PPP Options 111
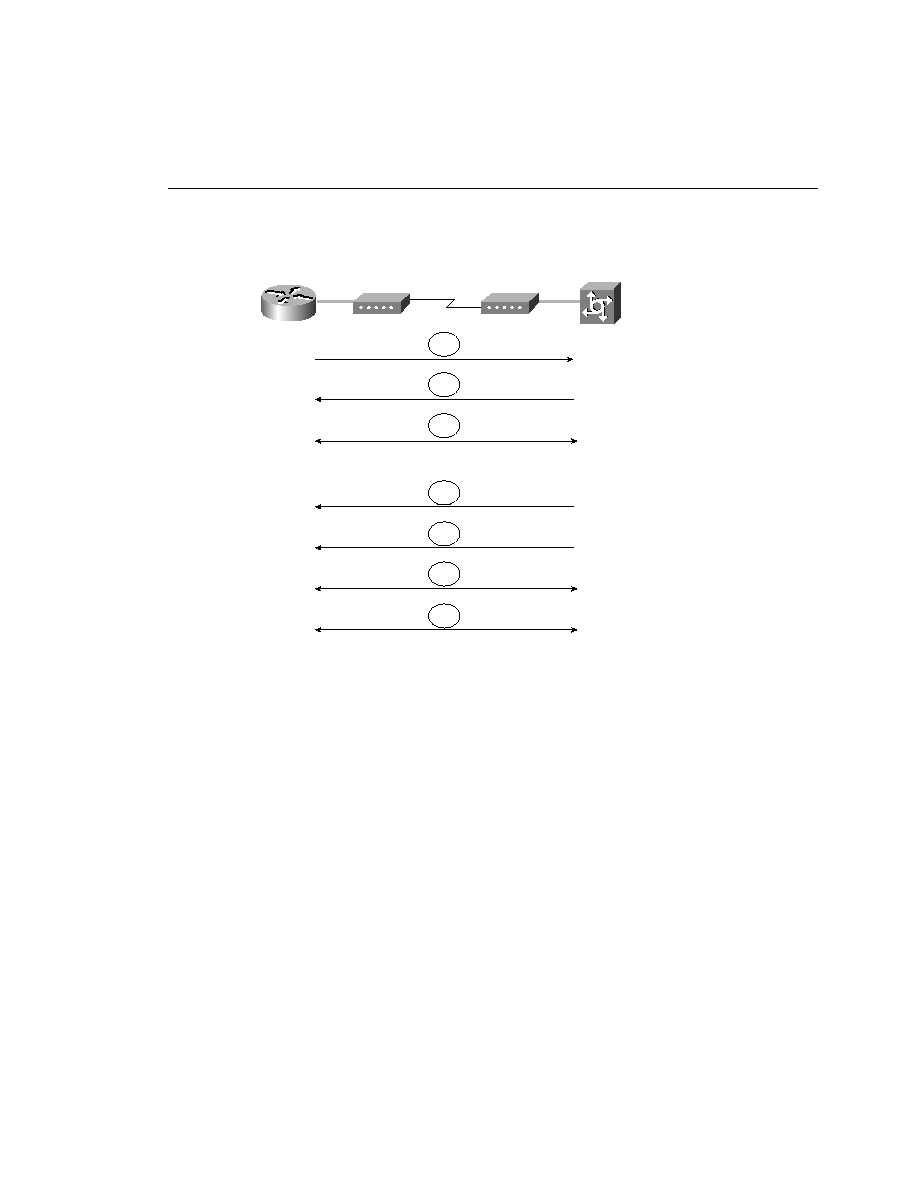
Figure 5-6
PPP Callback Procedure
When the client router dials, its hold queue timer begins to count down. No additional calls to
the same destination can be made until the time reaches zero. This value is configurable using
the dialer hold-queue command detailed later in this chapter.
PPP Compression
Compression is covered in Chapter 10, "Managing Network Performance with Queuing and
Compression," in more detail. This section is simply an overview of PPP's compression
capabilities.
Compression is most useful on slower-speed links. In routing, there comes a point when it is
faster to send information outright than it is to compress, send, and decompress it. Compression
simply serves to decrease transit time across the WAN.
PPP or Layer 2 compression is determined during LCP negotiation. Therefore, if one side of
the call doesn't support it or have it configured, it is not utilized for that call.
Cisco supports a number of compression algorithms. They include STAC, Predictor, MPPC,
and TCP header compression. These are discussed in Chapter 10 and are not therefore covered
here.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Call initiation
User authentication
Initiating call disconnected
Authentication
Connection proceeds
Client called
Server-to-client dial string identified
Call acknowledgment
Callback client
Callback server
