404 Chapter 11: Remote Access
Figure 11-15
Network Control Protocols
LCP
To establish communication over a serial link, the originating station first sends LCP frames at
Layer 2 to configure and test the link. Two routers must agree to "bring the link up." This is a
handshake that must happen before you can ever get to the PPP negotiation process, which
happens between Layer 2 and Layer 3.
The basic mechanics of LCP are that it goes through three different phases:
1
Establish the link and negotiate the configuration.
2
Determine link quality.
3
After a successful handshake and agreement at Layer 2, perform negotiation at the
network layer.
Before any packets can be transferred between two devices, LCP must establish a connection.
Using what is called a configuration acknowledgment frame, LCP negotiates configuration
parameters. After LCP does this and determines the link quality, network-layer protocols can
be brought up and taken down at any time. If a link is closed by LCP, the network-layer
protocols are informed so that they can take appropriate action.
After the link has been established, the originating PPP device sends NCP frames to figure out
which network protocols are to be used over the link. When this decision is made, packets from
the chosen network-layer protocol can be sent over the link. LCP retries allow a reestablishment
of the connection if it should fail. This reestablishment allows for missed or incorrect
negotiation.
HDLC Versus LAPB
Two other methods of encapsulation at Layer 2 are HDLC and LAPB. HDLC is Cisco's
proprietary protocol. It assumes a point-to-point link, developed from IBM's HDLC.
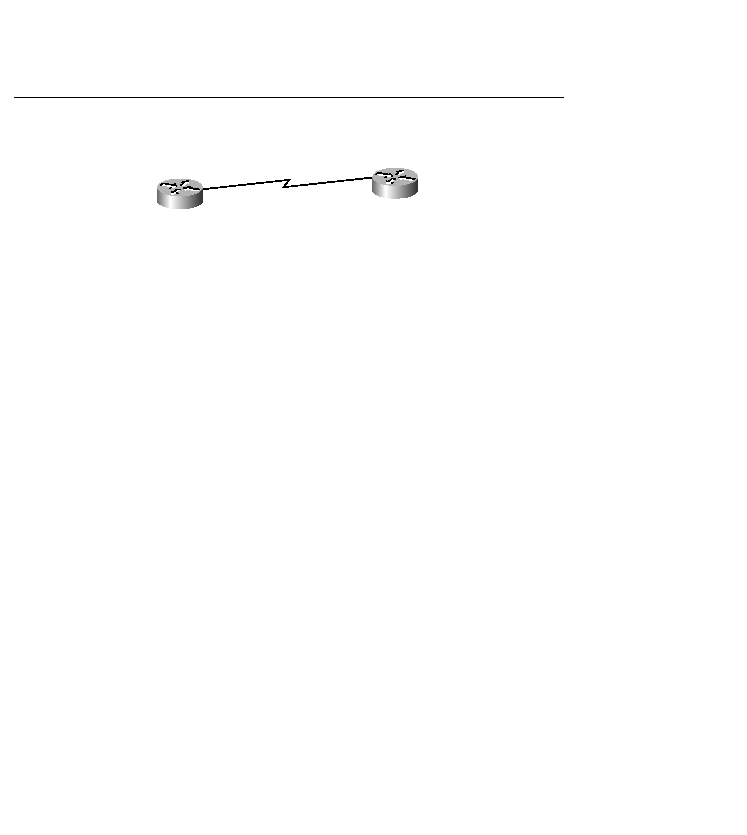
1. NCP: Hey Router B, can
you do IPX over this link?
2. NCP: Yes, I can do IPX
because it is configured
on my serial interface, can
you do AppleTalk?
Router A
Router B
3. NCP: Yes, I have
AppleTalk configured on
my serial interface, letХs
plan on sending IPX and
AppleTalk packets over this link.
87200333.book Page 404 Wednesday, August 22, 2001 2:53 PM
