traffic has consisted of data traffic, which was variable in nature, allowing large file transfers to
monopolize network bandwidth. Voice networks must support traffic that is more sensitive to
delay and delay variation. RSVP allows the end station to reserve resources in the network. This
allows you to allocate queues for different types of traffic, helping you reduce delay and delay
variation inherent in current IP networks.
types into specific QoS queues. This is designed to prioritize the transmittal of voice traffic over
data traffic. This reduces the potential of queuing delay.
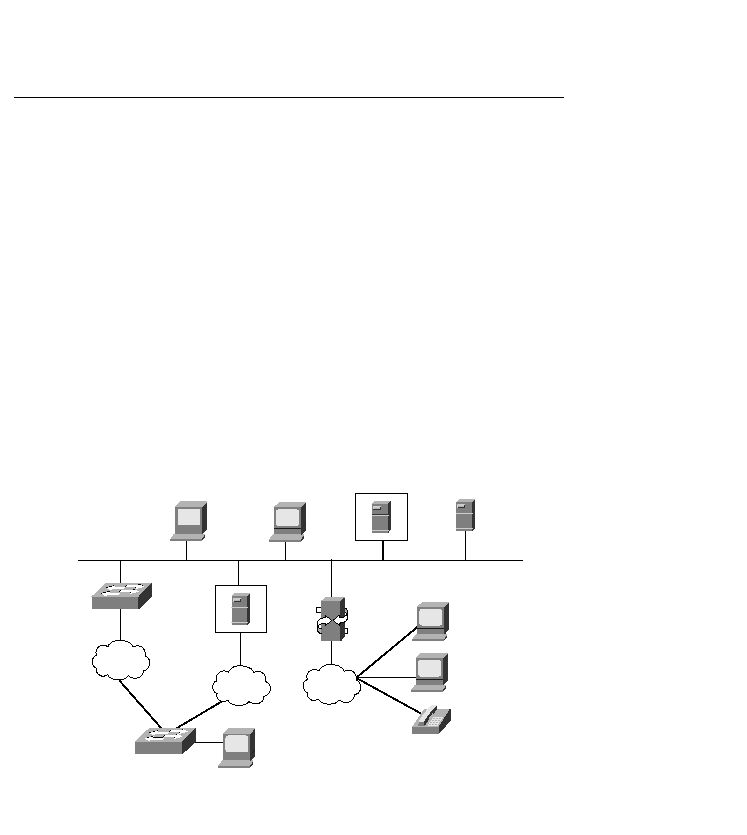
how audiovisual data is transmitted across networks. In a typical setting, H.323 lets users
participate in the same audio or video conference even though they are using different
videoconferencing applications.
multimedia communications service. Figure 16-7 illustrates an H.323 network.