IP Security (IPSec) 573
increase security. The principal differences between ESP and AH is that ESP does not protect
any IP header fields unless those fields are encapsulated in ESP tunnel mode.
Figure 15-15
Authentication Header
NOTE
IPSec is supported on the 1600, 2x00, 36x0, 4x00, 5x00, and 7x00 platforms.
Keys
Encryption keys are used to verify that a packet came from the real sender of the packet and not
from an impostor. Encryption keys do not scramble the payload data, but rather make the IPSec
connection secure by providing security association management with the exchange of session
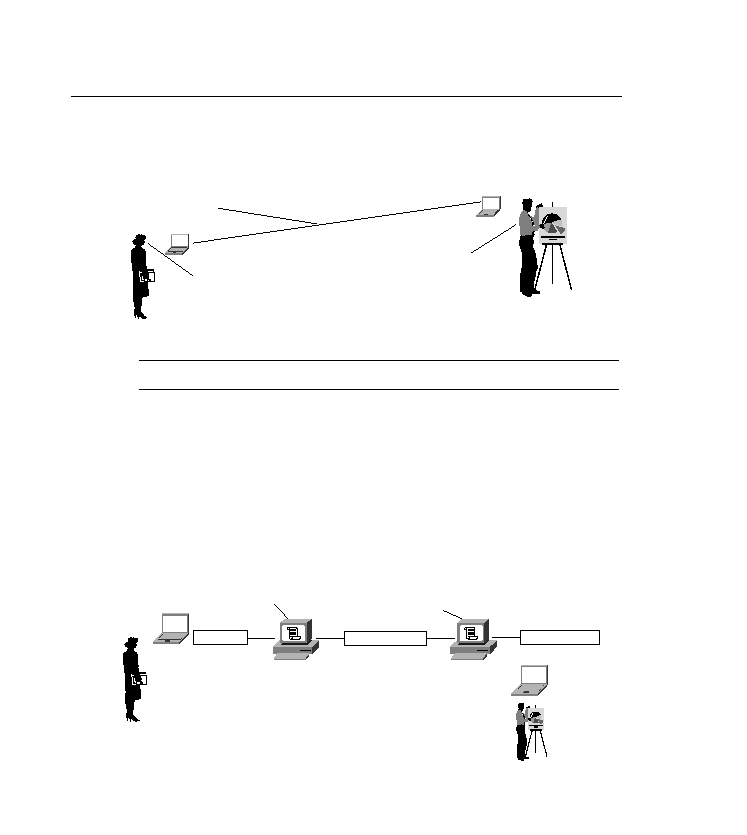
keys. In Figure 15-16, Carol is sending Steven a message that no one else must see. This
encrypted message or data is then sent to the destination device, and the key is applied at the
other end, which applies the secret key and decrypts the data, turning it back into cleartext.
Public keys and private keys are used with encryption technologies.
Figure 15-16
Encryption
Laptop computer
Carol
Message: Carol, we have
15 meetings today!
ТI just received a message
from Steven, it must have
come from him, but 15
meetings for today sounds
kind of low.У
Steven: ТI hope Carol
believes my message, she
must because she knows
we use AH here.У
Laptop computer
Laptop computer
Message
Encrypted Message
ТThe network is alive and well
Laptop computer
Encryption device adds
public secret key
Encryption device
removes secret key by
applying pin number
Carol
Steven
1. Message is plaintext.
2. Message is encrypted by router or encryption device.
3. Encrypted message traverses network.
4. Message arrives at destination and is de-encrypted by
router or de-encryption device and turned back into
plaintext for Steven to read.
Plain text message
ТThe network is
alive and wellУ
87200333.book Page 573 Wednesday, August 22, 2001 1:41 PM
