46
Chapter 2
Protocol Attributes
IP Addressing Review
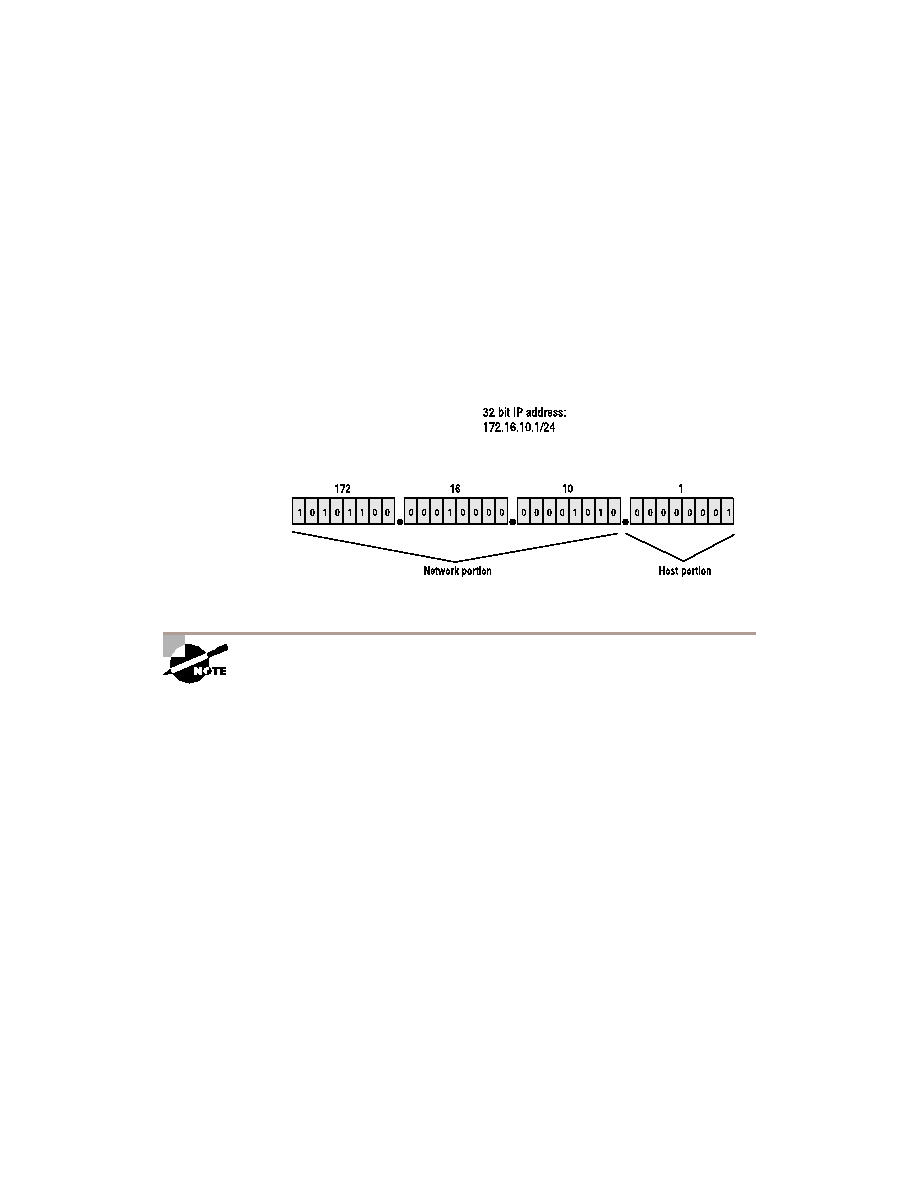
IP addresses are composed of a network portion and a host portion. They
can be compared to a two-part ZIP code, having a five-digit prefix and a
four-digit suffix. The prefix directs the post office to a general destination--
the city and state--and the suffix resolves to a street address or P.O. box. An
IP address, with its network and node portions, works much the same way,
as shown in Figure 2.9.
F I G U R E 2 . 9
The makeup of an IP address
This section is intended as a review of IP addressing. If you need a more
detailed explanation, see CCNA: Cisco Certified Network Associate Study
Guide, 2nd ed., by Todd Lammle (ISBN 0-7821-2647-2, Sybex, 2000).
The network portion works just like the five-digit prefix of a ZIP code; the
node, or host portion, is the unique identifier, which is similar to the four-
digit suffix of a ZIP code. An IP address consists of 32 bits, broken down into
four eight-bit segments known as octets. As shown in Figure 2.9, the first
three octets define the network portion, and the last octet defines the host.
The specification of the host and network portions within an IP address
establishes an inherent hierarchy, consisting of different network lengths
being advertised throughout a network or over the Internet. Figure 2.10
shows varying network portion length.
Copyright ©2000 SYBEX , Inc., Alameda, CA
www.sybex.com
