152
Chapter 4
Layer 2 Switching and the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP)
These functions of the layer 2 switch--address learning, forward and fil-
tering decisions, and loop avoidance--are discussed in detail in the following
sections.
Address Learning
The layer 2 switch is responsible for address learning. When a switch is pow-
ered on, the MAC filtering table is empty. When a device transmits and a
frame is received on an interface, the switch takes the source address and
places it in the MAC filter table. It remembers what interface the device is
located on. The switch has no choice but to flood the network with this
frame because it has no idea where the destination device is located.
If a device answers and sends a frame back, then the switch will take the
source address from that frame, place the MAC address in the database, and
associate this address with the interface on which the frame was received.
Because the switch now has two MAC addresses in the filtering table, the
devices can now make a point-to-point connection and the frames will be
forwarded only between the two devices. This is what makes layer 2 switches
better than hubs. In a hub network, all frames are forwarded out all ports
every time.
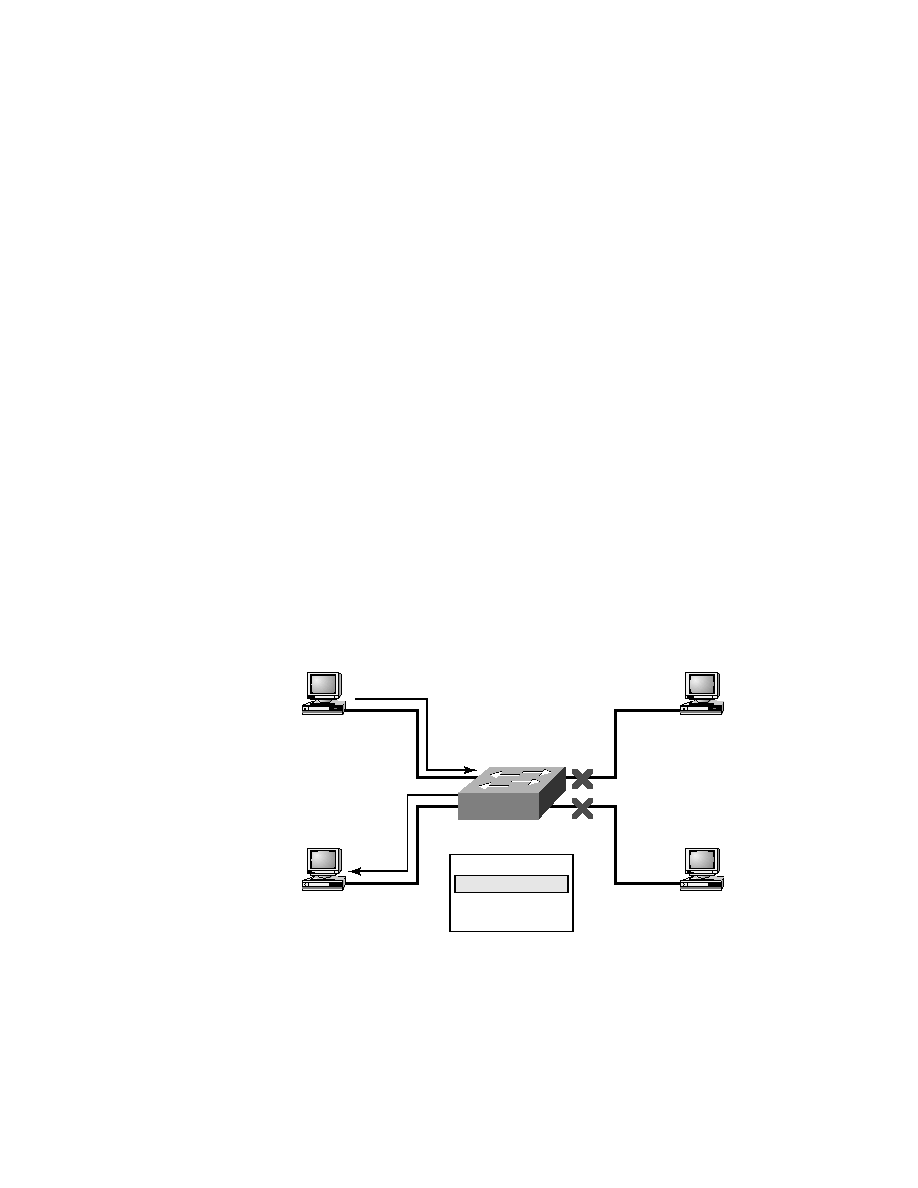
Figure 4.1 shows the procedures for building a MAC database.
F I G U R E 4 . 1
How switches learn hosts' locations
E0
E2
E1
E3
0000.8c01.1111
0000.8c01.3333
0000.8c01.2222
0000.8c01.4444
1
3
2
4
Station 1 sends a frame to station 3.
Destination is known; frame is not flooded.
E0/0: 0000.8c01.1111
E0/2: 0000.8c01.2222
E0/1: 0000.8c01.3333
E0/3: 0000.8c01.4444
MAC address table
Copyright ©2000 SYBEX , Inc., Alameda, CA
www.sybex.com
