| CONTENTS |
Appendix B. State and Sequence Diagrams
This appendix contains state and sequence diagrams for all the bean types discussed in this book: container-managed and bean-managed entity beans, stateless and stateful session beans, and message-driven beans. Although standard Unified Modeling Language (UML) is used in these diagrams, some extensions were required to model EJB runtime characteristics. In the state diagrams, for example, callback methods and class instantiation operations are shown as part of the transition event.
In the sequence diagrams, container-provided classes such as the container itself, the EJB object, and the EJB home are shown as separate classes but are also boxed together. Messages sent from classes in the container system box are considered to be sent from the container system as a whole, not necessarily from the specific container-provided class. This generalization is necessary because the container's interaction with the bean is characterized by these classes but differs from one vendor's implementation to the next. The exact source of the message is immaterial, as long as you realize that the container system sent it.
B.1 Entity Beans
B.1.1 Life Cycle State Diagram of the Entity Bean
Figure B-1. Life-cycle state diagram of the entity bean
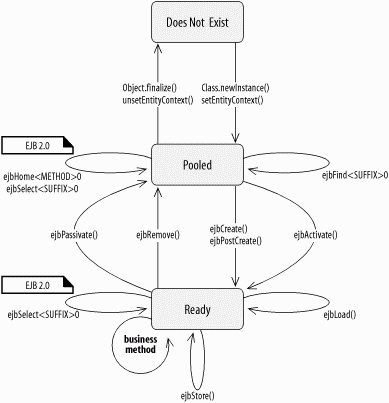
B.1.2 Sequence Diagrams for Container-Managed Persistence
Figure B-2. Creation and removal in container-managed persistence
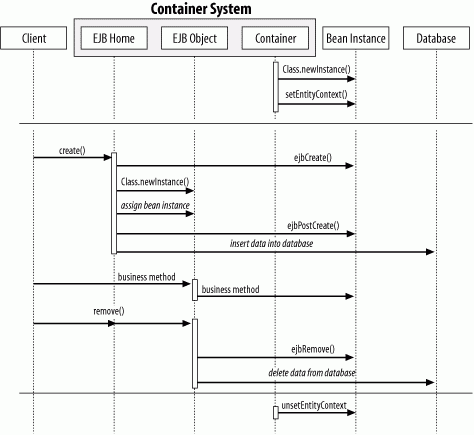
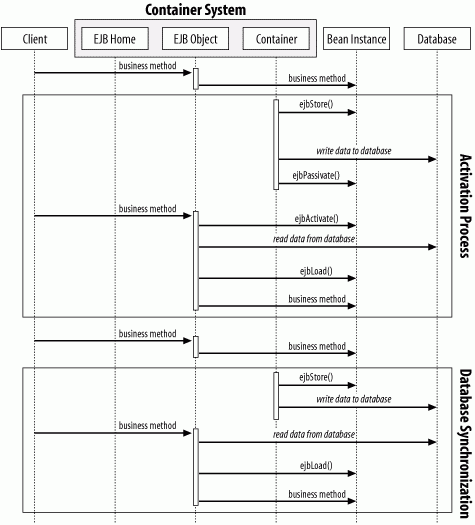
Figure B-3. Activation and synchronization in container-managed persistence
B.1.3 Sequence Diagrams for Bean-Managed Persistence
Figure B-4. Creation and removal in bean-managed persistence
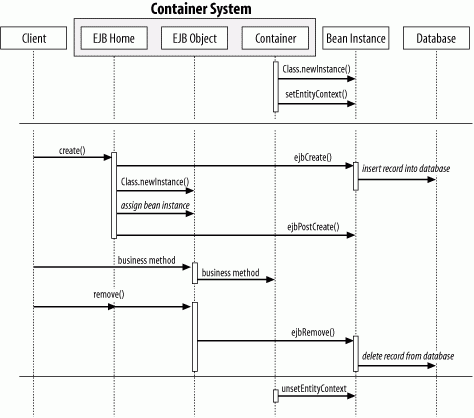
Figure B-5. Activation and synchronization in bean-managed persistence
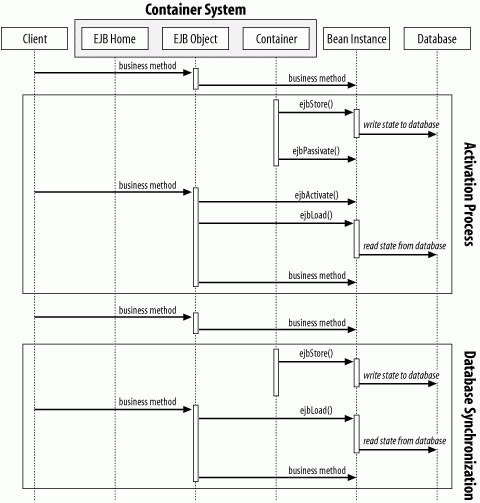
Table B-1 summarizes the operations an entity bean is allowed to perform in various stages of its life cycle. The allowed operations are the same for EJB 2.0 and 1.1, except for the EntityContext methods getEJBLocalHome() and getEJBLocalObject() and the operations allowed for ejbHome() methods, which are specific to EJB 2.0.
|
Method |
Allowed operations |
|---|---|
|
setEntityContext() unsetEntityContext() |
EntityContext methods: getEJBHome() getEJBLocalHome() JNDI ENC contexts: Properties: java:comp/env |
|
ejbCreate() ejbFind() ejbHome() |
EntityContext methods: getEJBHome() getEJBLocalHome() getCallerPrincipal() isCallerInRole() getRollbackOnly() setRollbackOnly() JNDI ENC contexts: Properties: java:comp/env Resource managers: java:comp/env/jdbc EJB references: java:comp/env/ejb |
|
ejbPostCreate() ejbLoad() ejbStore() ejbRemove() Business methods |
EntityContext methods: getEJBHome() getEJBLocalHome() getCallerPrincipal() isCallerInRole() getRollbackOnly() setRollbackOnly() getEJBObject() getEJBLocalObject() getPrimaryKey() JNDI ENC contexts: Properties: java:comp/env Resource managers: java:comp/env/jdbc EJB references: java:comp/env/ejb |
|
ejbActivate() ejbPassivate() |
EntityContext methods: getEJBHome() getEJBLocalHome() getEJBObject() getEJBLocalObject() getPrimaryKey() JNDI ENC contexts: Properties: java:comp/env |
Note that entity beans can never access the EJBContext.getUserTransaction() method, because entity beans are not allowed to manage their own transactions. Only session beans can access this method.
B.2 Session Beans
B.2.1 Stateless Session Beans
Figure B-6. Life-cycle state diagram of the stateless session bean
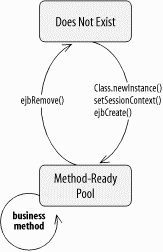
Figure B-7. Creation and removal of stateless session beans
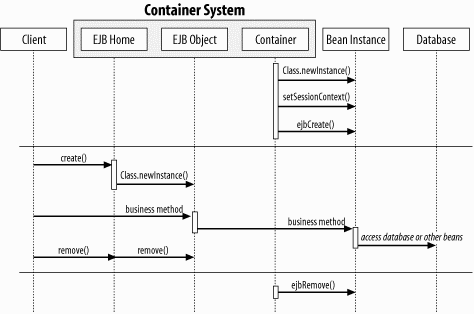
Table B-2 summarizes the operations that are legal for a stateless session bean. The allowed operations are the same for both EJB 2.0 and 1.1, except for the SessionContext methods getEJBLocalHome() and getEJBLocalObject(), which are specific to EJB 2.0.
|
Method |
Allowed operations |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Container-managed transactions |
Bean-managed transactions |
|
|
ejbCreate() ejbRemove() |
EntityContext methods: getEJBHome() getEJBLocalHome() getEJBObject() getEJBLocalObject() JNDI ENC contexts: Properties: java:comp/env |
EntityContext methods: getEJBHome() getEJBLocalHome() getEJBObject() getEJBLocalObject() getUserTransaction() JNDI ENC contexts: Properties: java:comp/env |
|
Business methods |
EntityContext methods: getEJHome() getEJBLocalHome() getCallerPrincipal() isCallerInRole() getRollbackOnly() setRollbackOnly() getEJBObject() getEJBLocalObject() JNDI ENC contexts: Properties: java:comp/env Resource managers: java:comp/env/jdbc EJB references: java:comp/env/ejb |
EntityContext methods: getEJHome() getEJBLocalHome() getCallerPrincipal() isCallerInRole() getEJBObject() getEJBLocalObject() getUserTransaction() JNDI ENC contexts: Properties: java:comp/env Resource managers: java:comp/env/jdbc EJB references: java:comp/env/ejb |
|
ejbActivate() ejbPassivate() |
Not supported (stateless beans do not use these methods) |
Not supported (stateless beans do not use these methods) |
B.2.2 Stateful Session Beans
Figure B-8. Life-cycle state diagram of the stateful session bean
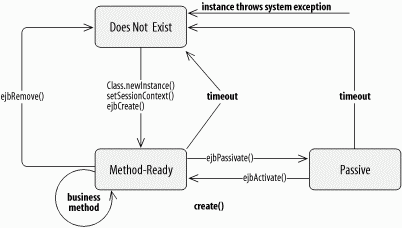
Figure B-9. Life cycle of a stateful session bean with the SessionSynchronization interface
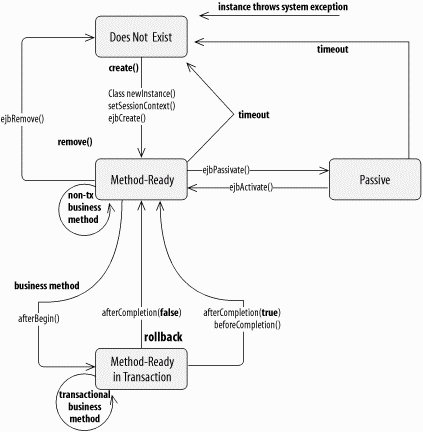
Figure B-10. Creation and removal of stateful session beans
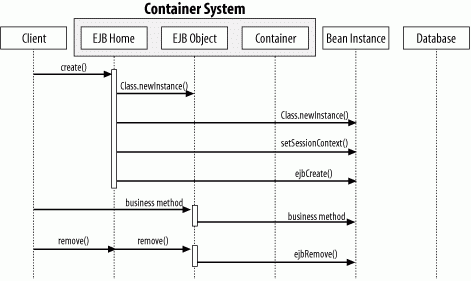
Figure B-11. Activation process of stateful session beans
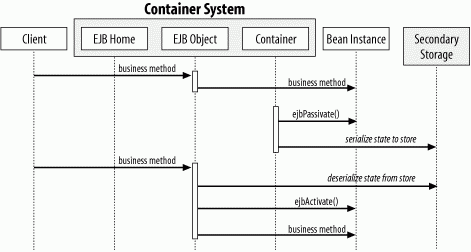
Figure B-12. Transaction notification in SessionSynchronization session beans
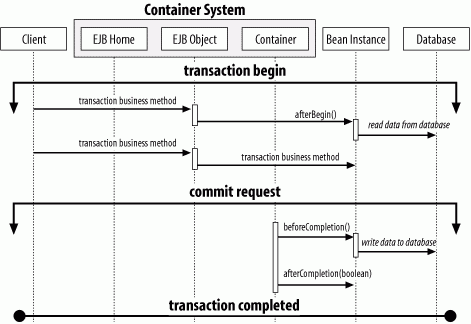
Table B-3 summarizes the operations that are legal for a stateful session bean. The allowed operations are the same for both EJB 2.0 and 1.1, except for the SessionContext methods getEJBLocalHome() and getEJBLocalObject(), which are specific to EJB 2.0.
|
Method |
Allowed operations |
|
|---|---|---|
|
Container-managed transactions |
Bean-managed transactions |
|
|
setSessionContext() |
EntityContext methods: getEJBHome() getEJBLocalHome() JNDI ENC contexts: Properties: java:comp/env |
EntityContext methods: getEJBHome() getEJBLocalHome() JNDI ENC contexts: Properties: java:comp/env |
|
ejbCreate() ejbRemove() ejbActivate() ejbPassivate() |
EntityContext methods: getEJBHome() getEJBLocalHome() getCallerPrincipal() isCallerInRole() getEJBObject() getEJBLocalObject() JNDI ENC contexts: Properties: java:comp/env Resource managers: java:comp/env/jdbc EJB references: java:comp/env/ejb |
EntityContext methods: getEJBHome() getEJBLocalHome() getCallerPrincipal() isCallerInRole() getEJBObject() getEJBLocalObject() getUserTransaction() JNDI ENC contexts: Properties: java:comp/ env Resource managers: java:comp/env/jdbc EJB references: java:comp/env/ejb |
|
Business methods |
EntityContext methods: getEJBHome() getEJBLocalHome() getCallerPrincipal() isCallerInRole() getRollbackOnly() setRollbackOnly() getEJBObject() getEJBLocalObject() JNDI ENC contexts: Properties: java:comp/env Resource managers: java:comp/env/jdbc EJB references: java:comp/env/ejb |
EntityContext methods: getEJHome() getEJBLocalHome() getCallerPrincipal() isCallerInRole() getEJBObject() getEJBLocalObject() getUserTransaction() JNDI ENC contexts: Properties: java:comp/env Resource managers: java:comp/env/jdbc EJB references: java:comp/env/ejb |
|
afterBegin() beforeCompetion() |
EntityContext methods: getEJBHome() getEJBLocalHome() getCallerPrincipal() isCallerInRole() getRollbackOnly() setRollbackOnly() getEJBObject() getEJBLocalObject() JNDI ENC contexts: Properties: java:comp/env Resource managers: java:comp/env/jdbc EJB references: java:comp/env/ejb |
Not supported (bean-managed transaction beans cannot implement the SessionSynchronization interface) |
|
afterCompletion() |
EntityContext methods: getEJBHome() getEJBLocalHome() getCallerPrincipal() isCallerInRole() getEJBObject() getEJBLocalObject() JNDI ENC contexts: Properties: java:comp/env |
Not supported (bean-managed transaction beans cannot implement the SessionSynchronization interface) |
B.2.3 Message-Driven Beans
Figure B-13. Message-driven bean life-cycle state diagram
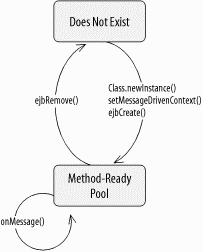
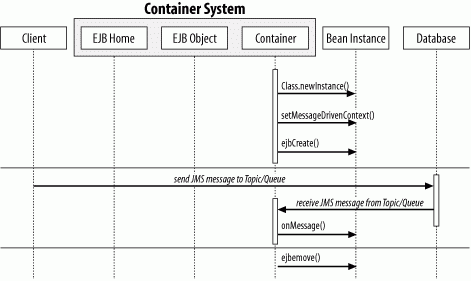
Figure B-14. Message-driven bean sequence diagram
B.2.4 Interactions Between Exceptions and Transactions
Table B-4 summarizes what happens to a transaction if an exception is thrown while the transaction is in process.
|
Transaction scope |
Transaction type attributes |
Exception thrown |
Container's action |
Client's view |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Client-initiated transaction. The transaction is started by the client (application or EJB) and is propagated to the enterprise bean method. |
transaction-type = Container transaction-attribute = Required | Mandatory | Supports |
Application exception |
If the EJB invoked setRollbackOnly(), mark the client's transaction for rollback. Rethrow the application exception. |
Receives the application exception. The client's transaction may or may not have been marked for rollback. |
|
System exception |
Mark the client's transaction for rollback. Log the error. Discard the instance. Rethrow the JTA TransactionRolledbackException to remote clients or the javax.ejb.TransactionRolledbackLocalException to EJB 2.0 local clients. |
Remote clients receive the JTA TransactionRolledbackException; local clients receive the javax.ejb.TransactionRolledbackLocalException. The client's transaction has been rolled back. |
||
|
Container-initiatedtransaction. The transaction started when the EJB's method was invoked and will end when the method completes. |
transaction-type = Container transaction-attribute = Required | RequiresNew |
Application exception |
If the EJB invoked setRollbackOnly(), roll back the transaction and rethrow the application exception. If the EJB did not explicitly roll back the transaction, attempt to commit the transaction and rethrow the application exception. |
Receives the application exception. The EJB's transaction may or may not have been rolled back. The client's transaction is not affected. |
|
System exception |
Roll back the transaction. Log the error. Discard the instance. Rethrow the RemoteException to remote clients or the EJBException to EJB 2.0 local clients. |
Remote clients receive the RemoteException; local EJB 2.0 clients receive the EJBException. The EJB's transaction was rolled back. The client's transaction may or may not be marked for rollback, depending on the vendor. |
||
|
The bean is not part of a transaction. The EJB was invoked but does not propagate the client's transaction and does not start its own transaction. |
transaction-type = Container transaction-attribute = Never | NotSupported | Supports | |
Application exception |
Rethrow the application exception. |
Receives the application exception. The client's transaction is not affected. |
|
System exception |
Log the error. Discard the instance. Rethrow the RemoteException to remote clients or the EJBException to EJB 2.0 local clients. |
Remote clients receive the RemoteException; local EJB 2.0 clients receive the EJBException. The client's transaction may or may not be marked for rollback, depending on the vendor. |
||
|
Bean-managed transaction. The stateful or stateless session EJB uses the EJBContext to explicitly manage its own transaction. |
transaction-type = Bean transaction-attribute = Bean-managed transaction EJBs do not use transaction attributes. |
Application exception |
Rethrow the application exception. |
Receives the application exception. The client's transaction is not affected. |
|
System exception |
Roll back the transaction. Log the error. Discard the instance. Rethrow the RemoteException to remote clients or the EJBException to EJB 2.0 local clients. |
Remote clients receive the RemoteException; local EJB 2.0 clients receive the EJBException. The client's transaction is not affected. |
Table B-5 summarizes the interactions between different types of exceptions and transactions in message-driven beans.
|
Transaction scope |
Transaction type attributes |
Exception thrown |
Container's action |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Container-initiated transaction. The transaction started before the onMessage() method was invoked and will end when the method completes. |
transaction-type = Container transaction-attribute = Required |
System exception |
Roll back the transaction. Log the error. Discard the instance. |
|
Container-initiated transaction. No transaction was started. |
transaction-type = Container transaction-attribute = NotSupported |
System exception |
Log the error. Discard the instance. |
|
Bean-managed transaction. The message-driven bean uses the EJBContext to explicitly manage its own transaction. |
transaction-type = Bean transaction-attribute = Bean-managed transaction EJBs do not use transaction attributes. |
System exception |
Roll back the transaction. Log the error. Discard the instance. |
| CONTENTS |