442
Chapter 8
Troubleshooting ISDN
ping
As with non dial-on-demand (DDR) connections, the ping command is one of the
most useful troubleshooting tools. ping verifies routes and other connections; in
DDR, the command triggers a call.
Bottom#ping 10.1.1.1
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.1.1.1, timeout is 2
seconds:
.
00:37:12: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface BRI0:1, changed state
to up
00:37:13: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
BRI0:1, changed state to up.!!!
Success rate is 60 percent (3/5), round-trip min/avg/max =
32/38/48 ms
Bottom#
00:37:14: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface BRI0:2, changed state
to up
00:37:15: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface
BRI0:2, changed state to up
Note that the five Pings generated by the router completed before the sec-
ond B channel came up. The ping command is perhaps the most common
troubleshooting tool in TCP/IP networks.
It is quite common for the first three Pings to fail in DDR ISDN connections.
This is due to the two- to three-second delay in establishing the connection. It
is usually not an indication of a problem.
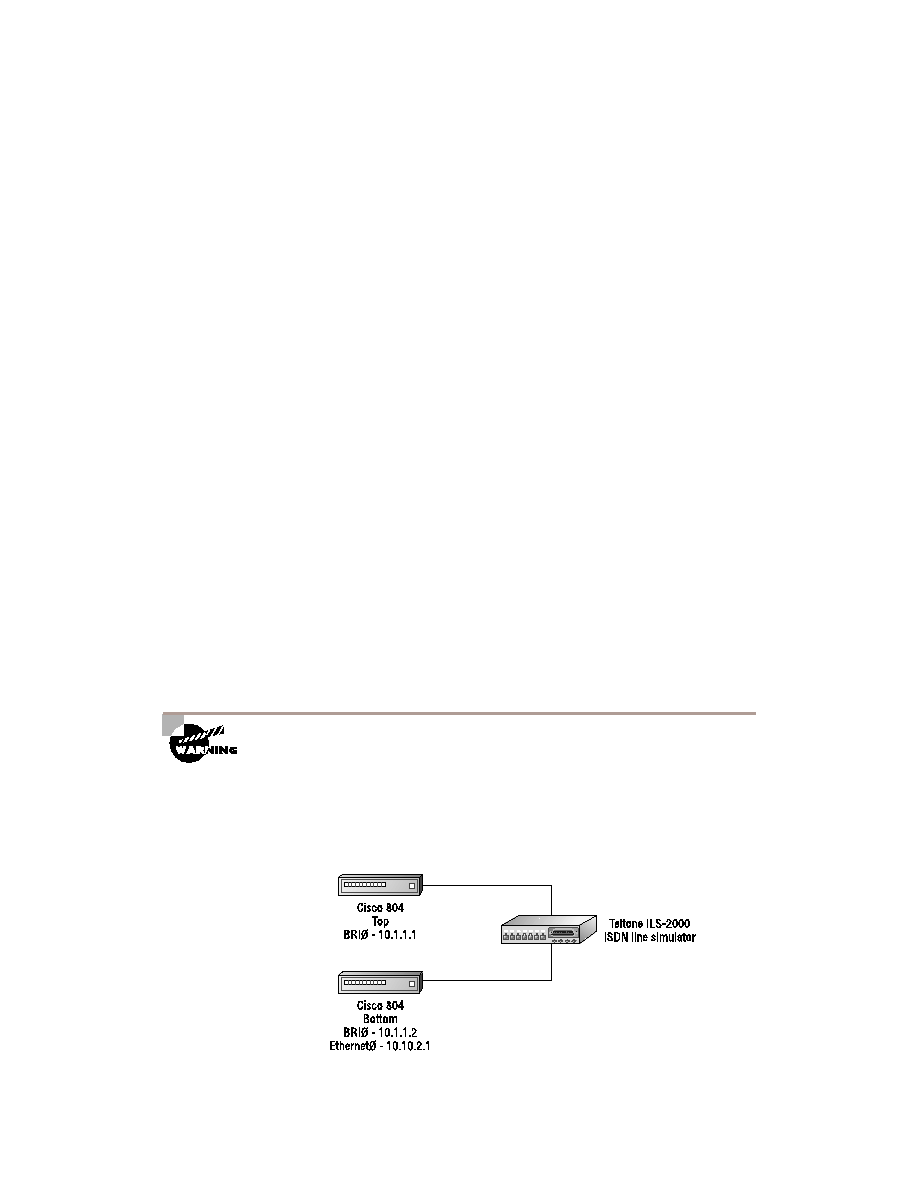
Figure 8.1 diagrams the network used for this chapter.
F I G U R E 8 . 1
ISDN Troubleshooting network design
Copyright ©2000 SYBEX , Inc., Alameda, CA
www.sybex.com

