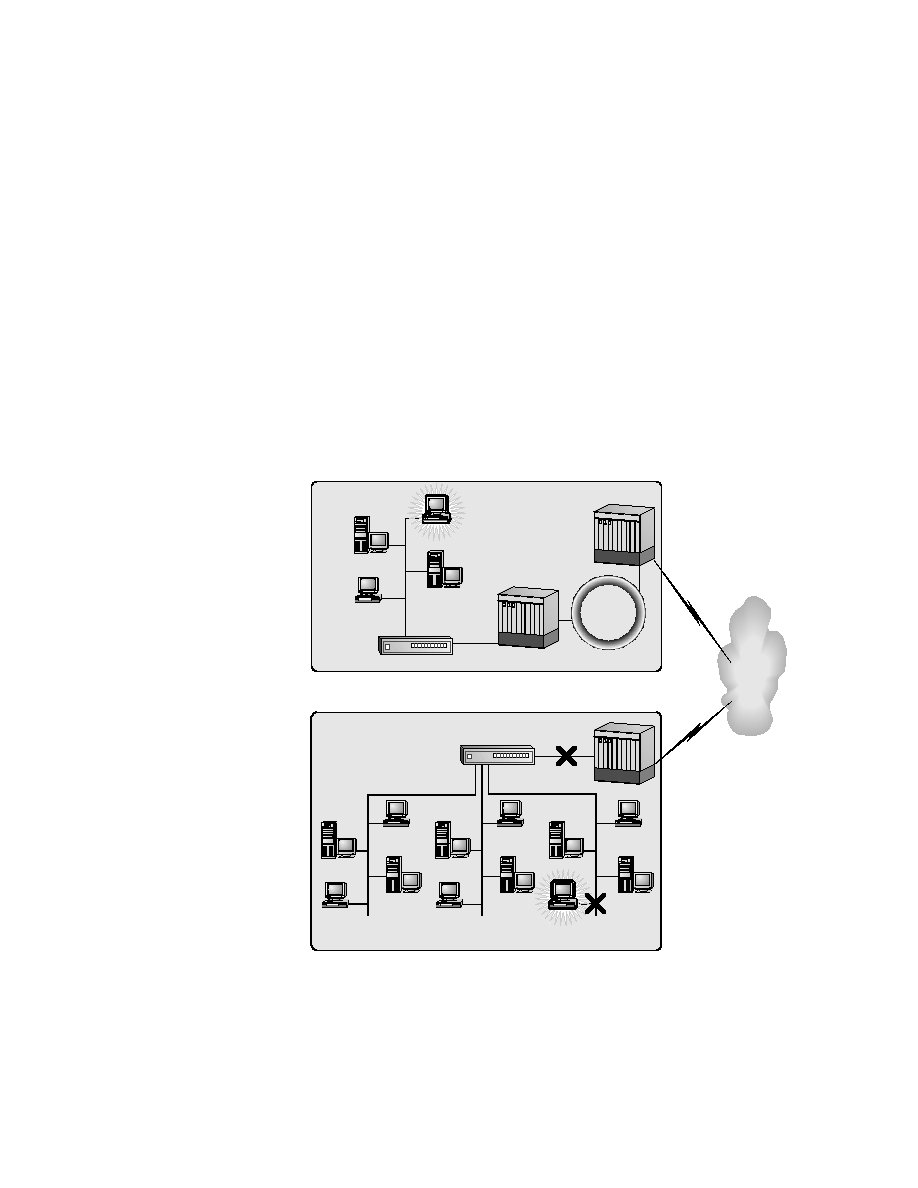
two ends of a network problem is used as a troubleshooting reference point.
Either half may be investigated first. In this example, you start by trying to
FTP to any machine within Campus B. Depending on the results, you
can divide in half again and test. If the test results in a successful FTP to
any machine on the Campus B network, then the new point to test is another
machine on VLAN 3. If the test fails, the new testing point is to try to FTP
to a local machine. In this case, the divide-by-half method takes three steps,
just as the inside-out method does.
Host A and Host Z
Host A and any host
on Campus B
network.