344
Chapter 9
Multicast
Multicast works in much the same way as a mailing list. You (as a user)
or an application will
subscribe
to a specific IP multicast group to become a
member. Once you're a member of the group, IP multicast packets contain-
ing the group address in the destination field in the header will arrive at your
host and be processed. If the host isn't subscribed to the group, it will not
process packets addressed to that group. Refer to Figure 9.3 for a visual ref-
erence on how multicast works.
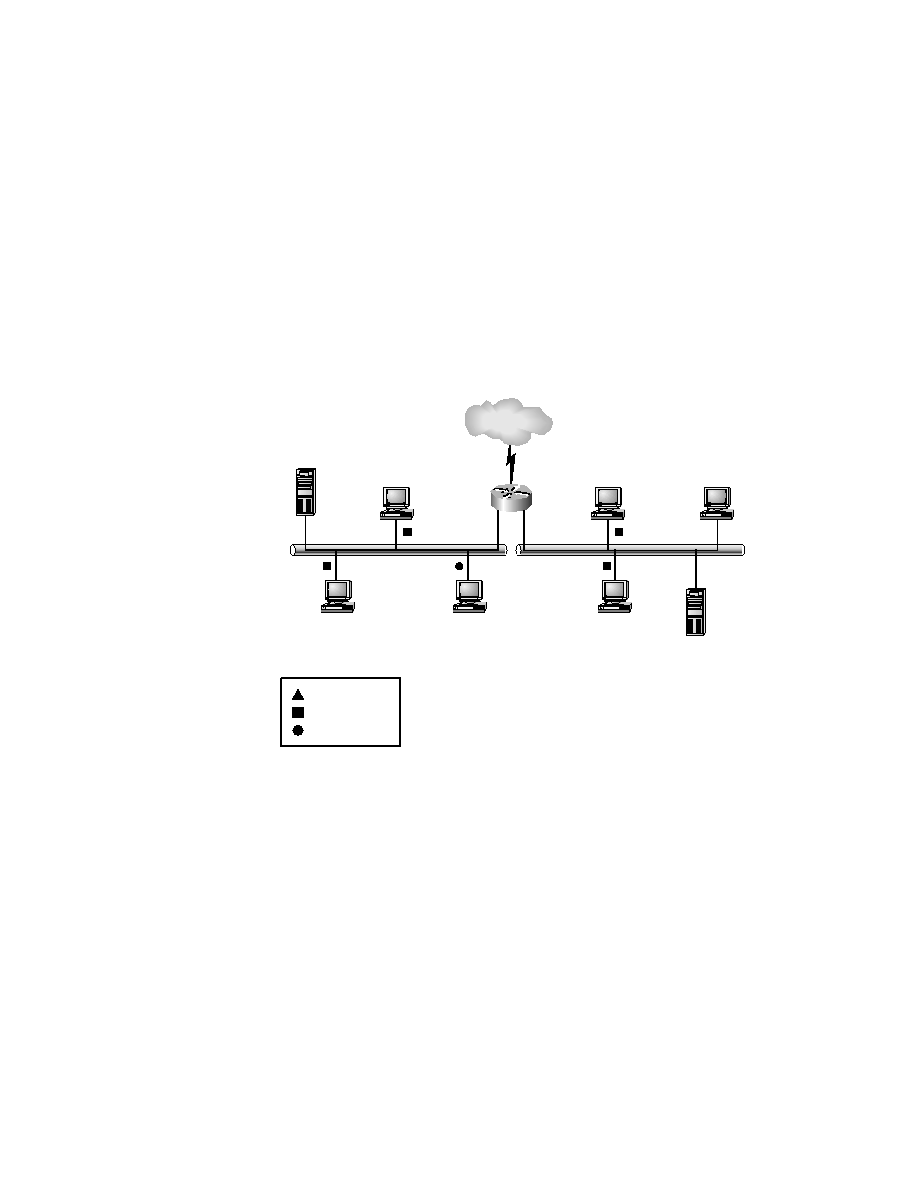
F I G U R E 9 . 3
Multicast communication
The key to multicast is the addressing structure. This is key because all
communication is based on addressing. In unicast communication, there is a
unique address for every host on a network. With broadcast communication,
a global address that all hosts will respond to is used. Multicast uses address-
ing that only some hosts will respond to. The next section will cover multi-
cast addressing in detail.
MBONE
Server
Server
Ethernet
Ethernet
S0
E0
E1
Computer subscribed to
IP multicast group
224.2.127.254
Computer subscribed to
IP multicast group
224.2.172.238
Computer subscribed to
IP multicast group
224.2.127.254
Computer subscribed to
IP multicast group
224.2.127.254
Computer subscribed to
IP multicast group
224.2.127.254
Computer
RouterA
224.2.127.255
224.2.127.254
224.2.172.238
1. Multiple IP multicast groups arrive at the router.
2. Copies of datagrams are sent out to interfaces that have
2.
subscribed hosts (in this case out E0 and E1).
3. The correct IP group packet reaches the intended
3.
subscriber and only that subscriber.
Note: The router did not forward packets
Note:
belonging to 224.2.127.255.
Copyright ©2000 SYBEX , Inc., Alameda, CA
www.sybex.com
