7.3. The Nuts and Bolts of ODBC
We'll now take a look at the main features of ODBC that set it apart from the DBI and that enable it to work well as a database-independent interface. The four main features are:
A standard SQL syntax
Standard error codes
Rich metadata
Many attributes and options
7.3.1. A Standard SQL Syntax
Standardized SQL syntax is something of a Holy Grail. ODBC drivers generally do a good job of implementing it, whereas the DBI just ducks the issue entirely! The problem is that while SQL may be a standardized language in theory, in practice it's far enough from the standard on most vendors' databases to cause portability problems.
For example, even a simple task like concatenating two database fields needs to be written like this (for databases conforming to the SQL-92 standard):
SELECT first_name || ' ' || last_name FROM table
Other databases require one of these forms:
SELECT first_name + ' ' + last_name FROM table SELECT CONCAT(first_name, ' ', last_name) FROM table SELECT CONCAT(CONCAT(first_name, ' ') last_name) FROM table SELECT first_name CONCAT ' ' CONCAT last_name FROM table
The SQL dialect used by different database systems is riddled with such inconsistencies, not to mention endless "extensions" to the standard. This is a major headache for developers wishing to write an application that will work with any of a number of databases.
The ODBC approach to this problem is rather elegant. It allows portability when using standard SQL, but doesn't prevent access to database-specific features. When an application passes an SQL statement to the driver, the driver parses it as an SQL-92 statement, and then rewrites it to match the actual syntax of the database being used.
If the parse fails because the SQL doesn't conform to the standard, then the original SQL is passed to the database unaltered. That way, database-specific features can be accessed, and the ODBC parsing doesn't get in the way.
The DBI ducked this whole issue because it would require drivers to be far more complicated than they are now. Parsing and rewriting SQL is not a trivial activity; therefore, the DBI does not try to offer SQL-level portability. In practice, that hasn't been a big problem for people. Perl makes it very easy for applications to build SQL statements as needed for the database being used, as we discussed in Chapter 5, "Interacting with the Database ".
7.3.2. Standard Error Codes
If an INSERT statement fails, how can you tell whether it was because the table already has a record with the same primary key? With ODBC, you'd check the SQLSTATE error indicator to see if it was "23000", regardless of the database being used. With DBI, you're on your own.
ODBC defines a large number of standard error codes that you can use to determine in reasonable detail what went wrong. They're not often needed, but when they are, they're very useful. Having said that, this idyllic picture is tarnished by the fact that many of the codes change depending on the version of the ODBC driver being used. For example, while an ODBC 2.x driver returns "S0011" when a CREATE INDEX statement names an index that already exists, an ODBC 3.x driver returns "42S11". So much for standards!
The DBI leaves you with having to check for different $DBI::err values or $DBI::errstr strings, depending on the database driver being used. The DBI does provide a $DBI::state variable and $h- >state() method that drivers can use to provide the standard error codes, but few do at the moment.
7.3.3. Rich Metadata
ODBC defines a wide range of metadata functions that provide information both about the structure of the data in the database and the datatypes supported by the database. The following table lists the functions and shows which are supported by the Win32::ODBC and DBI modules.
|
ODBC Function |
Win32::ODBC |
DBI |
|---|---|---|
|
Tables |
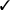 |
|
|
TablePrivileges |
||
|
Columns |
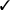 |
|
|
ColumnPrivileges |
||
|
SpecialColumns |
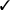 |
|
|
Statistics |
 |
|
|
PrimaryKeys |
 |
|
|
ForeignKeys |
 |
|
|
Procedures |
||
|
ProcedureColumns |
||
|
GetTypeInfo |
 |
|
As you can see, the DBI lags behind the Win32::ODBC module. By the time you read this book, the DBI may have defined interfaces for some of the functions, but how quickly the drivers actually implement the functions is harder to guess. The DBD::ODBC and DBD::Oracle modules will probably lead the way.
7.3.4. Many Attributes and Options
In trying to be a comprehensive interface to a very wide variety of real-world data sources, ODBC provides a way to tell the application about every minute detail of the driver and data source it's connected to. There are so many details available via the GetInfo() function -- over 200 at the last count -- that we're not going to waste paper listing any of them.
Though some books include the list as a great way of adding impressive bulk, we'll just direct you to the online version at Microsoft:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/library/sdkdoc/dasdk/odch5fu7.htm
If that URL ceases to work, then use the MSDN search facility at:
http://msdn.microsoft.com/us/dev/
and search for SQLGetInfo returns using the exact phrase option. The link you want will probably just be called SQLGetInfo.[65]
[65]Microsoft ODBC functions all have an SQL prefix.
ODBC also provides for a great many knobs and buttons that you can use to tailor the fine details of driver behavior to suit your application. These can be accessed via the following functions:
GetEnvAttr SetEnvAttr -- 4 attributes GetConnectAttr SetConnectAttr -- 16 attributes GetStmtAttr SetStmtAttr -- 33 attributes
Prior to ODBC 3.x, there was an older set of functions with names that end in Option instead of Attr. These functions are almost identical to those above, but accept a smaller range of attributes. To find details of all these functions, you can use the Microsoft MSDN search procedure described earlier in this section.
The Win32::ODBC module provides access to the GetInfo(), Get /SetConnectOption(), and Get /SetStmtOption() functions. The DBI defines only a very limited subset of this functionality via an assortment of DBI handle attributes.

Copyright © 2001 O'Reilly & Associates. All rights reserved.