OSI Layer 2: Data-Link Layer Protocols and Applications
93
Most of FDDI's specifications lie within Layer 1, but there are specifica-
tions that merge it with the MAC portion of Layer 2. Here is a summary of
the four specifications used by FDDI:
Physical Layer Medium Dependant (PMD)
Physical Layer Protocol (PHY)
Media Access Control (MAC)
Station Management (SMT)
The first standard defines physical transmission characteristics. This deals
with the light levels within the fiber optics, the allowable bit errors, decibel
loss, and actual physical equipment.
The second standard is just what it says. The protocol encodes and
decodes the data, before and after transmission over the physical media.
The third standard bridges FDDI with Layer 2 of the OSI model. This
specification is charged with the way FDDI runs as a Layer 2 technology, the
physical addresses, and the way the data is presented to the Physical layer.
Finally, there is station management. This specification is responsible for
station and ring configuration, fault recovery, and other management duties.
Frame Structure
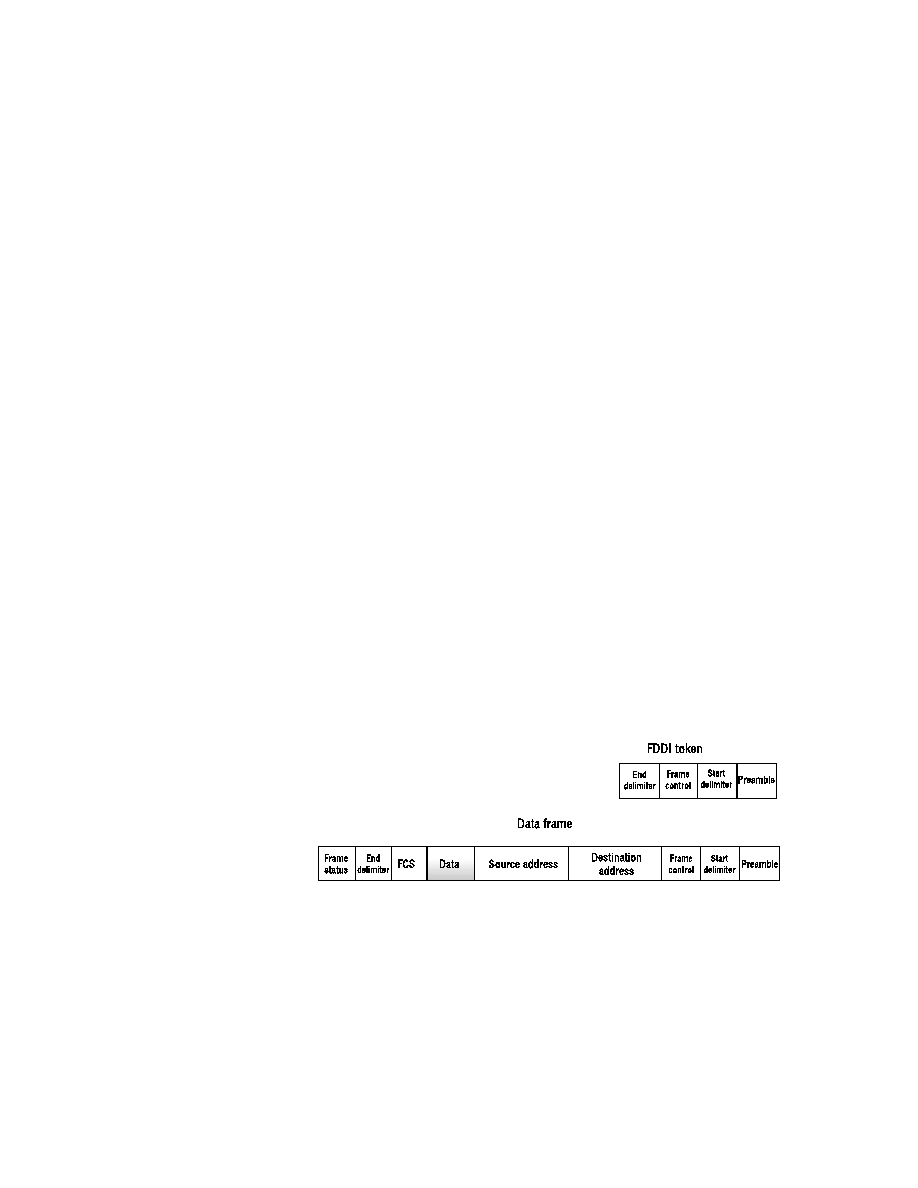
Figure 2.30 gives a picture of FDDI data and token frames. They are very
similar to those used by Token Ring/IEEE 802.5. We begin at the right and
work our way to the left.
F I G U R E 2 . 3 0
FDDI token and data frame structures
Both frames begin with the preamble field, which tells the stations that
they should get ready to process a frame. Following the preamble, both
frames have the Start delimiter field, which specifies the actual beginning
of the frame.
Copyright ©2000 SYBEX , Inc., Alameda, CA
www.sybex.com
