is chronic, queuing can compound the issue by introducing additional delay. At this point, it's
time to accept the fact that a bandwidth upgrade (and possibly a router upgrade) is in order. For
this type of congestion, the price and time involved in the upgrade is the better choice.
individual traffic types. The goal, typically, is to maintain the stability of the overall network,
even in the face of numerous traffic needs and types. Much time, unfortunately, can be spent
supporting traffic types that are not in line with company goals. "The traffic exists, we have to
transport it, so let's deal with it" mantra is a common one in today's enterprise networks.
(or significant) changes to the overall design that remedy the issues causing the delay. For
instance, if the core routers are overloaded while the distribution routers are hardly utilized, it
might be time to offload some traffic.
enough for an upgrade to be planned and put in place. Queuing itself is not the goal.
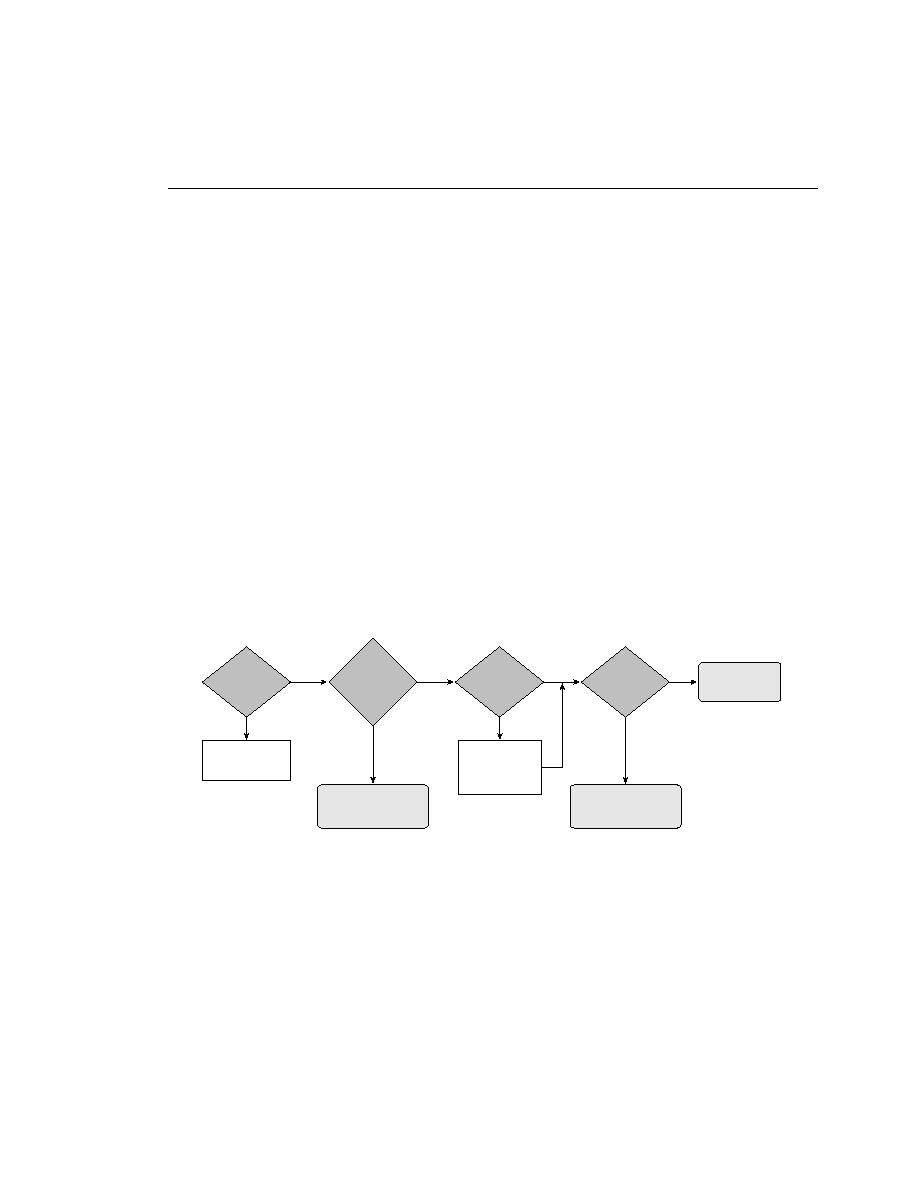
queuing strategy should be utilized. Figure 10-2 serves as a fundamental map to assist in that
decision.
condition that requires queuing. Once that determination is made, another decision awaits. How
strictly should the control of the queuing policy be enforced? Are the defaults OK, or should a
more granular approach be applied?