as the traffic started traversing an internetwork, the service classifications would be lost.
tos map or by using policy-based routing. For example, you could use this command:
could be called Static Routes Version 2, because in essence it is another flavor of static routing.
Policy routing is the ability to specify the path that traffic will take through the network based
on user-specific parameters. An added bonus is that the priority packets can be modified.
queuing, and other QoS capabilities work together to carry out the network management policy
framework. CCDPs can control the traffic path using extended ACLs, bypassing the lookup in
the routing table.
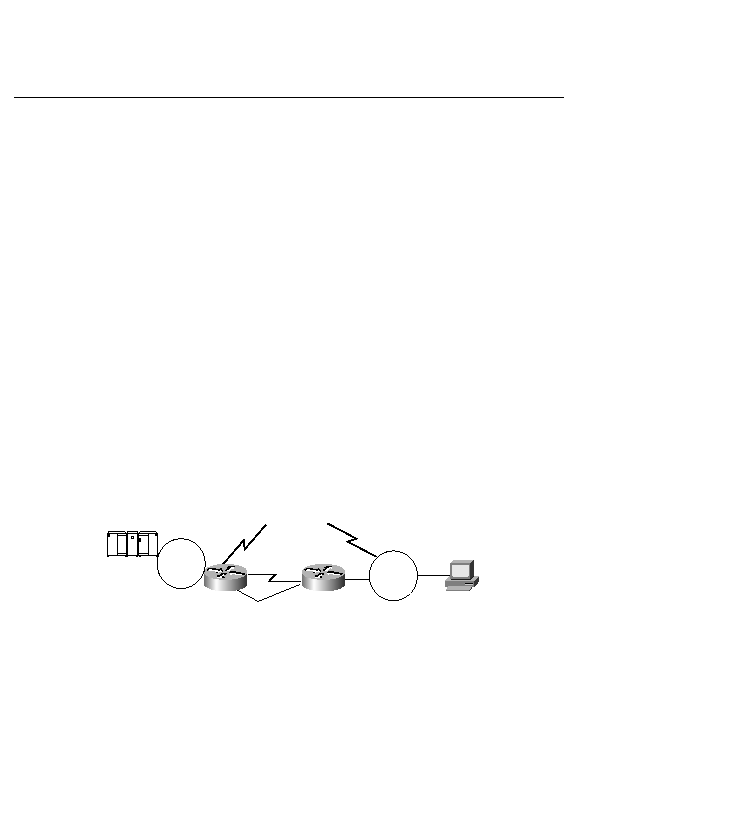
different characteristics. Figure 14-19 shows a low-bandwidth terrestrial link from Router A to
Router B and a high-bandwidth, high-propagation-delay satellite link. Policy routing is also
used in a particular situation in which the need is to route based on the source address and the
traditional destination address.
network bandwidth. RSVP lets an application dynamically reserve network bandwidth from