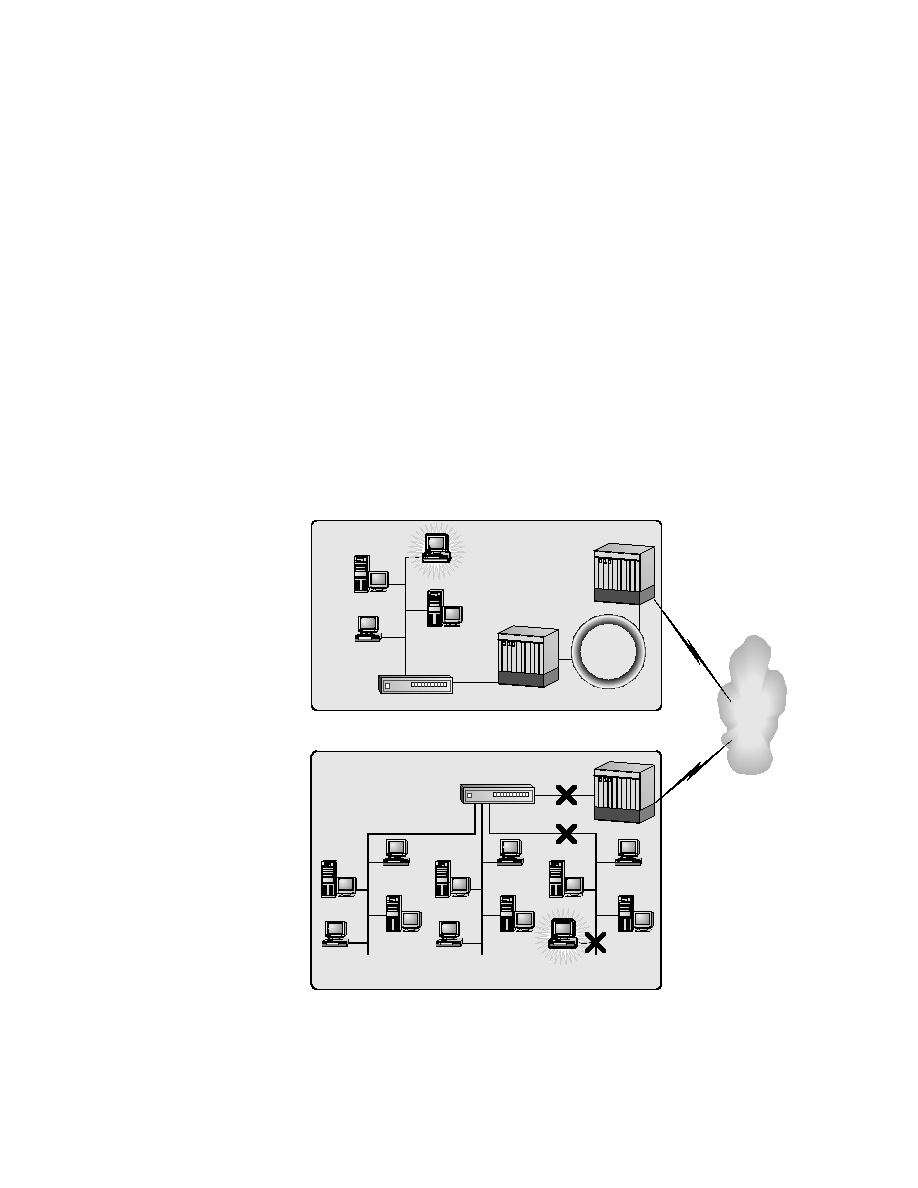
The first method consists of choosing the opposite end of the connection,
known as
depicted in Figure 1.6. The corresponding test would be for the user to try to
FTP to another machine on the same VLAN as Host Z, indicated by the
X (2) on the diagram. If the result of that test is negative, then we need to
come back one step. By coming back one step, we would try to FTP to a
machine on a different VLAN, indicated by the X (3) on the diagram. If
that test failed, the only thing left to try would be to FTP to another machine
on the user's segment. In our example, we assume that the user can FTP to
other hosts that are directly connected to the same Ethernet segment.
Host A and Host Z
Host A and any host
on VLAN 3
Host A and any host
on Campus B
network.