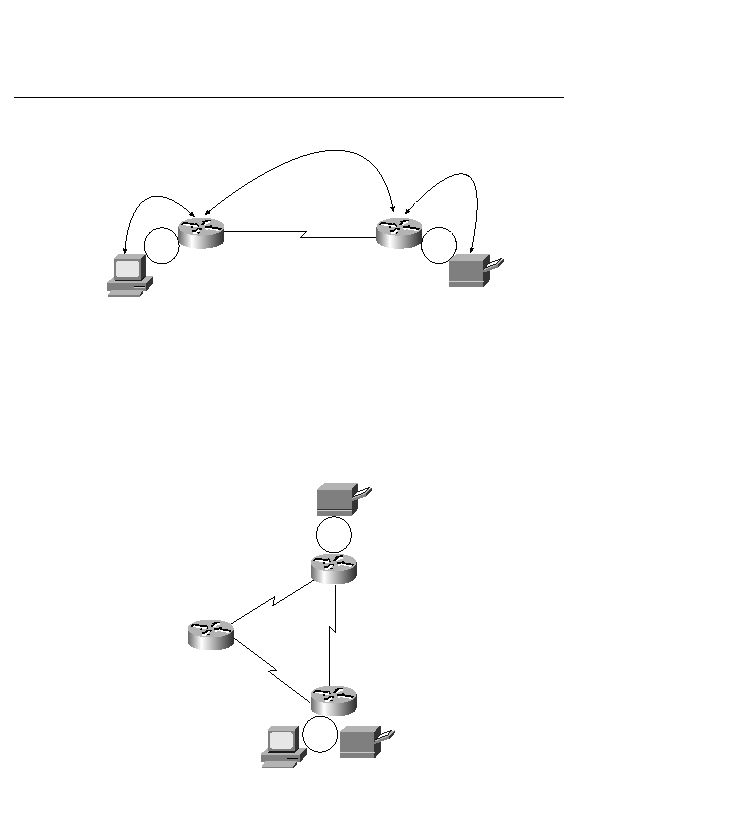
disrupting SNA sessions. Also, HPR does error checking at the end stations and not all the
intermediate hops as ISR does. In Figure 13-16, the PC on Router B can print to the printer on
Router A if either of the serial links connected to Router A fails. HPR accomplishes this by using
two networking layers. The first protocol to discuss is a connectionless layer called Automatic
Network Routing (ANR), which has some similarities to IP. ANR HPR has a second reliable
connection-oriented layer called Rapid Transport Protocol (RTP), which provides end-to-end
functionality and guarantees delivery of data. RTP is a transport layer protocol similar to TCP. It
provides functions including error recovery, packet resequencing, segmentation, and flow control.
Network node