Spanning Tree Operation
157
version of STP called 802.1d. By default, all Cisco switches run the IEEE
802.1d version of STP, which is not compatible with the DEC version.
The big picture is that STP stops network loops from occurring on your
layer 2 network (bridges or switches). STP is constantly monitoring the net-
work to find all links and make sure loops do not occur by shutting down
redundant links.
The Spanning Tree Protocol executes an algorithm called the spanning-
tree algorithm. This algorithm chooses a reference point in the network and
calculates the redundant paths to that reference point. After it finds all the
links in the network, the spanning-tree algorithm chooses one path on which
to forward frames and shuts down the other redundant links to stop any net-
work loops from occurring in the network. It does this by electing a root
bridge that will decide on the network topology.
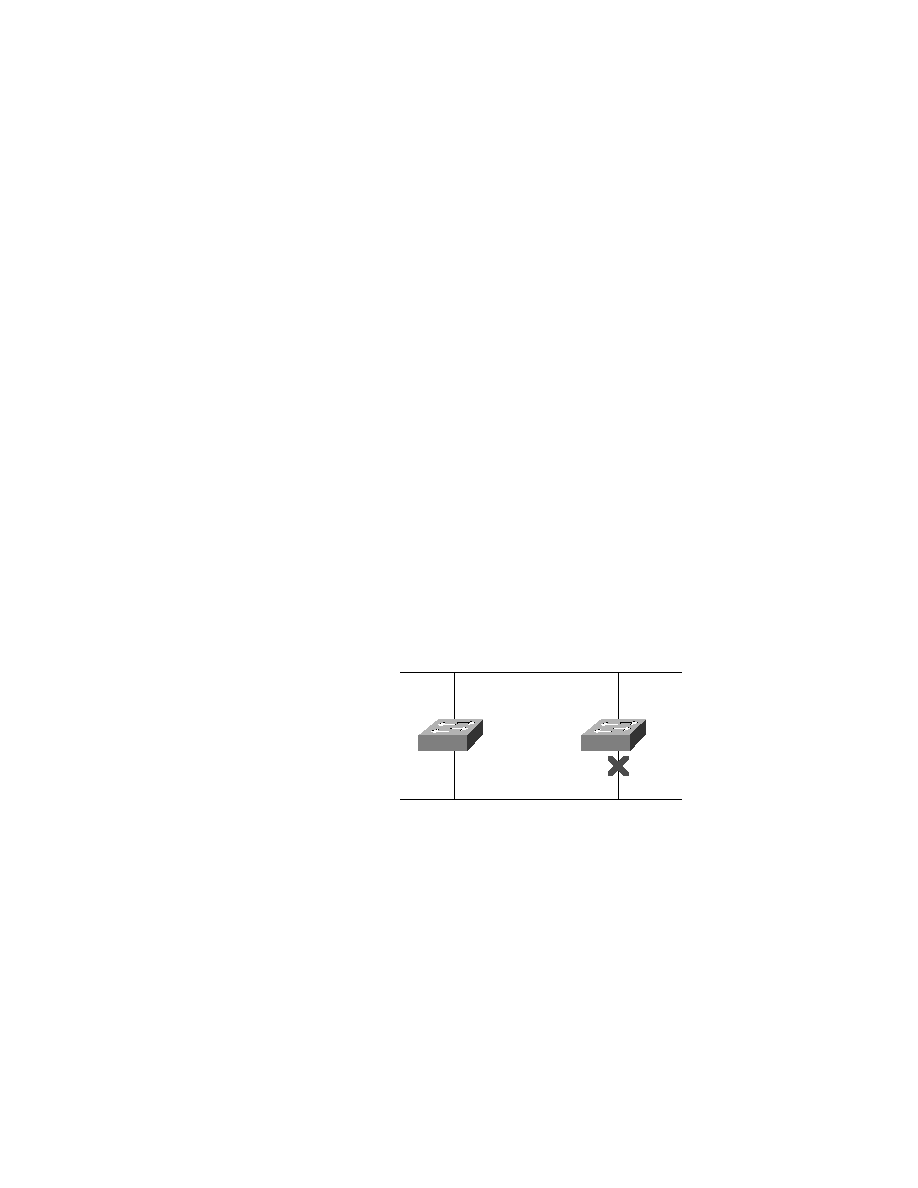
There can be only one root bridge in any given network. The root bridge
ports are called designated ports, and designated ports operate in what is
called forwarding state. Forwarding state ports send and receive traffic.
If you have other switches in your network, as shown in Figure 4.4, they
are called nonroot bridges. However, the port that has the lowest cost to the
root bridge is called a root port and sends and receives traffic. The cost is
determined by the bandwidth of a link.
F I G U R E 4 . 4
Spanning tree operations
Ports that are determined to have the lowest-cost path to the root bridge
are called the designated ports. The other port or ports on the bridge are con-
sidered nondesignated ports and will not send or receive traffic. This is called
blocking mode.
100BaseT
10BaseT
Designated port (F)
Designated port (F)
Root port (F)
Nondesignated port (B)
Root bridge
1900 A
Nonroot bridge
1900 B
Copyright ©2000 SYBEX , Inc., Alameda, CA
www.sybex.com
