6.4 CD WriterAt one time, writing a CD by using Linux was a common rite of passage for new Linux users. The command used to write a CD, cdrecord, is a sophisticated command having many options. Getting all the options just right was a challenge for many. However, GnomeToaster makes it easy to write CDs. GnomeToaster can create data and audio CDs. It can duplicate CDs on the fly, create CDs from ISO images, and create bootable El Torito CDs, such as those used to distribute Red Hat Linux. GnomeToaster can create multisession CDs and can erase CD-RW media. For more information on GnomeToaster, see its web site, http://gnometoaster.rulez.org. To launch GnomeToaster, choose Extras Figure 6-14. The Choose Recorder dialog box GnomeToaster's main screen, which may have been partially obscured by the Choose Recorder dialog box, is now plainly visible. Figure 6-15 shows the main screen. Figure 6-15. GnomeToaster's main screen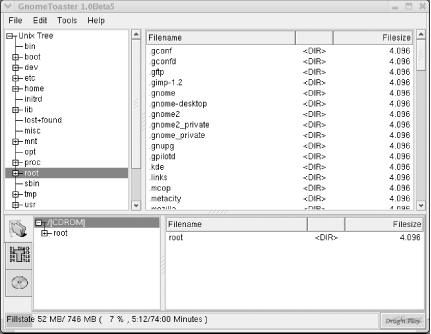 To specify the files to be written to the CD, simply navigate the filesystem using the left and right panes at the top of the GnomeToaster window. Then drag the desired files or directories into the panes at the bottom of the window. When you've specified all the files to be written, click the CD icon at the bottom left of the window. The appearance of the bottom panes changes to resemble that shown in Figure 6-16. Figure 6-16. The CD drive specifications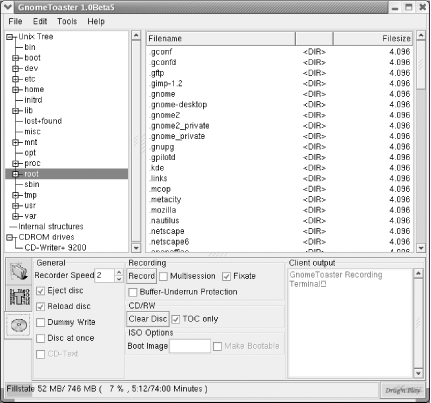 Use the bottom panel to specify the recorder speed and other options. If your drive supports buffer underrun protection, you can enable the corresponding check box. To create the CD, put blank media in the drive and click Record. The Writing CD dialog box appears, as shown in Figure 6-17. Your CD is a standard ISO9660 CD and should be readable under Windows, Linux and other Unix and Unix-like systems, Mac OS, and other platforms. Figure 6-17. Burning a CD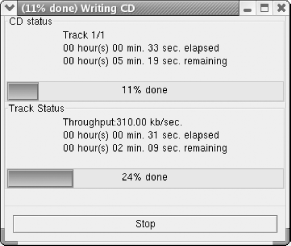 |