Route Summarization 199
·
Multiple IP addresses must share the same high-order bits.
·
Routing protocols must carry the prefix length or subnet mask in a separate field, along
with the 32-bit IP address.
·
Routing tables and protocols must base their routing decisions on a 32-bit IP address with
a prefix length that can be up to the entire 32-bit length of the field.
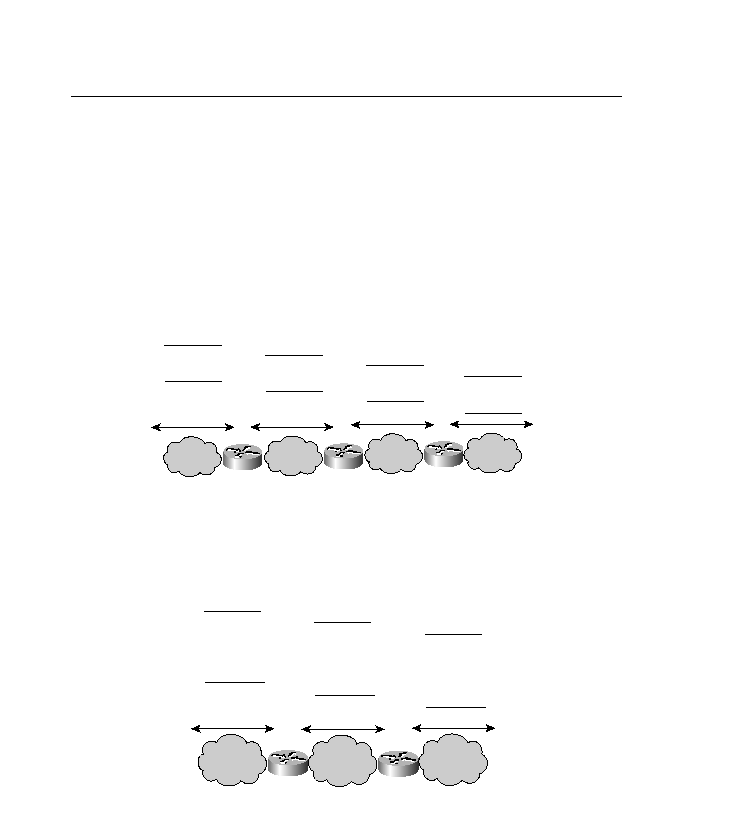
Figure 6-9 shows how classical distance-vector protocols perform route summarization. If a
router has an interface on a major network, it tracks all the subnets of that major network in its
routing table. If a router is not directly connected to a particular major network, it will not have
any subnet information about that network. Only a single network route will appear in the
routing table.
Figure 6-9
Summarization of Classful Routing
Configuration of route summarization with classless routing and VLSM is dependent on the
routing protocol. All subnets might be automatically summarized at network boundaries by
default. Manual configuration might be required to enforce this.
Figure 6-10 shows how summarization reduces routing tables.
Figure 6-10
Summarization of Classless Routing
131.108.1.0
131.108.2.0
131.108.3.0
131.109.0.0
131.110.0.0
131.111.0.0
131.108.0.0
131.108.0.0
131.109.1.0
131.109.2.0
131.109.3.0
131.110.0.0
131.111.0.0
131.109.0.0
131.108.0.0
131.109.0.0
131.110.1.0
131.110.2.0
131.110.3.0
131.111.0.0
131.110.0.0
131.108.0.0
131.109.0.0
131.110.0.0
131.111.1.0
131.111.2.0
131.111.3.0
131.111.0.0
131.108.1.0
131.108.2.0
131.108.3.0
131.108.4.4
131.108.4.8
131.108.4.12
131.109.0.0
131.110.0.0
131.111.0.0
131.108.0.0
131.108.0.0
131.109.1.0
131.109.2.0
131.109.3.0
131.109.4.4
131.109.4.8
131.109.4.12
131.110.0.0
131.111.0.0
131.109.0.0
131.108.0.0
131.109.0.0
131.110.1.0
131.110.2.0
131.110.3.0
131.110.4.4
131.110.4.8
131.110.4.12
131.111.0.0
131.110.0.0
87200333.book Page 199 Wednesday, August 22, 2001 2:37 PM
