142 Chapter 6: Using ISDN and DDR Technologies
The configuration tasks for implementing basic DDR are as follows:
Step 1
Set the ISDN switch type.
Step 2
Specify interesting traffic.
Step 3
Specify static routes.
Step 4
Define the interface encapsulation and ISDN addressing
parameters.
Step 5
Configure the protocol addressing.
Step 6
Define any additional interface information.
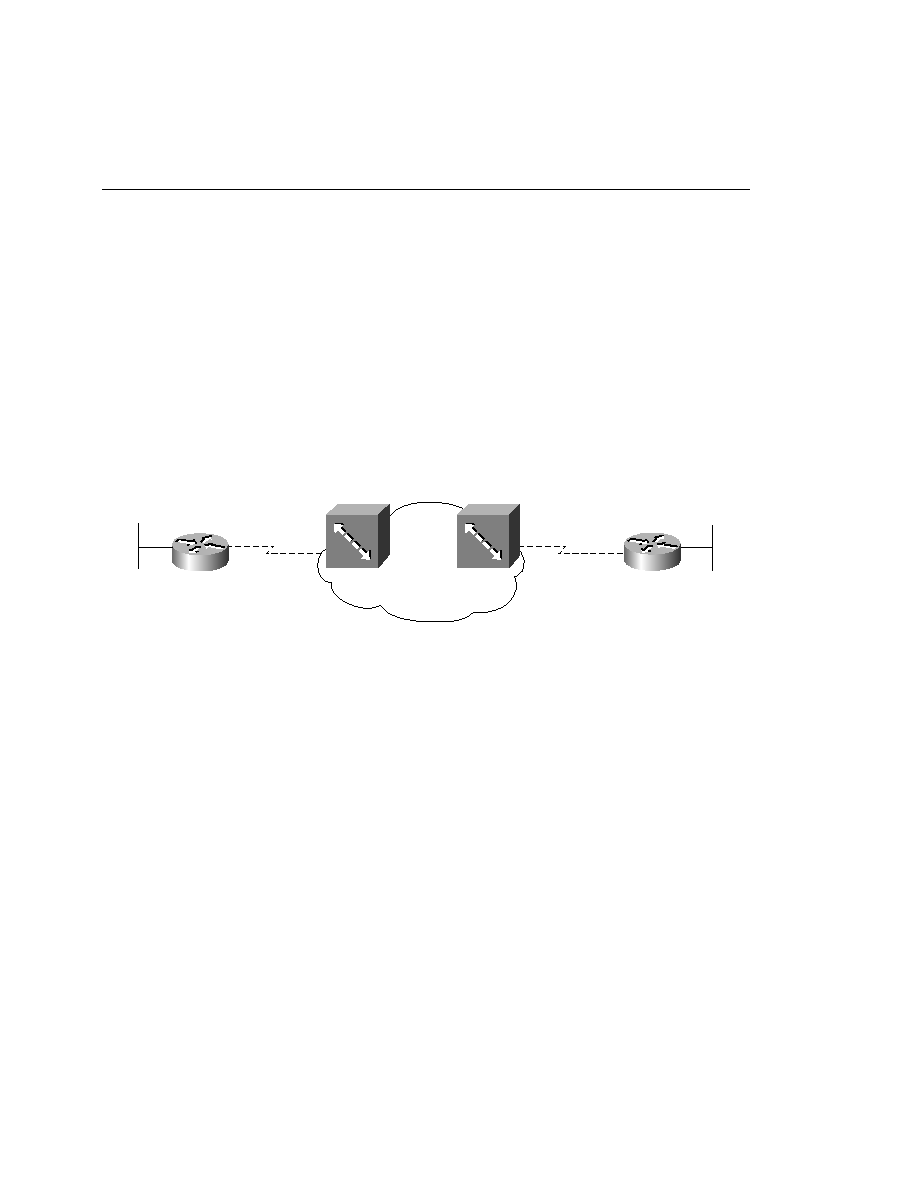
Figure 6-9 depicts the network topology that is referenced throughout this chapter.
Figure 6-9
Sample ISDN Topology
Step 1: Setting the ISDN Switch Type
The telephone company provides you the type of switch to which you are connecting.
Manufacturers of ISDN central office switches (also known as local exchange equipment)
divide the local exchange into two functions: local termination and exchange termination. The
local termination function primarily deals with the transmission facility and termination of the
local loop. The exchange termination function deals with the switching portion of the local
exchange.
To function, the switch type must be specified on the router. Use the isdn switch-type command
to configure the router for the type of switch to which the router connects. Your telephone
company provides you the type of switch that is located in the central office to which your router
will connect. For a listing of supported switch types, see Table 6-2.
The isdn switch-type command has historically been issued from the global configuration
prompt. However, as of IOS version 12.0, this command can be issued from the interface
configuration prompt as well. The usage of this command is included in Example 6-4.
ISDN
service
provider
10.11.1.1/24
10.13.1.2/24
10.12.1.1/24
10.12.1.2/24
Router A
Router B
214-555-2222
214-555-2223
214-555-1111
214-555-1112
