TCP/IP Router Diagnostic Tools
299
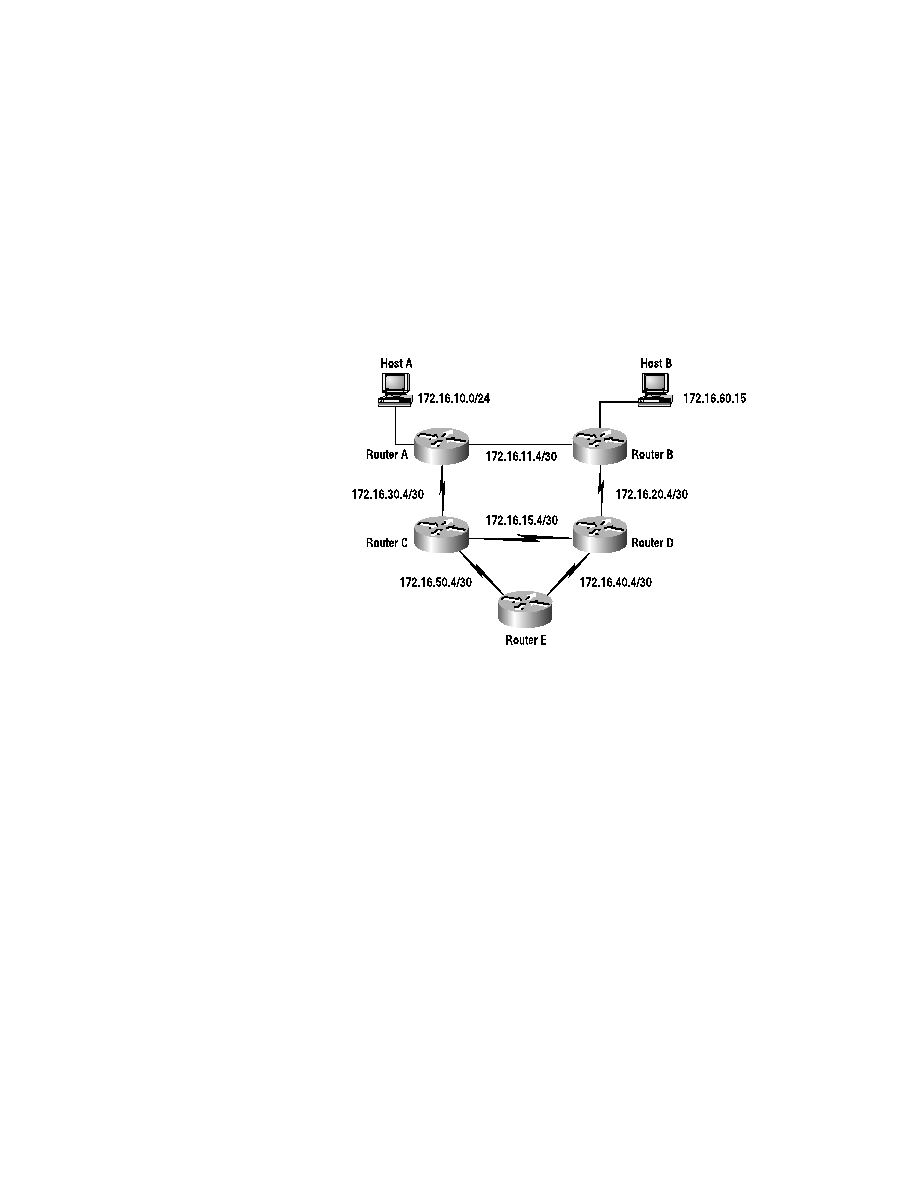
Figure 6.1 depicts how this can happen. Host A is able to ping Host B
without a problem. However, if the
traceroute
command is used to pro-
vide further information, the packet actually goes through five routers.
According to the topology, the traceroute should need to transit only two
routers in order to arrive at Host B.
F I G U R E 6 . 1
ping
vs.
traceroute
Let's look at the results as seen from Host A. First, you see the results of
the
ping
command, followed by the traceroute results.
Host_A >
ping 172.16.60.15
172.16.60.15 is alive
Host_A >
traceroute Host_B
traceroute to Host_B (172.16.60.15), 30 hops max, 40 byte
packets
1 Router_A (172.16.10.1) 1 ms 0 ms 0 ms
2 Router_C (172.16.30.6) 1 ms 1 ms 1 ms
3 Router_E (172.16.50.6) 1 ms 1 ms 1 ms
4 Router_D (172.16.40.6) 1 ms 1 ms 1 ms
5 Router_B (172.16.20.5) 1 ms 2 ms 3 ms
6 Host_B (172.16.60.15) 2 ms 2 ms 2 ms
Host_A >
Copyright ©2000 SYBEX , Inc., Alameda, CA
www.sybex.com

