266
Chapter 5
Applying Cisco's Diagnostic Tools
Scenario #1
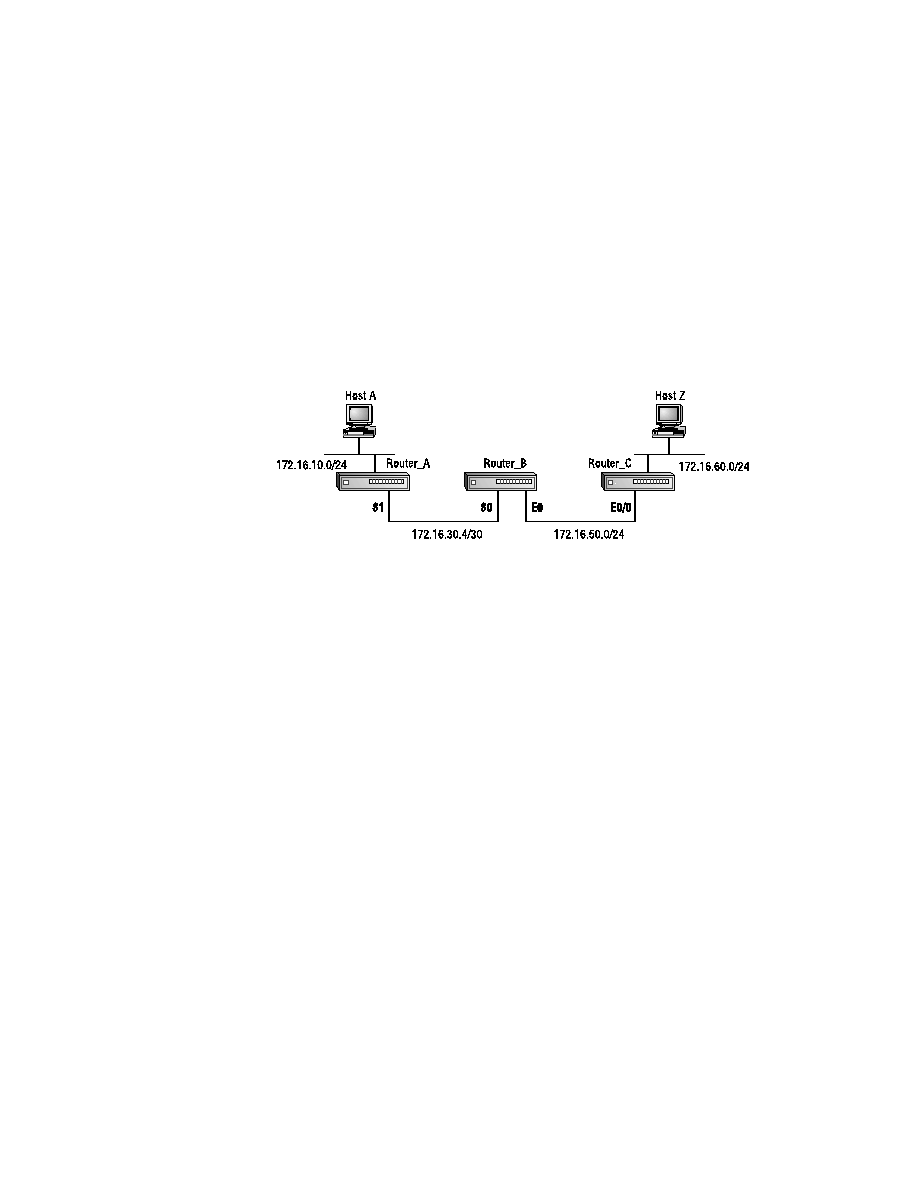
The problem here is that Host A cannot Telnet to Host Z. Figure 5.4 depicts
the network that is used for this scenario. Troubleshooting will begin after
the establishment of the boundary of dysfunctionality. You know that the
problem exists between Router C and Host Z. Because this is a troubleshoot-
ing scenario for Ethernet, you know what to look for.
F I G U R E 5 . 4
Network diagram for Ethernet scenario #1
List Observations
The first thing to do is verify that Host Z is still unreachable. Let's look at
the results of a ping test:
Router_C#ping 172.16.60.130
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 172.16.60.130, timeout
is 2 seconds:
.....
Success rate is 0 percent (0/5)
Router_C#
Because the ping test failed, the cause needs to be isolated. Let's look at
the interface:
Router_C#show interface ethernet0/1
Ethernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up
Hardware is AmdP2, address is 0010.7bd9.2881 (bia
0010.7bd9.2881)
Copyright ©2000 SYBEX , Inc., Alameda, CA
www.sybex.com
