tecture and queuing process within a 7000 series router. The architecture is similar
to the cache buffers that were explained with the switching methods.
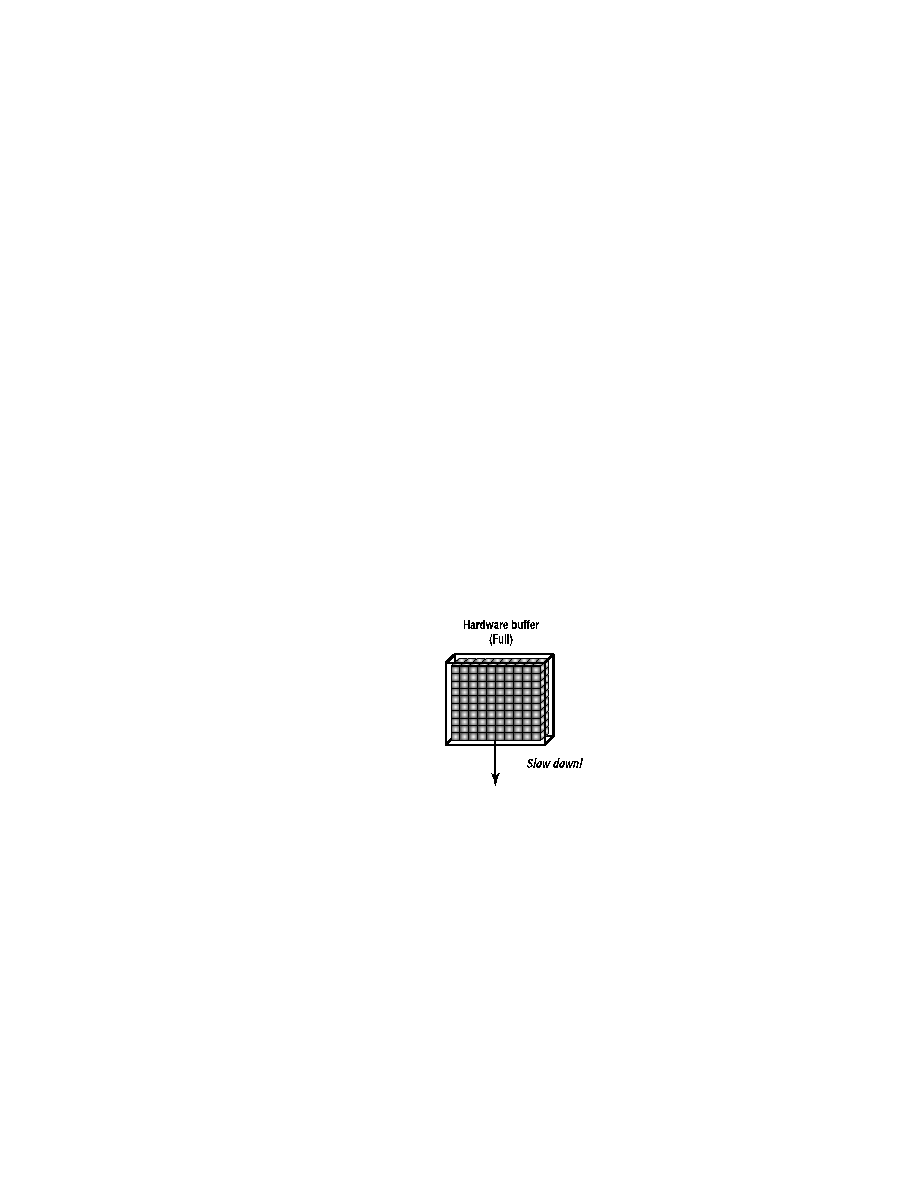
as a first line of defense for bursty traffic. If the hardware buffer on certain
interfaces fills up, the Layer 2 protocol will signal the sending interface to
slow down. This behavior is dependent on the Layer 2 protocol and whether
or not it supports congestion control.
first--the hardware buffer fills up and it signals to the transmitting interface
to throttle down. The second occurs when the interface is receiving frames
faster than the SP can pull them off. The third occurs when the CxBus is so
busy that the interface processor is unable to copy the packet from the hard-
ware buffer to the SP buffers. Figure 4.7 depicts all three of these scenarios.