updates only when changes occur in the network. An AURP configuration is unique in that it
does not require cable ranges or zones. Also, AURP allows for an extension of the hop-count.
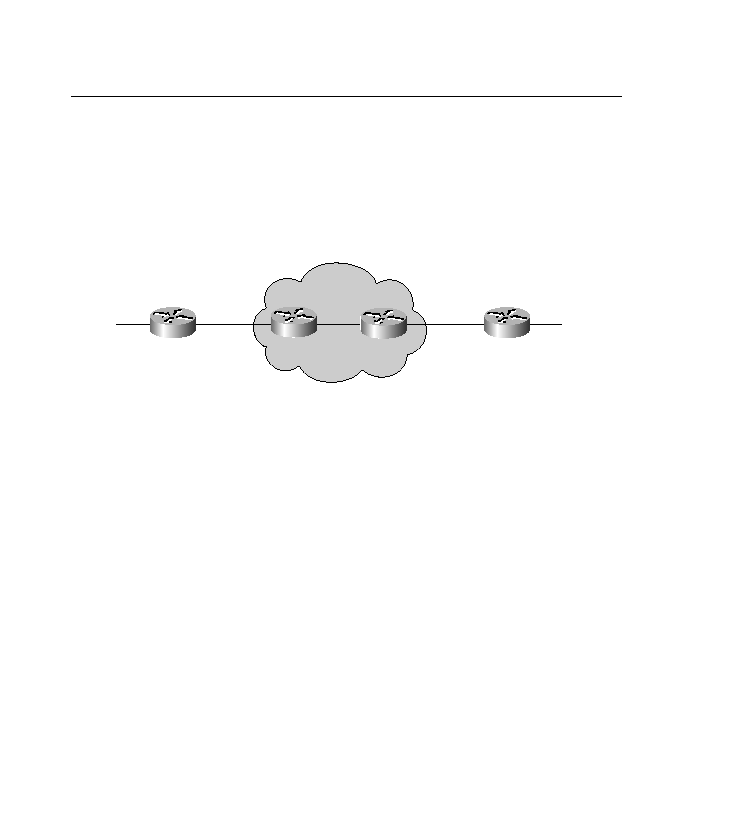
For example, a network that is 10 hops away with RTMP can appear to be two hops away via
the AURP tunnel. Figure 8-7 shows a network using AURP.
local-area networks. Even though it is still popular, Windows NT is replacing it in many new
installations. Its prime-time protocol, IPX, is also being replaced by TCP/IP as the standard
default protocol. Because many installations still use Novell and IPX, it is important that the
CCDP understand the design features, functionalities, and capabilities of IPX. Cisco's
implementation of IPX is certified to provide full IPX router functionality.
routing IPX data through an internetwork. Every network segment is assigned a unique network
address. Routers rely on this address to know how to get a packet to its final destination
network. Each host on a Novell IPX network has a unique 80-bit logical address.
to 32 bits, and the host number, usually the MAC address of the interface card.