data farms, the wide-area network is replacing the local-area network as the first point of access.
On many corporate networks, a user will soon be more likely to access a file from a centrally
located remote server via the WAN as a first choice. Almost every PC now has wide-area access
through dialup. DSL allows remote access via the existing LAN card. In addition, the ranks of
telecommuters and mobile users are growing every day, and they expect to use the same
multimedia applications at home and on the road.
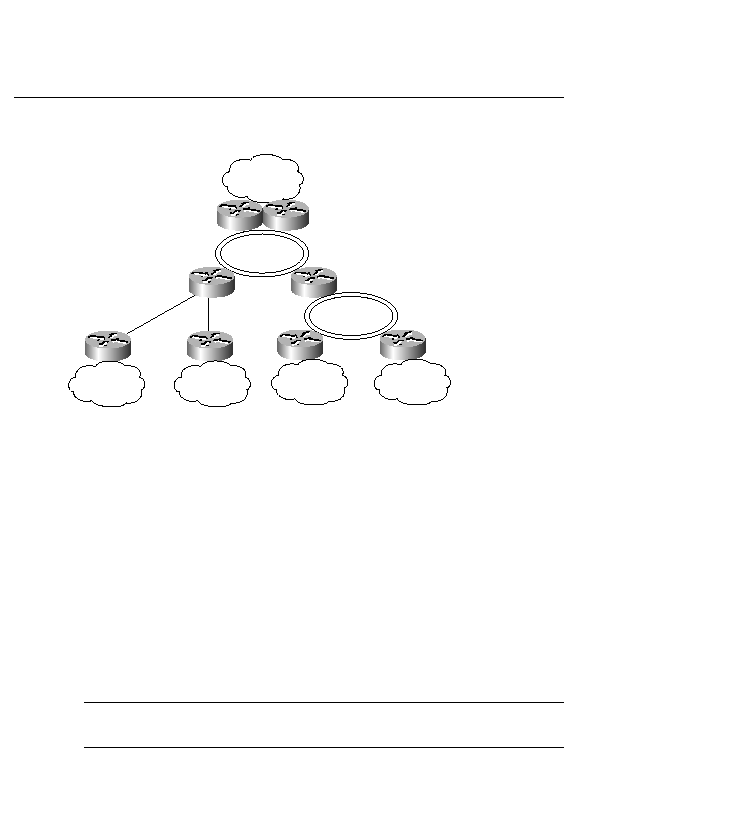
to consolidate their servers. Before long, the majority of traffic from the client networks is
expected to travel across the WAN backbone. The majority of the traffic will flow between
subnets. These new traffic patterns mean that Layer 3 devices will handle more and more traffic.
High-speed switches that can handle Layer 3 and Layer 4 requirements will be needed to handle
the new remote access requirements.
at least 80 percent of the traffic to travel out of the local network.