Configuring OSPF
131
A full mesh is not required when implementing this environment. PVCs
on the subinterface may fail, but there is still OSPF connectivity to other
PVCs on the same physical interface.
The drawback of this environment is inefficient flooding. Because of mul-
tiple PVCs per interface and depending on the mesh of the PVCs, one LSA
update can be flooded multiple times.
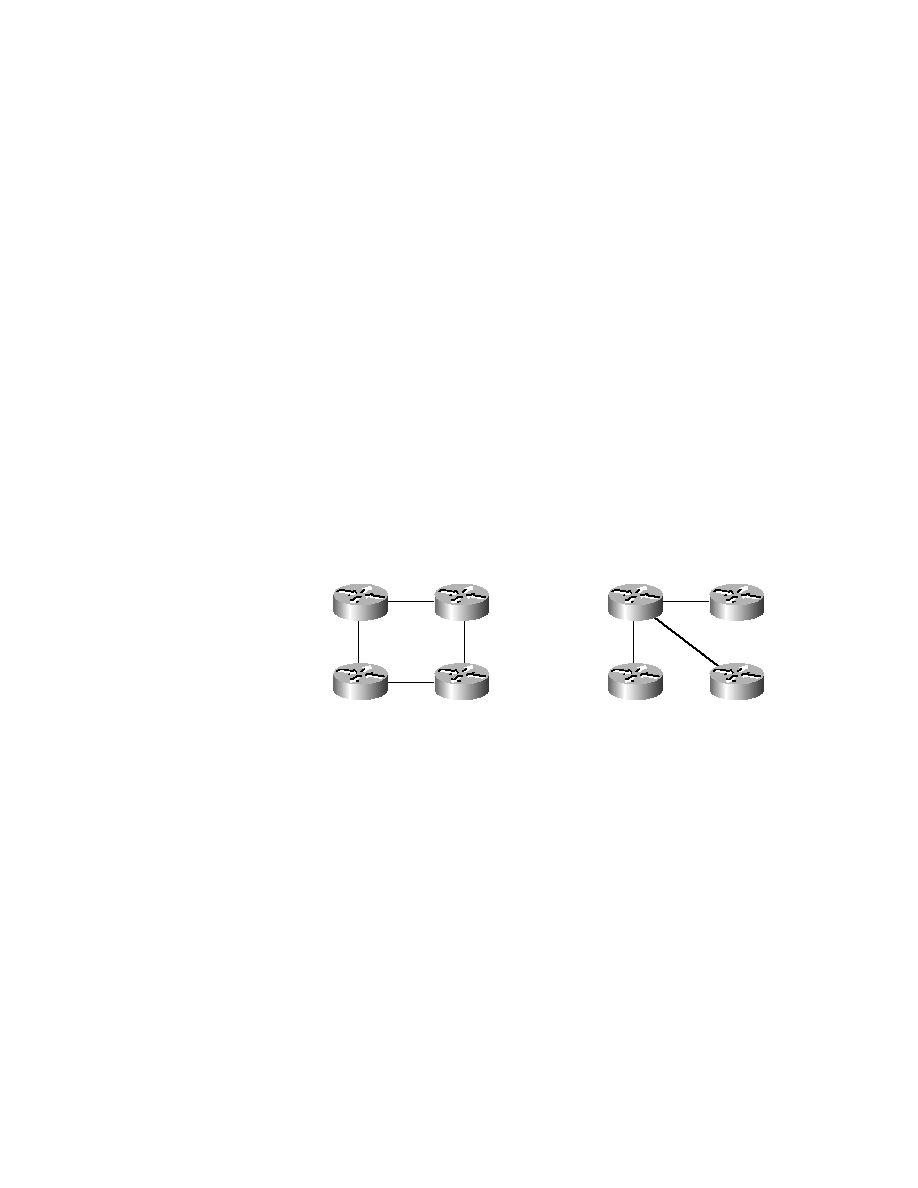
Point-to-Multipoint
This environment is very similar to the point-to-point environment. No DR
or BDR is chosen. All PVCs are treated as point-to-point links. The only dif-
ference is that all the PVCs go back to a single router. Figure 4.5 depicts the
difference between a true point-to-point environment and a point-to-
multipoint deployment.
F I G U R E 4 . 5
Point-to-point vs. point-to-multipoint
Configuring OSPF
C
onfiguring OSPF is a simple task. There are many options that are
allowed within OSPF, such as statically configuring neighbors, creating a vir-
tual link between an area that is not physically connected to Area 0, neigh-
bor/adjacency encryption, and many more. The following sections describe
how to configure OSPF in different environments.
NBMA (point-to-point)
NBMA (point-to-multipoint)
RouterA
RouterB
RouterC
RouterD
RouterA
RouterB
RouterC
RouterD
Copyright ©2001 SYBEX , Inc., Alameda, CA
www.sybex.com
