Routing Multicast Traffic
363
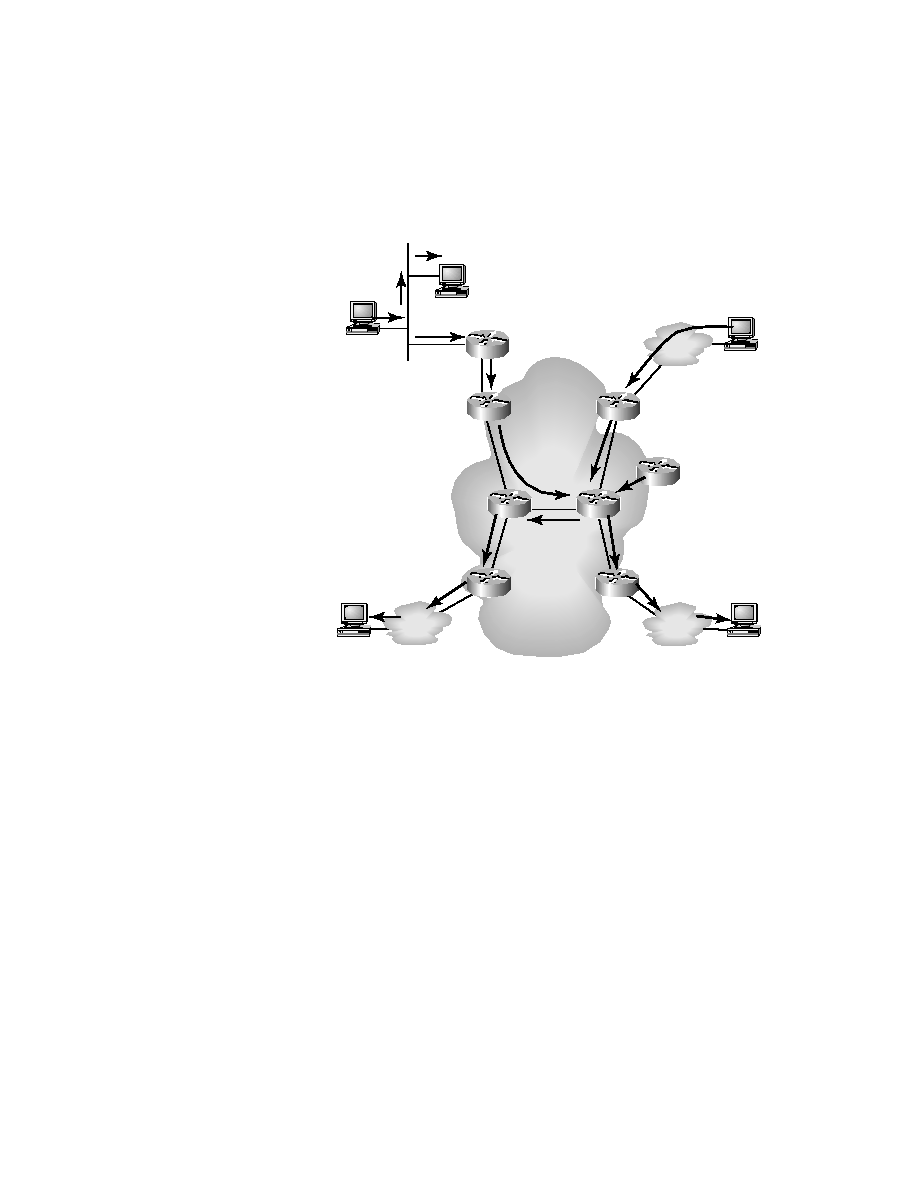
F I G U R E 9 . 1 4
Bidirectional shared tree
Managing Multicast Delivery
Even though the tree distributions explain how source information is man-
aged, we must now discuss how the actual data delivery is managed. There
are several methods of making sure that delivery is as efficient as possible.
The ones that will be discussed here are Reverse Path Forwarding (RPF),
Time-to-Live (TTL) attributes, and routing protocols.
RPF works in tandem with the routing protocols, but it will be described
briefly here. As you have seen in the figures, specifically Figures 9.13 and
9.14, the traffic goes only to the multicast group receivers. We also broached
HostA
HostB
HostE
HostD
Router3
Router4
Router1
Router2
Router7
Router6
Router5
RP
(Shared Root)
Source for
224.2.127.254
10.10.2.5
HostC
Source for
224.2.127.254
172.16.1.51
Member
224.2.127.254
Member
224.2.127.254
Member
224.2.127.254
Copyright ©2000 SYBEX , Inc., Alameda, CA
www.sybex.com
