor
position.
2.3.3 Changing Text
[c]
You can replace any text in your file with the change command,
c
.
In order to tell c
how much text to change, you combine
c
with a movement command.
In this way, a movement command serves as a text object
for the
c
command to affect.
For example, c
can be used to change text from the cursor:
After issuing a change command, you can replace the identified text
with any amount of new text, with no characters at all, with one word,
or with hundreds of lines. c
, like i
and a
, leaves you in insert mode
until you press the
[ESC]
key.
When the change only affects the current line,
vi
marks the end of the text that will be
changed with a $
,
so that you can see what part of the line is affected.
(See the example for cw
, below.)
2.3.3.1 Words
[cw]
To change a word, combine the c
(change) command with
w
for word.
You can replace a word (cw
) with a longer
or shorter word (or any amount of text).
cw
can be thought of as "delete the word marked and insert
new text until
[ESC]
is pressed."
Suppose you have the following line in your file practice :
With an editor you can scroll the page,
and want to change an to a screen . You need to change only one word:
| Keystrokes | Results |
|---|---|
w
|
 Move with |
cw
|
 Give the change word command. The end of the text to be
changed will be marked with a |
a screen
|
 Type in the replacement text, and then press [ESC] to return to command mode. |
cw
also works on a portion of a word. For example,
to change spelling
to spelled
,
you can position the cursor on the i
, type
cw
, then type ed
, and finish
with [ESC]
.
2.3.3.2 Lines
[cc]
To replace the entire current line, there is the special change
command, cc
.
cc
changes an entire line, replacing that line with any
amount of text entered before pressing
[ESC]
.
It doesn't matter where the
cursor is located on the line; cc
replaces the entire line of text.
A command like cw
works differently from a command like
cc
. In using cw
, the old text remains until you type
over it, and any old text that is left over (up to the $
)
goes away when you press
[ESC]
.
In using cc
, though, the old text is wiped out first, leaving you
a blank line on which to insert text.
The "type over" approach happens with any change command that affects less than a whole line, whereas the "blank line" approach happens with any change command that affects one or more lines.
[C]
C
replaces characters from the current cursor position to the
end of the line.
It has the same effect as combining
c
with the
special end-of-line indicator $
(c$
).
The commands cc
and C
are really shortcuts for other
commands, so they don't follow the general form of vi
commands.
You'll see other shortcuts when we discuss the delete and yank commands.
2.3.3.3 Characters
[r]
One other replacement edit is given by the r
command.
r
replaces a single character with another single character.
You do not
have to press
[ESC]
to return to command mode after making the edit.
There is a misspelling in the line below:

Only one letter needs to be corrected.
You don't want to use cw
in this instance because you would
have to retype the entire word.
Use r
to replace a single character at the cursor:
| Keystrokes | Results |
|---|---|
rW
|
 Give the replace command |
2.3.3.4 Substituting text
[s]
Suppose you want to change just a few characters, and not a whole
word. The substitute command (s
), by itself,
replaces a single character. With a preceding count, you can replace
that many characters. As with the change command (c
),
the last character of the text will be marked with a $
so that you can see how much text will be changed.
[S]
The S
command, as is usually the case with uppercase
commands, lets you change whole lines. In contrast to the
C
command, which changes the rest of the line
from the current cursor position, the S
command
deletes the entire line, no matter where the
cursor is. vi
puts you in insert mode at the
beginning of the line.
A preceding count replaces that many lines.
Both s
and S
put you in
insert mode; when you are finished entering new text, press
[ESC]
.
[R]
The R
command, like its lowercase counterpart,
replaces text. The difference is that it simply enters overstrike
mode. The characters you type replace what's on the screen,
character by character, until you type [ESC]
.
You can only overstrike a maximum of one line; as you type
[RETURN]
, vi
will open a new line,
effectively putting you into insert mode.
2.3.4 Changing Case
[~]
Changing the case of a letter is a special form of replacement. The
tilde (~
) command will change a lowercase letter to uppercase, or an
uppercase letter to lowercase. Position the cursor on the letter
whose case you want to change, and type a ~
. The case of the
letter will change, and the cursor will move to the next character.
In older versions of vi
, you
cannot specify a numeric prefix or text object for the ~
to affect.
Modern versions do allow a numeric prefix.
If you want to change the case of more than one line at a time, you
must filter the text through a UNIX command like tr
, as
described in Chapter 7
.
2.3.5 Deleting Text
[d]
You can also delete any text in your file with the delete command
d
.
Like the change command, the delete command requires a
text object (the amount of text to be operated on).
You can delete by word (dw
), by line (dd
and D
),
or by other movement commands that you will learn later.
With all deletions, you move to where you want the edit to take
place, then give the delete command (d
) and the text object,
such as w
for word.
2.3.5.1 Words
[dw] Suppose you have the following text in the file:

with the cursor positioned as shown. You want to delete one are in the first line.
| Keystrokes | Results |
|---|---|
2w
|
 Move the cursor to where you want the edit to begin (are ). |
dw
|
 Give the delete word command ( |
dw
deletes a word beginning where the cursor is
positioned. Notice that the space following the word is
deleted.
dw
can also be used to delete a portion of a word.
In this example:

you want to delete the ed from the end of allowed .
| Keystrokes | Results |
|---|---|
dw
|
 Give the delete word command ( |
dw
always deletes the space before the next word on
a line, but we don't want to do that in the previous example.
To retain the space between words, use de
, which will delete
only to the end of a word. Typing dE
will delete to the
end of a word, including punctuation.
You can also delete backward (db
) or to the end or
beginning of a line (d$
or d0
).
2.3.5.2 Lines
[dd]
The dd
command deletes the entire line that the cursor is on.
dd
will not delete part of a line.
Like its complement cc
, dd
is a special command.
Using the same text as in the previous example, with the
cursor positioned on the first line as shown below:

you can delete the first two lines:
| Keystrokes | Results |
|---|---|
2dd
|
 Give the command to delete two lines ( |
If you are using a "dumb" terminal[2 ] (or a very slow one), line deletions look different. The dumb terminal will not redraw the screen until you scroll past the bottom of the screen. On a dumb terminal the deletion looks like this:
[2] Dumb terminals are rather rare these days. Most of the time, you will run vi inside a terminal emulator on a bitmapped screen.
| Keystrokes | Results |
|---|---|
2dd
|
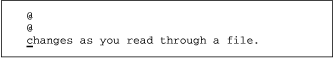 Give the command to delete two lines ( |
[D]
The D
command deletes from the cursor position
to the end of the line. (D
is a shortcut for
d$
.) For example, with the cursor positioned as shown:

you can delete the portion of the line to the right of the cursor.
| Keystrokes | Results |
|---|---|
D
|
 Give the command to delete the portion of the line to the
right of the cursor ( |
2.3.5.3 Characters
[x]
Often you want to delete only one or two characters.
Just as r
is a special change
command to replace a single character, x
is a special delete
command to delete a single character.
x
deletes only the character the cursor is on.
In the line below:
z You can move text by deleting text and then
you can delete the letter z
by pressing x
.[3
]
A capital X
deletes the character before the cursor.
Prefix either of these commands with a number to delete that number of
characters.
For example, 5x
will delete the five characters
under and to the right of the cursor.
[3] The mnemonic for
xis that it is supposedly like "x-ing out" mistakes with a typewriter. Of course, who uses a typewriter any more?
2.3.5.4 Problems with deletions
You've deleted the wrong text and you want to get it back.
There are several ways to recover deleted text. If you've just deleted something and you realize you want it back, simply type
uto undo the last command (for example, add). This works only if you haven't given any further commands, sinceuonly undoes the most recent command. On the other hand, aUwill restore the line to its pristine state; the way it was before any changes were applied to it.You can still recover a recent deletion, however, by using the
pcommand, since vi saves the last nine deletions in nine numbered deletion buffers. If you know, for example, that the third deletion back is the one you want to restore, type:"3p
to "put" the contents of buffer number 3 on the line below the cursor.
This works only for a deleted line . Words, or a portion of a line, are not saved in a buffer. If you want to restore a deleted word or line fragment, and
uwon't work, use thepcommand by itself. This restores whatever you've last deleted. The next few subsections will talk more about the commandsuandp.
2.3.6 Moving Text
In vi
, you move text by deleting it and then placing that deleted
text elsewhere in the file, like a "cut and paste."
Each time you delete a text block, that deletion is temporarily saved in a
special buffer.
Move to another position in your file and use
the put command (p
) to place that text in the new position.
You can move any block of text, although moving is more useful
with lines than with words.
[p]
The put command (p
)
puts the text that is in the buffer after
the
cursor position. The uppercase version of the command,
P
, puts the text before
the cursor. If you delete one or more lines,
p
puts the deleted text on a new line(s) below the cursor.
If you delete less than an entire line, p
puts the deleted text on the current line, after the cursor.
Suppose in your file practice you have the text:
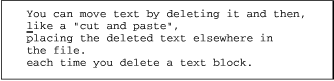
and want to move the second line, like a "cut and paste", below the third line. Using delete, you can make this edit.
| Keystrokes | Results |
|---|---|
dd
|
 With the cursor on the second line, delete that line. The text is placed in a buffer (reserved memory). |
p
|
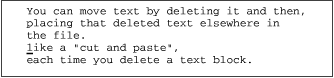 Give the put command, |
NOTE: Once you delete text, you must restore it before the next change command or delete command. If you make another edit that affects the buffer, your deleted text will be lost. You can repeat the put over and over, so long as you don't make a new edit. In Chapter 4, Beyond the Basics , you will learn how to save text you delete in a named buffer so you can retrieve it later.
2.3.6.1 Transposing two letters
You can use xp
(delete character and put after cursor) to
transpose two letters.
For example, in the word mvoe
, the letters vo
are
transposed (reversed).
To correct a transposition, place the cursor on v
and press
x
, then p
.
By coincidence, the word transpose
helps you remember the
sequence xp
; x
stands for trans
,
and p
stands for pose
.
There is no command to transpose words. The section "More Examples of Mapping Keys" in Chapter 7 discusses a short sequence of commands that transposes two words.
2.3.7 Copying Text
[y]
Often you can save editing time (and keystrokes) by copying a
part of your file to use in other places.
With the two commands y
(for yank) and p
(for put),
you can copy any amount of text and put that copied text in another
place in the file.
A yank command copies the selected text into a special buffer,
where it is held until another yank (or deletion) occurs.
You can then place this copy elsewhere in the file with the put command.
As with change and delete, the yank command can be combined
with any movement command (yw
, y$
, 4yy
).
Yank is most frequently used with a line (or more) of text,
because to yank and put a word usually takes longer than
simply to insert the word.
The shortcut yy
operates on an entire line,
just as dd
and cc
do. But the shortcut Y
,
for some reason, does not operate the way D
and C
do.
Instead of yanking from the current position to the end of the line,
Y
yanks the whole line. Y
does the same thing
as yy
.
Suppose you have in your file practice the text:
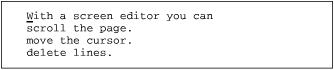
You want to make three complete sentences, beginning each with With a screen editor you can . Instead of moving through the file, making this edit over and over, you can use a yank and put to copy the text to be added.
| Keystrokes | Results |
|---|---|
yy
|
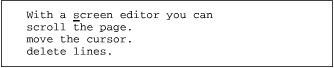 Yank the line of text that you want to copy into the buffer. The cursor can be anywhere on the line you want to yank (or on the first line of a series of lines). |
2j
|
 Move the cursor to where you want to put the yanked text. |
P
|
 Put the yanked text above the cursor line with |
jp
|
 Move the cursor down a line and put the yanked text below
the cursor line with |
Yanking uses the same buffer as deleting. Each new deletion or yank replaces the previous contents of the yank buffer. As we'll see in Chapter 4 , up to nine previous yanks or deletions can be recalled with put commands. You can also yank or delete directly into up to 26 named buffers, which allows you to juggle multiple text blocks at once.
2.3.8 Repeating or Undoing Your Last Command
Each edit command that you give is stored in a temporary buffer until you give the next command. For example, if you insert the after a word in your file, the command used to insert the text, along with the text that you entered, is temporarily saved.
2.3.8.1 Repeat
[period] Any time you make the same editing command over and over, you can save time by duplicating it with the repeat command, the period (.). Position the cursor where you want to repeat the editing command, and type a period.
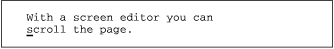
Suppose you have the following lines in your file:
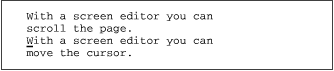
You can delete one line, and then, to delete another line, simply type a period.
| Keystrokes | Results |
|---|---|
dd
|
 Delete a line with the command |
.
|
 Repeat the deletion. |
Older versions of vi
had problems repeating commands.
For example, such versions may
have difficulty repeating
a long insertion when wrapmargin
is set.
If you have such a version, this bug
will probably bite you sooner or later.
There's not a lot you can do about it after the fact,
but it helps to be forewarned.
(Modern versions do not seem to have this problem.)
There are two ways you can guard against a
potential problem when repeating long insertions.
You can write your file (:w
) before repeating the
insertion (returning to this copy if the insertion doesn't work
correctly).
You can also turn off wrapmargin
like this:
:set wm=0
In Section 7.3.5, "More Examples of Mapping Keys " in Chapter 7 , we'll show you an easy way to ause the wrapmargin solution. In some versions of vi , the command [CTRL-@] repeats the most recent insertion. [CTRL-@] is typed in insert mode and returns you to command mode.
2.3.8.2 Undo
[u]
As mentioned earlier, you can undo your last command if you make an error.
Simply press u
.
The cursor need not be
on the line where the original edit was made.
To continue the example above, showing deletion of lines in the file practice :
| Keystrokes | Results |
|---|---|
u
|

|
U
, the uppercase version of u
, undoes all
edits on a single line, as long as the cursor remains on that line
.
Once you move off a line, you can no longer use U
.
Note that you can undo your last undo with u
, toggling between
two versions of text. u
will also undo U
, and U
will undo any changes to a line, including those made with u
.
(A tip: the fact that u
can undo itself leads to a nifty way
to get around in a file.
If you ever want to get back to the site of
your last edit, simply undo it. You will pop back to the appropriate line.
When you undo the undo, you'll stay on that line.)





